#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ElemType int
#define MaxSize 100
//创建顺序栈
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;
}SqStack; //顺序栈类型定义
void InitStack (SqStack *&s){ //顺序栈初始化
s=(SqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SqStack));
s->top=-1;
}
bool StackEmpty(SqStack *s){ //判断顺序栈是否为空
return(s->top==-1);
}
bool Pop(SqStack *&s,ElemType &e) { //出栈
if (s->top==-1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e=s->data[s->top] ; //取栈 顶指针元素的元素
s->top--; //栈顶指针减1
return true;
}
bool Push(SqStack *&s,ElemType e){ //入栈
if(s->top==MaxSize-1) //栈满的情况,即栈上溢出
return false;
s->top++; //栈顶指针 增1
s->data[s->top]=e; //元素e放在栈顶指针处
return true;
}
//数制转换代码
void conversion(int n,int r){ //数制转换
int e=0;
SqStack *s;
InitStack(s); // 初始化栈指针
while(n){
Push(s,n%r);
n=n/r;
}
while(!StackEmpty(s)){ // 栈非空时循环
Pop(s,e);
printf("%d",e);
}
}
//主函数部分
int main(){
int n=0;
int r=0;
printf("请输入待转换的十进制数:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入所要转换的进制: \n");
scanf("%d",&r);
printf("转换所得数为:");
conversion(n,r);
return 0;
}
任意输入一个十进制整数n,要求借助栈将其转换为对应的r进制整数并输出。
运行结果图
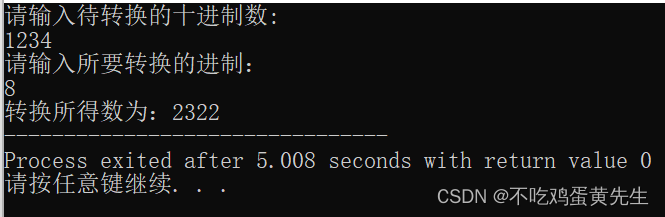
解题思路
将一个十进制整数 N 转换为 r 进制的数,其转换方法为辗转相除法。以 N=1234,r=8 为例,转换方法如下。
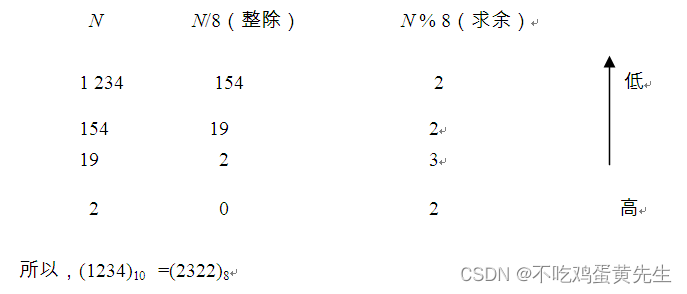
辗转相除法步骤如下:
(1)初始化一个栈(顺序栈或链栈均可),并输入N和r。
(2)判断N的值,若N为非0时,将 N % r所得结果压入栈中;若N为0时,转(4)。
(3)用N / r代替N,转(2)。
(4)将栈中所有元素出栈,出栈序列即为结果。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid1, pid2;
pid1 = fork(); // 创建第一个子进程
if (pid1 == -1) {
perror("fork 1 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (pid1 == 0) { // 第一个子进程
printf("Hello from child 1!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
pid2 = fork(); // 创建第二个子进程
if (pid2 == -1) {
perror("fork 2 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (pid2 == 0) { // 第二个子进程
printf("Hello from child 2!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
printf("Hello from parent!\n");
wait(NULL); // 等待第一个子进程结束
wait(NULL); // 等待第二个子进程结束
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid1, pid2;
pid1 = fork();
if (pid1 == 0) {
// 子进程1
printf("学号-02
");
exit(0);
} else if (pid1 > 0) {
// 父进程
pid2 = fork();
if (pid2 == 0) {
// 子进程2
printf("学号-03
");
exit(0);
} else {
// 父进程
printf("学号-01
");
wait(NULL);
wait(NULL);
}
} else {
// fork失败
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
。。。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid1, pid2;
int fd[2];
off_t offset;
char lock_data[1] = "A";
// 创建两个子进程
pid1 = fork();
if (pid1 == 0) {
// 子进程1
printf("子进程1输出一句话
");
exit(0);
} else if (pid1 > 0) {
// 父进程
pid2 = fork();
if (pid2 == 0) {
// 子进程2
printf("子进程2输出一句话
");
exit(0);
} else {
// 父进程
printf("父进程输出一句话
");
// 使用lockf()给每个进程加锁
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
fd[i] = open("lockfile", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0644);
offset = lseek(fd[i], 0, SEEK_SET);
lockf(fd[i], F_TLOCK, 0);
write(fd[i], lock_data, 1);
close(fd[i]);
}
wait(NULL);
wait(NULL);
}
} else {
// fork失败
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
,,,,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid1, pid2;
int lockfd;
// 创建一个文件作为锁文件
lockfd = open("lockfile", O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0666);
if (lockfd == -1) {
perror("open failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pid1 = fork(); // 创建第一个子进程
if (pid1 == -1) {
perror("fork 1 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (pid1 == 0) { // 第一个子进程
// 加锁
if (lockf(lockfd, F_LOCK, 0) == -1) {
perror("lockf 1 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Hello from child 1!\n");
// 解锁
if (lockf(lockfd, F_ULOCK, 0) == -1) {
perror("lockf 1 unlock failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
pid2 = fork(); // 创建第二个子进程
if (pid2 == -1) {
perror("fork 2 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (pid2 == 0) { // 第二个子进程
// 加锁
if (lockf(lockfd, F_LOCK, 0) == -1) {
perror("lockf 2 failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Hello from child 2!\n");
// 解锁
if (lockf(lockfd, F_ULOCK, 0) == -1) {
perror("lockf 2 unlock failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
printf("Hello from parent!\n");
wait(NULL); // 等待第一个子进程结束
wait(NULL); // 等待第二个子进程结束
}
}
// 关闭文件描述符
close(lockfd);
// 删除锁文件
if (unlink("lockfile") == -1) {
perror("unlink failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 0;
}
11111
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid;
int status;
pid = fork(); // 创建一个新进程
if (pid < 0) {
printf("Fork failed.\n");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
printf("Hello from child!\n");
execlp("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", NULL); // 使用exec函数执行一个新的程序
printf("Exec failed.\n"); // 如果exec函数返回,那么说明执行失败了
return 1;
} else { // 父进程
wait(&status); // 等待子进程结束
printf("Child has finished executing.\n");
}
return 0;
}





















 783
783











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








