二叉树的最大深度
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
题目描述
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
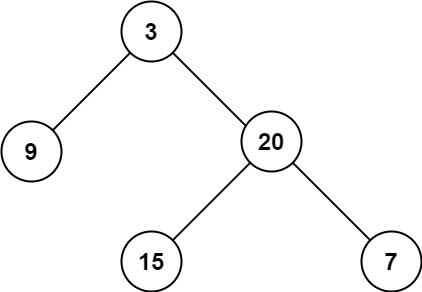
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题思路
1.迭代法—>使用层序遍历
最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
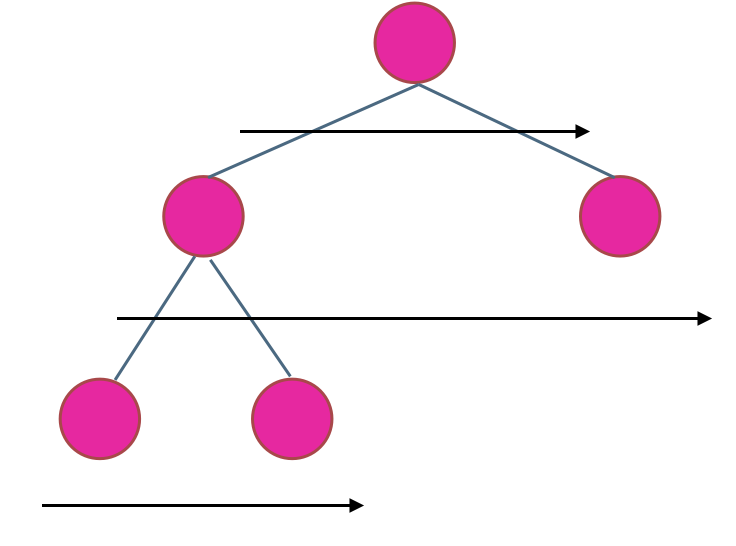
模版:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return resList; // 如果根节点为空,直接返回空的结果列表
}
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root); // 将根节点加入到队列中
while (!que.isEmpty()) { // 队列不为空时进行循环
List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<>(); // 当前层的节点值列表
int len = que.size(); // 当前层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll(); // 获取并移除队列头节点
itemList.add(tmpNode.val); // 将节点值加入到当前层的节点值列表中
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.left); // 将左子节点加入到队列中
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.right); // 将右子节点加入到队列中
}
}
resList.add(itemList); // 将当前层的节点值列表加入到结果列表中
}
return resList; // 返回结果列表
}
}
按模板做修改:
在层序遍历代码上做修改,不需要做存取,当一层遍历完毕后 depth++即可
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int depth=0;
if (root == null) {
return depth;//如果根节点为空,直接返回0
}
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root); // 将根节点加入到队列中
while (!que.isEmpty()) { // 队列不为空时进行循环
int len = que.size(); // 当前层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll(); // 获取并移除队列头节点
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.left); // 将左子节点加入到队列中
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.right); // 将右子节点加入到队列中
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth; // 返回结果列表
}
}
2.递归法
前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
左孩子高度 右孩子高度(左右子树高度) 取最大值+1就是当前父节点的高度 返回给上一层。
递归三部曲
后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root)
2.确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
3.确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
自己解题
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);//左
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);//右
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;//中
}
}
补充
先确定递归三部曲
二叉树的最小深度
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
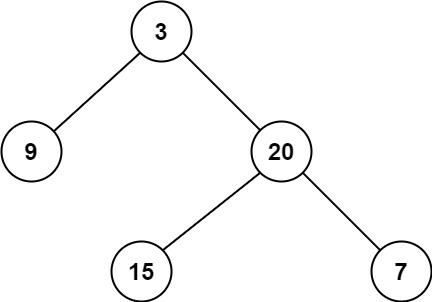
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题思路
层序遍历
自己解题(层序遍历)
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
int depth = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;//如果根节点为空,直接返回0
}
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);// 将根节点加入到队列中
while (!que.isEmpty()) {//队列不为空时进行循环
int levelSize = que.size();//当前层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();//获取并移除队列头节点
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.left);//将左子节点加入队列
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.right);//将右子节点加入队列
}
//左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了
if (tmpNode.left == null && tmpNode.right == null) {
depth++;
return depth;
}
}
depth++;// 走到这说明这一层遍历完毕了
}
return depth;
}
}
参考解题(层序遍历)
在判断完队列不为空的时候就做深度的自增
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
depth++;
TreeNode cur = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cur = queue.poll();
//如果当前节点的左右孩子都为空,直接返回最小深度
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null){
return depth;
}
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return depth;
}
递归
自己解题(递归)
递归三部曲
后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root)
2.确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
3.确定单层递归的逻辑:如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
// 左右子节点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
避免出现这种情况:

参考解题(递归)
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法,相比求MaxDepth要复杂点
* 因为最小深度是从根节点到最近**叶子节点**的最短路径上的节点数量
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
// 左右结点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
层序遍历,模板题
层序遍历(自己解题)
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
int nums = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;// 如果根节点为空,直接返回0
}
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root); // 将根节点加入到队列中
while (!que.isEmpty()) { // 队列不为空时进行循环
int len = que.size(); // 当前层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll(); // 获取并移除队列头节点
nums++;
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.left); // 将左子节点加入到队列中
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.right); // 将右子节点加入到队列中
}
}
}
return nums; // 返回结果
}
}
层序遍历(参考解题)
class Solution {
// 迭代法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result++;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return result;
}
}
递归
递归(自己解题)
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
public int countNodes(TreeNode root)
2.确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示节点数为0。
代码如下:
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
3.确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的节点数量,再求右子树的节点数量,最后取总和再加一 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的节点数量。
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return 0;
}else {
int a=countNodes(root.left);
int b=countNodes(root.right);
return a+b+1;
}
}
}
递归(参考解题)
通用递归解法
class Solution {
// 通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
针对完全二叉树的解法
class Solution {
/**
* 针对完全二叉树的解法
*
* 满二叉树的结点数为:2^depth - 1
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left != null) { // 求左子树深度
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right != null) { // 求右子树深度
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {//左侧深度等于右侧深度 说明是一个满二叉树
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
补充
针对完全二叉树的相关内容见代码随想录
层序遍历 迭代模板
相关题目在此模板上稍作修改即可
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
int nums = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;// 如果根节点为空,直接返回0
}
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root); // 将根节点加入到队列中
while (!que.isEmpty()) { // 队列不为空时进行循环
int len = que.size(); // 当前层的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll(); // 获取并移除队列头节点
nums++;
if (tmpNode.left != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.left); // 将左子节点加入到队列中
}
if (tmpNode.right != null) {
que.offer(tmpNode.right); // 将右子节点加入到队列中
}
}
}
return nums; // 返回结果
}
}
ps:部分图片和代码来自代码随想录和Leetcode官网






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








