强化学习(Reinforcement Learning)是机器学习中的重要分支之一,它通过“试错”机制使智能体学习如何在环境中做出最优决策。本文将通过一个经典的 Cliff Walking(悬崖漫步) 环境,手把手带你实现并理解 Q-Learning 算法的基本原理和应用。并在总结附上源代码。
一、什么是 Q-Learning?
Q-learning 是一种基于值的强化学习算法。它的目标是学习一个 Q 表(Q-table),每个状态-动作对(state-action pair)都有一个 Q 值,用来表示该动作在该状态下能获得的期望回报。
更新公式如下:
-
s,a:当前状态与动作
-
r:环境给出的即时奖励
-
s′:执行动作后到达的新状态
-
α:学习率
-
γ:折扣因子
二、环境设计:Cliff Walking(悬崖漫步)
环境规则
-
一个
4 行 × 12 列的网格。 -
起点在
(0,3),终点在(11,3)。 -
(1~10, 3)是“悬崖”,掉下去会得到 -100 奖励并重新开始。 -
其余位置每一步都是 -1 奖励。
class CliffWalkingEnv:
def __init__(self, ncol, nrow):
self.nrow = nrow
self.ncol = ncol
self.x = 0 # 记录当前智能体位置的横坐标
self.y = self.nrow - 1 # 记录当前智能体位置的纵坐标
def step(self, action): # 外部调用这个函数来改变当前位置
# 4种动作, change[0]:上, change[1]:下, change[2]:左, change[3]:右。坐标系原点(0,0)
# 定义在左上角
change = [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]
self.x = min(self.ncol - 1, max(0, self.x + change[action][0]))
self.y = min(self.nrow - 1, max(0, self.y + change[action][1]))
next_state = self.y * self.ncol + self.x
reward = -1
done = False
if self.y == self.nrow - 1 and self.x > 0: # 下一个位置在悬崖或者目标
done = True
if self.x != self.ncol - 1:
reward = -100
return next_state, reward, done
def reset(self): # 回归初始状态,坐标轴原点在左上角
self.x = 0
self.y = self.nrow - 1
return self.y * self.ncol + self.x
智能体的动作空间:
-
上(0)下(1)左(2)右(3)
动作会使坐标发生如下变化:
change = [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]
三、Q-learning 智能体设计
class QLearning:
""" Q-learning算法 """
def __init__(self, ncol, nrow, epsilon, alpha, gamma, n_action=4):
self.Q_table = np.zeros([nrow * ncol, n_action]) # 初始化Q(s,a)表格
self.n_action = n_action # 动作个数
self.alpha = alpha # 学习率
self.gamma = gamma # 折扣因子
self.epsilon = epsilon # epsilon-贪婪策略中的参数
def take_action(self, state): #选取下一步的操作
if np.random.random() < self.epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(self.n_action)
else:
action = np.argmax(self.Q_table[state])
return action
def best_action(self, state): # 用于打印策略
Q_max = np.max(self.Q_table[state])
a = [0 for _ in range(self.n_action)]
for i in range(self.n_action):
if self.Q_table[state, i] == Q_max:
a[i] = 1
return a
def update(self, s0, a0, r, s1):
td_error = r + self.gamma * self.Q_table[s1].max(
) - self.Q_table[s0, a0]
self.Q_table[s0, a0] += self.alpha * td_error
核心方法说明:
-
take_action: ε-贪婪策略(探索 vs 利用) -
update: 使用 Q-learning 更新公式 -
best_action: 输出当前状态下的最优动作(用于策略可视化)
四、训练智能体
设置训练参数:
ncol = 12
nrow = 4
env = CliffWalkingEnv(ncol, nrow)
np.random.seed(0)
epsilon = 0.1
alpha = 0.1
gamma = 0.9
agent = QLearning(ncol, nrow, epsilon, alpha, gamma)
num_episodes = 500 # 智能体在环境中运行的序列的数量循环训练 500 个回合,记录每轮回报:
return_list = [] # 记录每一条序列的回报
for i in range(10): # 显示10个进度条
# tqdm的进度条功能
with tqdm(total=int(num_episodes / 10), desc='Iteration %d' % i) as pbar:
for i_episode in range(int(num_episodes / 10)): # 每个进度条的序列数
episode_return = 0
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.take_action(state)
next_state, reward, done = env.step(action)
episode_return += reward # 这里回报的计算不进行折扣因子衰减
agent.update(state, action, reward, next_state)
state = next_state
return_list.append(episode_return)
if (i_episode + 1) % 10 == 0: # 每10条序列打印一下这10条序列的平均回报
pbar.set_postfix({
'episode':
'%d' % (num_episodes / 10 * i + i_episode + 1),
'return':
'%.3f' % np.mean(return_list[-10:])
})
pbar.update(1)五、结果可视化
我们记录每一轮的总回报并绘制如下:
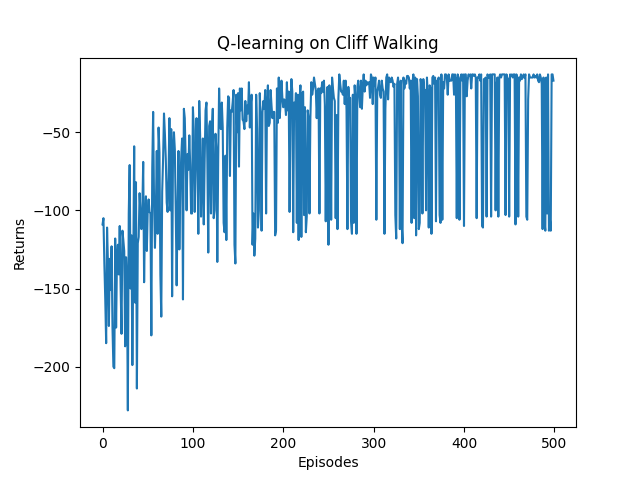
六、策略输出示例
action_meaning = ['^', 'v', '<', '>']
print('Q-learning算法最终收敛得到的策略为:')
print_agent(agent, env, action_meaning, list(range(37, 47)), [47])输出的策略图中:
-
^v<>表示可能选择的动作方向 -
****表示悬崖 -
EEEE表示终点
示例输出:
Q-learning算法最终收敛得到的策略为:
^ooo ovoo ovoo ^ooo ^ooo ovoo ooo> ^ooo ^ooo ooo> ooo> ovoo
ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ^ooo ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ovoo
ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ooo> ovoo
^ooo **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** EEEE
七、总结
完整代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm # tqdm是显示循环进度条的库
class CliffWalkingEnv:
def __init__(self, ncol, nrow):
self.nrow = nrow
self.ncol = ncol
self.x = 0 # 记录当前智能体位置的横坐标
self.y = self.nrow - 1 # 记录当前智能体位置的纵坐标
def step(self, action): # 外部调用这个函数来改变当前位置
# 4种动作, change[0]:上, change[1]:下, change[2]:左, change[3]:右。坐标系原点(0,0)
# 定义在左上角
change = [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]
self.x = min(self.ncol - 1, max(0, self.x + change[action][0]))
self.y = min(self.nrow - 1, max(0, self.y + change[action][1]))
next_state = self.y * self.ncol + self.x
reward = -1
done = False
if self.y == self.nrow - 1 and self.x > 0: # 下一个位置在悬崖或者目标
done = True
if self.x != self.ncol - 1:
reward = -100
return next_state, reward, done
def reset(self): # 回归初始状态,坐标轴原点在左上角
self.x = 0
self.y = self.nrow - 1
return self.y * self.ncol + self.x
class QLearning:
""" Q-learning算法 """
def __init__(self, ncol, nrow, epsilon, alpha, gamma, n_action=4):
self.Q_table = np.zeros([nrow * ncol, n_action]) # 初始化Q(s,a)表格
self.n_action = n_action # 动作个数
self.alpha = alpha # 学习率
self.gamma = gamma # 折扣因子
self.epsilon = epsilon # epsilon-贪婪策略中的参数
def take_action(self, state): #选取下一步的操作
if np.random.random() < self.epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(self.n_action)
else:
action = np.argmax(self.Q_table[state])
return action
def best_action(self, state): # 用于打印策略
Q_max = np.max(self.Q_table[state])
a = [0 for _ in range(self.n_action)]
for i in range(self.n_action):
if self.Q_table[state, i] == Q_max:
a[i] = 1
return a
def update(self, s0, a0, r, s1):
td_error = r + self.gamma * self.Q_table[s1].max(
) - self.Q_table[s0, a0]
self.Q_table[s0, a0] += self.alpha * td_error
def print_agent(agent, env, action_meaning, disaster=[], end=[]):
for i in range(env.nrow):
for j in range(env.ncol):
if (i * env.ncol + j) in disaster:
print('****', end=' ')
elif (i * env.ncol + j) in end:
print('EEEE', end=' ')
else:
a = agent.best_action(i * env.ncol + j)
pi_str = ''
for k in range(len(action_meaning)):
pi_str += action_meaning[k] if a[k] > 0 else 'o'
print(pi_str, end=' ')
print()
ncol = 12
nrow = 4
env = CliffWalkingEnv(ncol, nrow)
np.random.seed(0)
epsilon = 0.1
alpha = 0.1
gamma = 0.9
agent = QLearning(ncol, nrow, epsilon, alpha, gamma)
num_episodes = 500 # 智能体在环境中运行的序列的数量
return_list = [] # 记录每一条序列的回报
for i in range(10): # 显示10个进度条
# tqdm的进度条功能
with tqdm(total=int(num_episodes / 10), desc='Iteration %d' % i) as pbar:
for i_episode in range(int(num_episodes / 10)): # 每个进度条的序列数
episode_return = 0
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.take_action(state)
next_state, reward, done = env.step(action)
episode_return += reward # 这里回报的计算不进行折扣因子衰减
agent.update(state, action, reward, next_state)
state = next_state
return_list.append(episode_return)
if (i_episode + 1) % 10 == 0: # 每10条序列打印一下这10条序列的平均回报
pbar.set_postfix({
'episode':
'%d' % (num_episodes / 10 * i + i_episode + 1),
'return':
'%.3f' % np.mean(return_list[-10:])
})
pbar.update(1)
episodes_list = list(range(len(return_list)))
plt.plot(episodes_list, return_list)
plt.xlabel('Episodes')
plt.ylabel('Returns')
plt.title('Q-learning on {}'.format('Cliff Walking'))
plt.show()
action_meaning = ['^', 'v', '<', '>']
print('Q-learning算法最终收敛得到的策略为:')
print_agent(agent, env, action_meaning, list(range(37, 47)), [47])























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








