AQS
全称是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,是阻塞锁和相关的同步器工具的框架
特点
1、用state属性来表示资源的状态(分为独享状态与共享模式)
getState - 获取state状态
setState - 设置state状态
compareAndSetState - 乐观锁机制设置state状态
独占模式是只有一个线程能够访问资源,而共享模式允许多个线程访问资源
2、提供了FIFO的等待队列,类似于Monitor的EntryList
3、条件变量来实现等待、唤醒机制,支持多个条件变量,类似Monitor的WaitSet
子类主要实现这些方法
tryAcquire 获取锁
tryRelease 释放锁
tryAcquireShared
tryReleaseShared
isHeldExclusively
ReentrantLockd概述
相比synchronized具备如下特点
1、可中断
2、可以设置超时时间
3、可以设置为公平锁
4、支持多个条件变量
与synchronized一样都支持可重入
可重入
可重入是指同一个线程如果首次获得了这把锁,那么因为它是这把锁的拥有者,因此有权利再次获取这把锁。
如果是不可重入锁,那么第二次获取锁的时候,自己也会被锁挡住
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("lock1~");
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("lock2~");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}

可打断
在获取锁的时候可被打断避免一直阻塞等待获取锁
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
System.out.println("lock1获取到了锁");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("lock1中被打断了");
}
});
lock.lock(); // 主线程获取到锁
t1.start(); // t1线程启动
