目录
ApplicationContext VS BeanFactor ...
1.创建 Spring 项目
1.1创建一个 Maven 项目
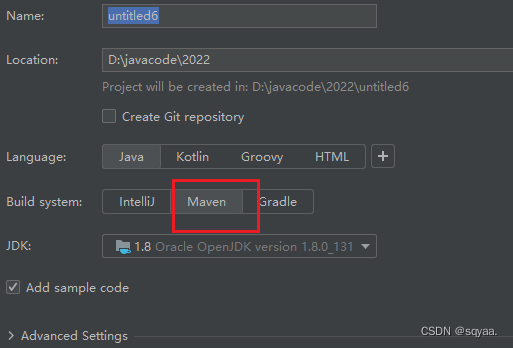
1.2添加 Spring 框架支持(pom.xml)
在pom.xml中注入依赖(从maven仓库https://mvnrepository.com/) ,版本号与jdk版本要相对应。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring_demo2</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <!--这里的5.2.3和jdk版本号有关--> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
1.3添加启动类
public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { } }
2.存储 Bean 对象
2.1创建 Bean
public class HelloWorld {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello, " + message);
}
}
2.2将 Bean 注册到容器(Spring)
💡这段是直接复制的无需了解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> </beans>💡这段是需要自己加入到file中的
注意这里的id不能和别的名字重复,后续还会被用到,class是你创建的Bean的类名字(包名+类名,这里没创建包,就只写了类名)
完整代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 定义HelloWorld Bean ,这里的class是包名+类名,没有包名就不用管了;id就是给bean对象取的名字--> <bean id="helloWorld" class="HelloWorld"> <!--<property name="message" value="Spring World" />--> </bean> </beans>
3.获取并使用 Bean 对象
3.1创建 Spring 上下文(获取全局配置文件)

// 加载Spring配置文件即创建Spring上下文;
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");ApplicationContext VS BeanFactor ...
引入BeanFactory /**💡1.Spring上下文对象可以使用ApplicationContext; * ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); * 💡2.使用BeanFactory,ApplicationContest属于BeanFactory的子类, * BeanFactory beanFactory =new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResourse("application.xml")) * **/ApplicationContext 与 BeanFactory :
1.都可以得到 Spring 上下文对象;2.都是来自 Spring 的顶级接口。
不同点:
1.继承关系和功能: ApplicationContext 属于 BeanFactory 的子类; BeanFactory 只有最基础访问 Bean 的能力,而ApplicationContext 除了拥有 BeanFactory 功能之外,还包了更多的功能,如:国际化支持、资源访问、事件传播等。
2.性能: ApplicationContext 加载方式是将 Bean 对象一次性加载,所以在后面访问 Bean 对象时会很快; BeanFactory 需要某个时,采取加载 Bean 对象,所以它在执行 Bean 获取时,比较慢。(就相当于现做的餐和快餐的区别)
3.2获取指定的 Bean 对象

HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
3.2.1注意事项 以及 getBean 方法的更多用法
/**💡1.getBean和XML中配置的bean id是相互对应的;
* 💡2.不仅可以通过名称来找bean,也可以通过类型来找bean
* context.getBean("HelloWorld.class")
*但是对于这个写法,如果user有两个,那就会出错;
* eg:一个班有两个学生叫张三,那这还怎末找?
* */
/**💡3.HelloWorld helloWorld = context.getBean("helloWorld",User.class);
* 此时就不需要强转!
* */
3.3使用 Bean
MainApp完整代码
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载Spring配置文件即创建Spring上下文;
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
/**💡1.Spring上下文对象可以使用ApplicationContext;
* ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
* 💡2.使用BeanFactory,ApplicationContest属于BeanFactory的子类,
* BeanFactory beanFactory =new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResourse("application.xml"))
*
* **/
// 获取定义的Bean对象
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
/**💡1.getBean和XML中配置的bean id是相互对应的;
* 💡2.不仅可以通过名称来找bean,也可以通过类型来找bean
* context.getBean("HelloWorld.class")
*但是对于这个写法,如果user有两个,那就会出错;
* eg:一个班有两个学生叫张三,那这还怎末找?
* */
/**💡3.HelloWorld helloWorld = context.getBean("helloWorld",User.class);
* 此时就不需要强转!
* */
// 调用Bean对象的方法
helloWorld.sayHello();
}
}
4.运行

































 2126
2126

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










