1.1if语句
//colddays.c --找出0摄氏度以下的天数占总天数的百分比
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
const int FREEZING = 0;
float temperature;
int cold_days = 0;
int all_days = 0;
printf("Enter the list of daily low temperature.\n");
printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%f", &temperature) == 1)
{
all_days++;
if (temperature < FREEZING)
cold_days++;
}
if (all_days != 0)
printf("%d days total: %.1f%% were below freezing.\n", all_days, 100.0 * (float)cold_days / all_days);
if (all_days == 0)
printf("No data enterd!\n");
return 0;
}
程序结果:

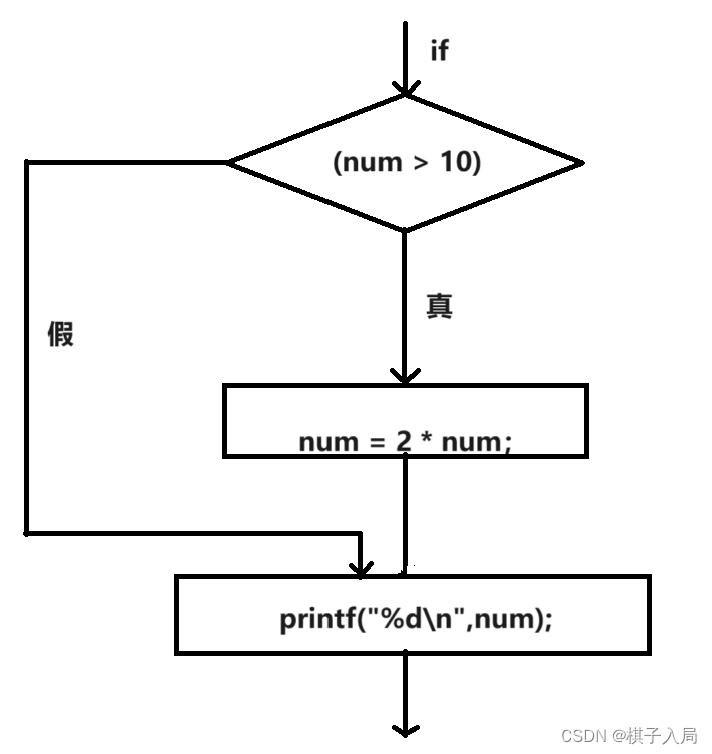
if语句被称为分支语句或选择语句,相当于一个交叉点,程序要在两条分支中行选择执。
通用形式:
if(表达式)
语句
表达式一般是关系表达式,如果对表达式求值,为真,执行语句;为假,跳过语句。
语句可以是一条简单的语句,也可以是一个花括号里多条的复合语句。
if语句和while语句的区别:
当满足条件语句可执行时,if语句只能测试和执行一次,但是while语句可以测试和执行多次。
注:即使if语句由复合语句构成,整个if语句也是一条语句。
1.2if else语句
//colddays.c --找出0摄氏度以下的天数占总天数的百分比
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
const int FREEZING = 0;
float temperature;
int cold_days = 0;
int all_days = 0;
printf("Enter the list of daily low temperature.\n");
printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%f", &temperature) == 1)
{
all_days++;
if (temperature < FREEZING)
cold_days++;
}
if (all_days != 0)
printf("%d days total: %.1f%% were below freezing.\n", all_days, 100.0 * (float)cold_days / all_days);
else
printf("No data enterd!\n");
return 0;
}
程序结果:

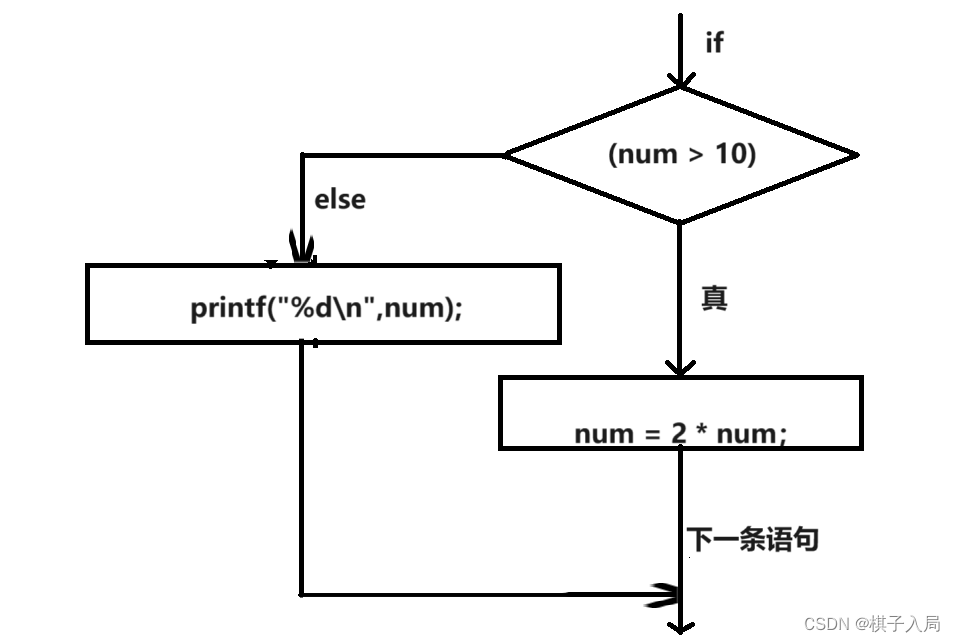
if else形式在两条语句之间做选择。
if else通用形式:
if(表达式)
语句1
else
语句2
if else之间的多条语句必须用花括号括起来形成一个块。
if和if else之间的区别:
if用于选择是否执行一个行为,if else用于在两个行为之间进行选择。
1.2.1getchar()和putchar()
getchar()函数不带任何参数,它从输入队列中返回下一个字符。
例:读取下一个字符输入,并把该字符的值赋给变量ch
ch = getchar(); == scanf("%c", &ch);
putchar()函数打印它的参数。
例:把之前赋给ch的值作为字符打印出来
putchar(ch); == printf("%c",ch);
注:这两个函数只处理字符,因此比scanf()和printf()函数更快,更简洁。且这两个函数不需要转换说明,通常定义在头文件stdio.h中,通常时预处理宏。
cypher1.c --更改输入,空格不变
#include <stdio.h>
#define SPACE ' '
int main(void)
{
char ch;
ch = getchar(); //读取一个字符
while(ch != '\n')
{
if(ch == SPACE)
putchar(ch);
else
putchar(ch + 1); //获取下一个字符
ch = getchar();
}
putchar(ch); //打印换行符
return 0;
}1.2.2多重选择else if
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
scanf("%d", &a);
if(a % 3 == 0)
printf("余数是0\n");
else if(a % 3 == 1)
printf("余数是1\n");
else
printf("余数是2\n");
return 0;
}它的另一种写法是:
if(a % 3 == 0)
printf("……");
else
if(a % 3 == 1)
printf("……");
else
printf("……");
该程序由一个if else语句组成,else部分包含了一个if else语句。
配对规则是在没有花括号的前提下,else和最近的if配对。
1.2.3嵌套if语句
for(div = 2; (div * div) <= num; div++)
{
if(num % div == 0)
{
if(div * div != num)
printf("%d is divisible by %d and %d.\n", num, div, num / div);
else
printf("%d is divisible by %d.\n", num, div);
}
}1.3逻辑运算符
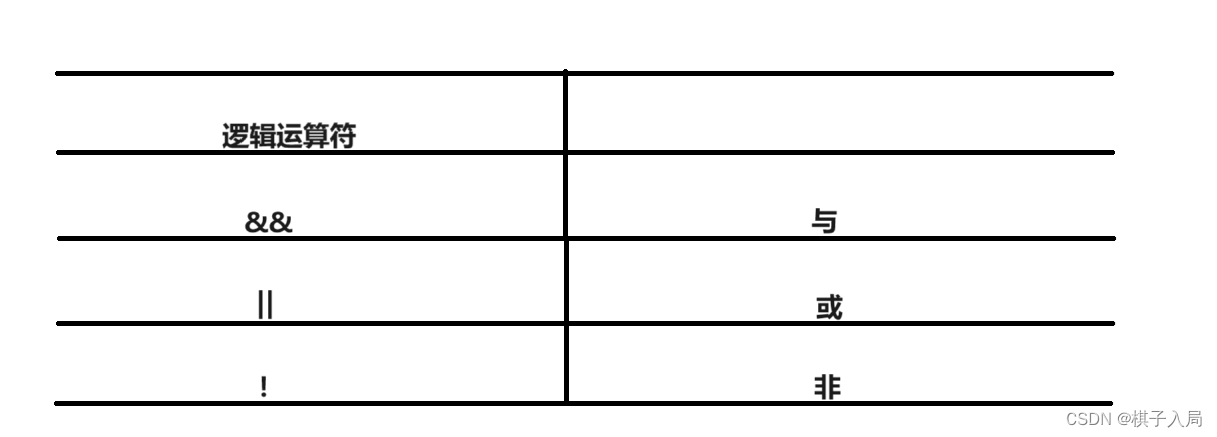
&&全真才为真;||全假才为假;!取反。
1.3.1优先级
!优先级最高,与递增运算符相同,比()低;&&比||高,比关系运算符低,比赋值运算符高。
1.4条件运算符:?:
三元运算符,通式:
expression1?expression2:expression3
如果expression是真的,那么执行expression,否则执行expression3.。
例:max = (a > b)? a : b;
1.5continue和break
1.5.1continue语句
执行到该语句时,会跳过本次迭代的剩余部分,并开始下一轮迭代。如果continue语句嵌套在循环内,只会影响包含该语句的内层循环。
/*skippart.c --使用continue跳过部分循环*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
const float MIN = 0.0f;
const float MAX = 100.0f;
float score;
float total = 0.0f;
int n = 0;
float min = MAX;
float max = MIN;
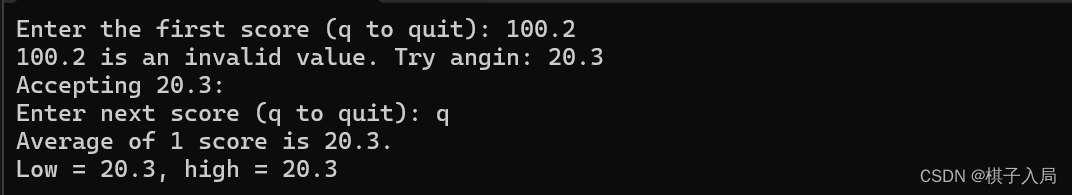
printf("Enter the first score (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%f", &score) == 1)
{
if (score < MIN || score > MAX)
{
printf("%0.1f is an invalid value. Try angin: ", score);
continue; //跳转至while循环
}
printf("Accepting %0.1f:\n", score);
min = (score < min) ? score : min;
max = (score > max) ? score : max;
total += score;
n++;
printf("Enter next score (q to quit): ");
}
if (n > 0)
{
printf("Average of %d score is %0.1f.\n", n, total / n);
printf("Low = %0.1f, high = %0.1f\n", min, max);
}
else
printf("No valid scores were entered.\n");
return 0;
}程序结果:
1.5.2break语句
当程序执行到break时,会终止包含它的循环。如果break位于嵌套循环内,只影响包含它的循环。