//打断
t1.interrupt();
}
}

可超时
与可打断类似,只是打断是被动,超时是主动,超时了就自动不获取锁了
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
boolean flag = lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (flag){
System.out.println("lock1获取到了锁");
}else {
System.out.println("lock1没有获取到锁");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
lock.lock(); // 主线程获取到锁
t1.start(); // t1线程启动
}
}
可设置公平锁
不容易代码实现
使用公平锁是为了解决饥饿但是会降低并发度
可设置多个条件变量
ReentrantLockd相比synchronized,ReentrantLockd可支持多个条件变量,这好比synchronized是那些不满足条件的线程都在一间休息室里面等,而ReentrantLockd支持多间休息室
await前需要获得锁
await执行后,会释放锁,进入condition等待
await的线程被唤醒去重新竞争锁
竞争锁成功后执行await后的
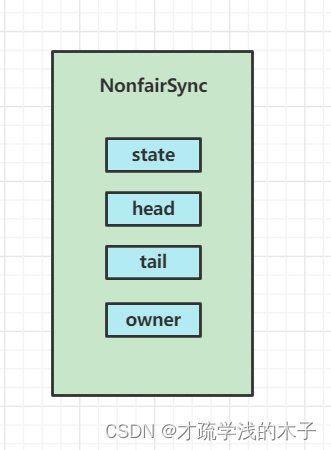
state 就是加锁状态
head 就是等待队列的头
tail 就是等待队列的尾
owner 就是当前是那个线程,全名为ExclusiveOwnerThread我这里简写的
加锁流程
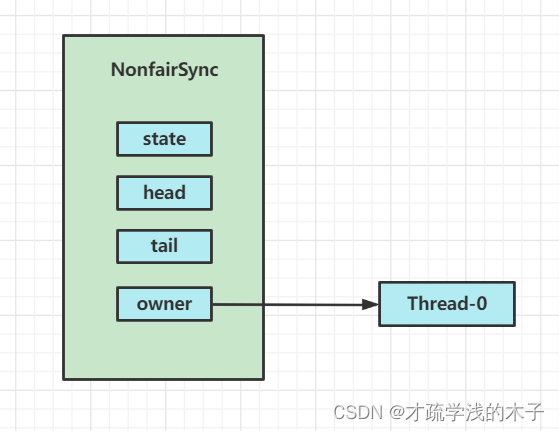
最开始没有线程竞争,加锁成功
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
// 加锁成功
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 加锁失败
acquire(1);
}
第二个线程来竞争 CAS失败,进入acquire(1)
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 尝试获取锁失败,所以!tryAcquire(arg)为true
//acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) 创建一个节点对象然后放入等待队列中
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
进入acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果是第二个节点再尝试一次
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//前驱节点waitStatus改为-1代表有责任唤醒下一个节点
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
蓝色三角形为Node是waitStatus状态,其中0为默认状态
Node的创建是懒惰的
其中第一个Node为哨兵或者哑元用来占位并不关联线程
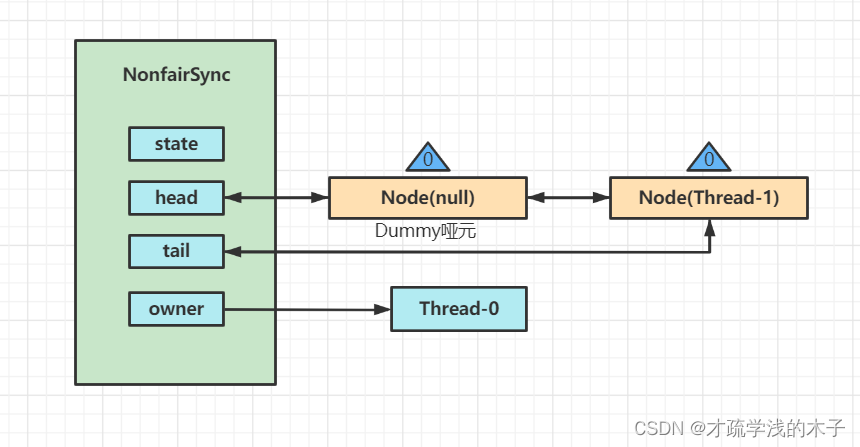
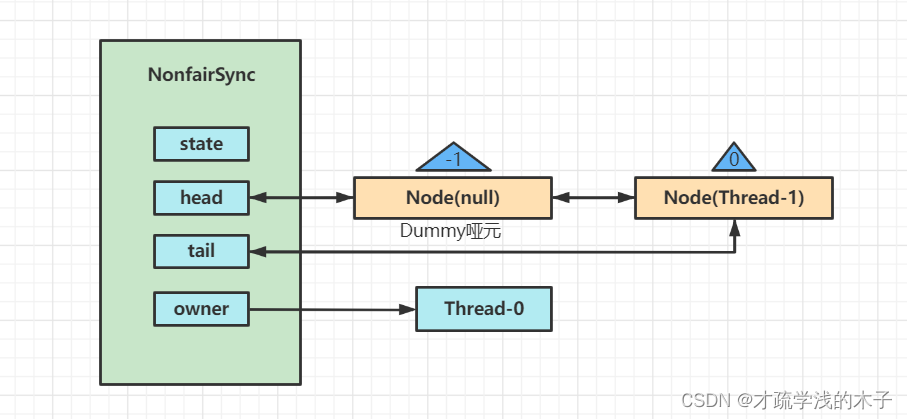
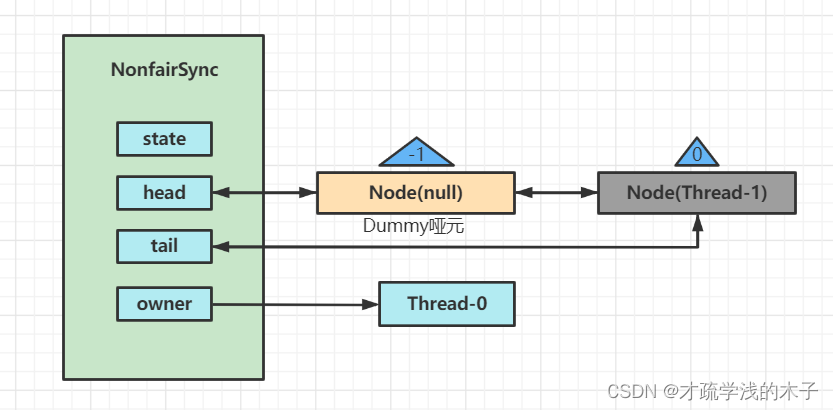
然后当前线程Thread-1 阻塞住
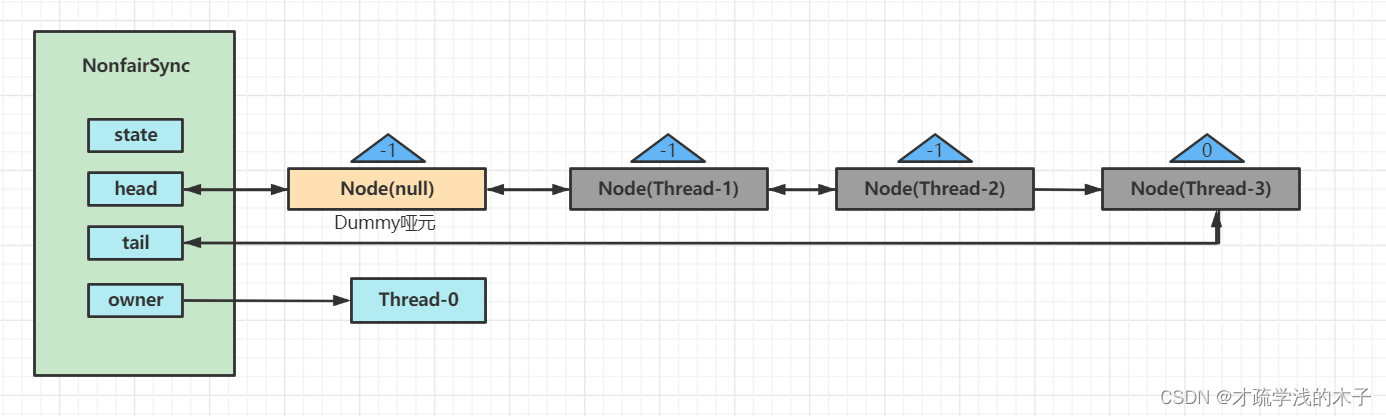
假如有多个线程经历上述过程
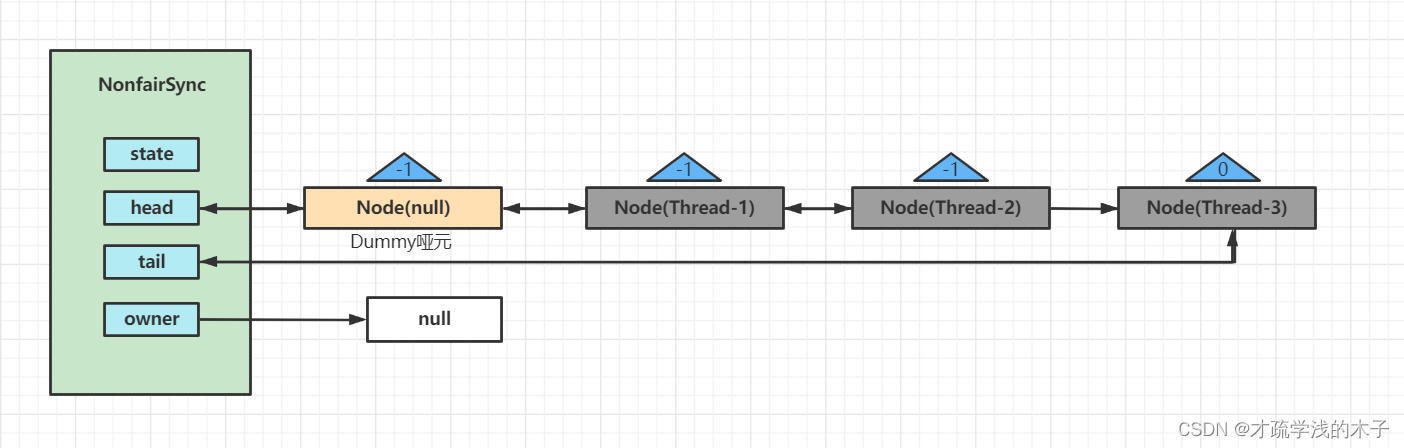
Thread-0 释放锁
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases; // 这就是可重入的原因,当前线程如果是获取锁的线程state++
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
当前队列不为空唤醒下一个
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
// 唤醒下一个节点
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
唤醒Thread-1