在for循环中的break和continue,执行beak后直接执行循环后面的第1条语句,连更新部分也跳过。嵌套循环内层的break只会让程序跳出包含它当前循环
int p, q;
scanf("%d", &p);
while(p > 0)
{
printf("%d\n", p);
scanf("%d", &q);
while(q > 0)
{
printf("%d\n", p * q);
if(q > 100)
break; //跳出内层循环
scanf("%d", &q);
}
if(q > 100)
break; //跳出外层循环
scanf("%d", &p);
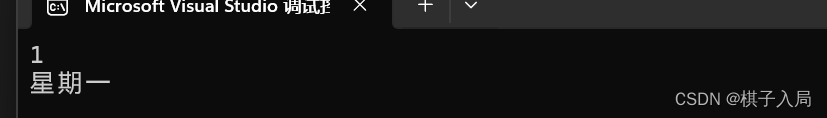
}1.6多重选择:switch和break
int main()
{
int day = 0;
scanf("%d", &day);
switch (day)
{
case 1:
printf("星期一\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("星期二\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("星期三\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("星期四\n");
break;
case 5:
printf("星期五\n");
break;
case 6:
printf("星期六\n");
break;
case 7:
printf("星期日\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误: \n");
break;
}
return 0;
}程序结果:
1.6.1switch语句
break作用是让程序离开switch语句,跳至switch语句后的下一条语句。如果没有break语句,就会从匹配标签开始执行到switch末尾。break语句可用于switch和循环中,continue只能用于循环。
switch在圆括号中的测试表达式是一个整数值(包含char),case标签必须是整数类型的常量或整型常量表达式。
switch构造:
switch(整形表达式)
{
case 常量1:
语句
case 常量2:
语句
default:
语句
}
1.7goto语句
goto语句两部分:goto和标签名。
goto part2;
part2: printf("……");
可以快速跳出循环,但是慎用,可能会导致循环混乱。





















 40
40











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