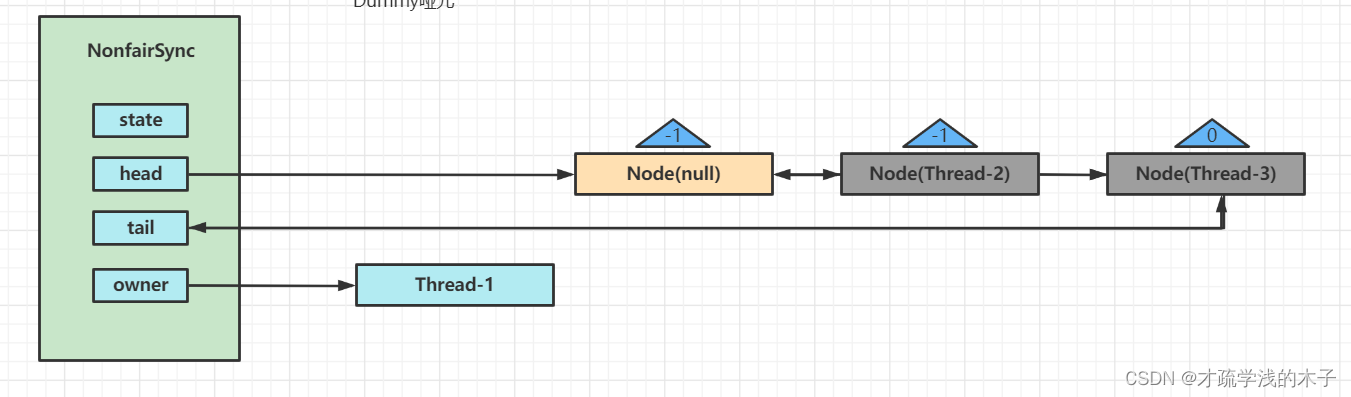
因为我们这是非公平锁,如果Thread-1在获取的时候Thread-4来获取,Thread-4抢夺成功
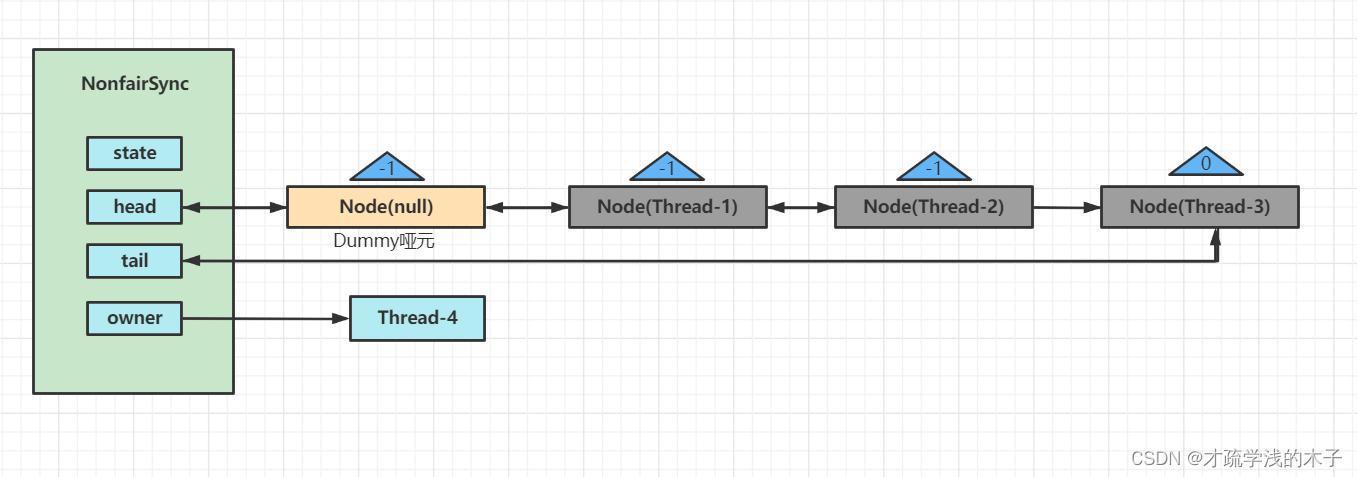
可重入原理
加锁
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) { // 首次获得锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 判断是否当前是当前线程是否是owner线程
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
释放锁
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases; // 释放锁state减少
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
可打断原理
抛出异常
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 抛出异常
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
公平锁原理
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// hasQueuedPredecessors() 判断队列中是否有其它线程等待
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
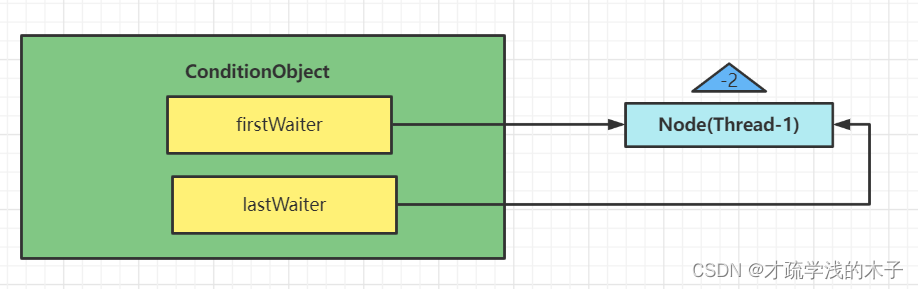
条件变量实现原理
每个条件变量都对应着一个等待队列,其实现类就是ConditionObject
waitState标志位设置为-2
并且调用fullRelease方法释放线程上的锁,避免重入时候多把锁没释放完























 2098
2098











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










