一.相关说明
1.代码运行相关软件VS2022
2.主要使用的语言C++
3.没有存储功能,仅能实现模拟文件管理相关操作
4.模拟使用一系列Linux操作系统相关命令
例如:mkdir---创建目录
三.代码
#include <conio.h> // 定义了一些控制台操作函数,例如getch、clrscr和gotoxy等。这些函数只在Windows平台上可用,在Linux或macOS上不可用。
#include <iostream> // 标准输入输出头文件,包含cout,cin等
#include <string> // 定义了字符串类string
#include <stdio.h> // 定义了输入输出函数,例如printf
#include <stdlib.h> // 定义了一些常用的函数和变量类型,例如malloc、exit、size_t和NULL等
#include <time.h> // 获取当前系统时间,用于记录文件创建时间等信息。
using namespace std; //命名空间std
//函数声明
void register_user(); //1.用户注册
int login(); //2.登录,返回用户在用户目录数组中的下标
int create(string); //3.文件创建(文件名)
void mkdir(string); //4.创建文件夹(文件夹名)
int open(string name); //5.打开文件(文件名)
int close(string); //6.关闭文件(文件名)
int read(string); //7.读取文件(文件名)
int del(string); //8.删除文件(文件名)
void remove(string name);//9.删除目录(文件名)
void cd(); //10.切换目录
void dir(); //11.列文件目录
void ls(); //12.显示当前目录的文件
int write(string, char*, int); //13.写入文件(文件名,物理块要存入的数据内容,文件内数据总长度)
void change(string name);//14.修改文件属性(文件名)
void input_operation(); //用户交互
void display(); //列出所有命令以及用法
bool login_or_not(); //检测是否有用户登录
//-------第一级:顶层目录(所有的用户)
struct MFD // 16个用户-----------------------2的幂次方
{
string username; //用户名
string password; //登录密码
struct USER_UFD* next; //指向用户目录
};
//-------第三层:用户的某个目录文件下的所有文件(包含一个用户的所有文件)
struct UFD //一个用户可以用16个文件夹
{
struct file_message //每个文件夹下可以有64个文件
{
string filename; //文件名
int protect_code; //保护码
int length; //文件长度
int addr; //存放该文件的物理块的第一个的块号
}ufd[64];
string directname; //用户目录名(文件夹的名称)
int cur_file_size = 0; //不能在结构体内附初始值。
};
//-------第二级:单个用户的文件目录
struct USER_UFD
{
struct UFD direct[16]; //每个用户最多有16个目录
int cur_user_direct_size = 0; //当前用户的目录数
};
// user open file:当前打开的文件控制块
struct UOF //假设一个用户最多同时打开16个文件
{
struct uof
{
string filename;//文件名
int pointer; //文件的读写指针,其实就是文件的大小
int protect_code; //2表示可读可写,1表示可读不可写, 0表示不可读不可写
int addr; //存放文件的第一个磁盘块号
}uof[16];
int cur_openfilesize = 0; //打开的文件数
};
//-------记录文件占用磁盘块情况:物理块,假设一个磁盘的每个物理块大小为 512个字节 = 64*2*4字节
struct fat //文件分配表 用一块物理块存放,那么最多可以记录64块数据块的信息。
{
int next = -1; //下一个磁盘块号
int used = 0; //1表示被使用,0表示未被使用
}fat[64];
int max_usersize = 16; //最大用户数量
int max_userfilesize = 64; //每个用户最大文件夹数量
int max_openfilesize = 16; //用户可以同时打开的文件数量
MFD mfd[16]; //-------用户信息:16个用户(身份登录信息)
USER_UFD cur_all_direct[16]; //-------第一级:16个用户的所有目录的对象(文件目录信息)
MFD cur_user; //-------第二级:当前用户,可检索到当前用户下所有的目录(同时只能有一个用户处于登录状态)
UOF openfile[16]; //当前用户的文件打开表对象,为全局变量
UOF* cur_opentable; //指向当前文件打开表
char* fdisk; //虚拟磁盘的起始位置
int cur_user_size = 0; //记录当前用户的人数(上限16)
string path; //记录当前用户的路径
bool login_or = false; //记录当前是否有用户登录
//文件创建
int create(string name)
{
// 0 判断当前路径
if (path == "")
{
cout << "当前不处于文件目录下,请在文件夹下创建文件" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 1 获取文件夹下标
int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++) //遍历当前用户所有的文件夹
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //判断
{
break;
}
}
// 2 文件重名判断
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //遍历当前目录,查看是否有文件重名
{
if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)
break;
}
if (i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size) //判断文件名是否重复
{
cout << "文件名重复" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 3 文件数目判断 s
if (cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size == 64) //判断当前目录的文件到达64个
{
cout << "用户文件已经达到64个" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 4 文件是否可分配到新的空闲块
//寻找空闲块
int j;
for (j = 0; j < 64; j++) //判断是否有空的空闲块。
{
if (fat[j].used == 0)
break;
}
if (j >= 64)
{
cout << "磁盘没有空闲块了" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 5 创建文件:修改ufd信息
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].filename = name;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].addr = j; //文件起始盘块号
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].length = 0; //文件初始没有数据
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size].protect_code = 2; //表示可读可写
cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size++;//用户文件数量加1
fat[j].used = 1; //被使用
fat[j].next = -1; //只是个空文件,所有没有后序的块
//写入文件打开表中,就是调用open()
cout << "文件创建成功" << endl;
int fd = open(name);
return fd;
}
//打开文件
int open(string name)
{
// 1 遍历该用户所有的文件夹,获取当前文件夹的文件目录下标
int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数
for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录
{
break;
}
}
// 2 遍历该文件夹下的文件,获取文件下标
//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开
{
if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)
break;
}
// 3 判断文件是否存在
//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于
if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size)
{
cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 4 判断文件是否可以被打开(是否达到打开上限)
//cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize 代表 UOF指针->打开的文件数
if (cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize == max_openfilesize) //如果打开文件的数量达到最大值,那么就无法打开
{
cout << "文件打开数量已经达到最大值" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 5 判断文件是否已经被打开
for (int j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //如果文件已经打开,就无需打开
{
if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name)
{
cout << "文件已经打开" << endl;
return -1;
}
}
// 6 更新文件打开表信息
//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 当前文件数
int k;
for (k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; k++) //找到要打开的文件在文件数组中的第几个
{
if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].filename == name)
break;
}
//打开文件:更新打开表(保存被打开文件的信息),
cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].filename = name;
cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].protect_code;
cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].pointer = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].length;
cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[k].addr;
cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize++; //文件打开数量加1
cout << "文件打开成功" << endl;
return k; //返回文件在文件打开表中的第几项
}
//修改文件属性
void change(string name)
{
// 1 遍历该用户所有的文件夹
int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
//cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size 代表 目录数
for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname) //找指定名称的目录
{
break;
}
}
// 2 遍历该文件夹下的文件
//cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size 代表 文件数
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //当前目录有没有这个文件,没有就自然不能打开
{
if (name == cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename)
break;
}
// 3 判断文件是否存在
//-------这里的判断应当是大于等于,而不是大于
if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size)
{
cout << "该用户没有这个文件" << endl;
return;
}
// 4 修改文件属性:修改ufd信息
cout << "请输入需要修改的属性对应的数字(1--文件名)(2--文件读写保护码):";
int which;
cin >> which; //选项
if (which == 1)
{
cout << "请输入需要新的文件名:";
string name;
cin >> name; //文件名
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = name;
}
if (which == 2)
{
cout << "请输入文件的读写权限对应的数字(0--禁止读写)(1--仅可读)(2--可读可写):";
int code;
cin >> code; //读写权限
if (code == 0 || code == 1 || code == 2)
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = code;
else
cout << "输入有误,请重新change" << endl;
}
cout << "文件属性修改成功!" << endl;
}
//关闭文件
int close(string name)
{
// 1 获取当前文件在文件打开表的对应下标
int fd;
for (int i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++) //找到要关闭的文件在表中的第几项
{
if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name) //根据文件名查找
{
fd = i;
break;
}
}
if (fd >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize)
{
cout << "没有这个文件或者文件没有打开" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 2 将要删除的项目与最后一个项目交换,因为是数组存放。(这样,仅仅需要将cur_openfilesize--,就等价于删除)
cur_opentable->uof[fd].filename = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].filename;
cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].pointer;
cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].protect_code;
cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr = cur_opentable->uof[cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize - 1].addr;
cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize--;
cout << "文件关闭成功" << endl;
return 0;
}
//删除文件
int del(string name) //删除文件打开表的文件数量不用减一,因为文件打开就不能删除文件
{
// 1 找到当前目录
int index; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
for (index = 0; index < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index].directname)
{
break;
}
}
// 2 遍历当前目录下的文件
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //判断当前目录下有没有这个文件
{
if (cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename == name)
break;
}
if (i >= cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size)
{
cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 3 遍历打开的文件
int j;
for (j = 0; j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; j++) //判断该文件是否被打开
{
if (cur_opentable->uof[j].filename == name)
break;
}
if (j < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize) //说明文件被打开了
{
cout << "这个文件被打开了,请先关闭" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 4 更新当前用户目录下文件数组信息,就是将最后一个文件的信息替换到要删除的文件的位置
fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].filename;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].addr;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].length;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size - 1].protect_code;
cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size--; //用户文件数量减1
// 5 回收磁盘:更新文件分配表fat
//cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr 即 起始地址的块号(下标表示,所以从0开始)
//temp 记录文件分配表下标
int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;
while (temp != -1)
{
fat[temp].used = 0;
temp = fat[temp].next;
}
cout << "删除文件成功" << endl;
return 0;
}
//读取文件
int read(string name)
{
// 1 文件目录下标
int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname)
{
break;
}
}
// 2 文件下标
int a; //遍历文件
for (a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //判断文件是否存在
{
if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename == name)
break;
}
if (a >= cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size)
{
cout << "没有这个文件" << endl;
return -1;
}
int i;
// 3 判读文件是否打开(通过在文件打开情况结构体的实例中寻找待读取文件的文件名)
for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++)
{
if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)
break;
}
if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize)
{
cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 4 如果文件已经打开,那么此时的 i 就是打开的文件数组uof的下标
int fd = i; //获取文件描述字
//判断读文件的合法性
if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code == 0) //创建的文件都是默认可读可写的
{
cout << "文件不可读" << endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
int len = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer; //文件的长度
int block_size = len / 512; //磁盘的个数
int offset = len % 512; //偏移量
if (offset != 0)
block_size++; //包含偏移量的磁盘
//如果用一个文件表示磁盘的引导块,用另一个文件表示磁盘的数据块,那么我们计算文件的起始位置就不用加上磁盘的引导块了
//关于文件的存放文件,我们char *fdisk表示一整个磁盘,然后不同文件的内容存放在这个指针所指向的不同字符段
char* first = fdisk + cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr * 512; //文件的起始地址
char* buf = (char*)malloc(512 * sizeof(char)); //缓冲区(大小等于一个空闲块大小)
cout << "文件的内容为 :";
for (int k = 0; k < block_size; k++) //遍历文件包含的块,k代表相对起址的块号
{
if (k == block_size - 1) //如果是最后一个磁盘块,就不是将全部512字节输出,而是输出偏移量大小的数据
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - k * 512; j++) //赋值文件剩余的字符------偏移量
{
buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区存放待输出的字符
}
for (int u = 0; u < len - k * 512; u++)
{
cout << buf[u + k * 512]; //输出剩余长度,之所以这样输出,printf(),将整个buf的内容全部输出,如果没有读满就会出现乱码
}
}
else //不在最后一个磁盘块,也就是在其他已经读满的磁盘块
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - i * 512; j++)
buf[j + k * 512] = first[j]; //缓冲区读满就输出内容
printf("%s\n", buf); //输出文件的内容
int next_block = fat[cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr].next; //读完一个磁盘块后,在接着读下一个磁盘块
first = fdisk + next_block * 512;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << "文件读取成功" << endl;
free(buf); //释放缓冲区
return 0;
}
}
//类似于文件拷贝,每次赋值缓冲区到虚拟磁盘中
//待完成问题:更新表的文件长度
int write(string name, char* buf, int len)
{
// 1 获取文件目录数组下标(当前是哪个文件夹)
int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname)
{
break;
}
}
// 2 从已打开文件寻找文件下标 i (之后重命名为 fd )
int i;
//判读文件是否打开
for (i = 0; i < cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize; i++)
{
if (cur_opentable->uof[i].filename == name)
break;
}
if (i >= cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize)
{
cout << "文件没有打开, 无法读取" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 3 文件共享和保护
int fd = i; //获取文件描述字
//判断读文件的合法性
if (cur_opentable->uof[fd].protect_code != 2)
{
cout << "文件不可写" << endl;
return -1;
}
else //文件可写入
{
int temp; //保存当前所写的文件在用户文件目录表的第几项,为了后面修改文件的大小
int first_block = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr; //用户文件存放的第一个磁盘块
// 4 遍历当前目录下所有文件,获取文件下标temp(打开表下标是fd ; 文件下标是temp)
for (int k = 0; k < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; k++)
{
if (cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[k].addr == first_block)
{
temp = k;
break;
}
}
//追加写
// 5 找到该文件存放的最后一个磁盘块
while (fat[first_block].next != -1)
{
first_block = fat[first_block].next;
}
//计算该文件存放的最后一个地址
char* first;
first = fdisk + first_block * 512 + cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512;
// 6 如果最后一个文件剩下的空间大于要写入的长度(不需要继续分配新的空闲块)
if (len <= 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512)
{
//strcpy(first, buf); 这句代码出现问题,可能是由于buf没有读满,后面的值被访问了,非法!
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
first[i] = buf[i];//将缓冲区的内容写入虚拟磁盘中
}
cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + len; //更新文件打开表
cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + len; //更新用户目录文件表
}
else // 7 如果之前的半块磁盘剩下的空间不足写入
{
// 7.1 写入一部分的内容到最后一个磁盘块的剩余空间
for (i = 0; i < 512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512; i++)
{
first[i] = buf[i];
}
// 7.2 计算分配完最后一个磁盘的剩余空间后,还剩下多少字节没有存储,计算还需要分配多少空闲块
int last_size = len - (512 - cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer % 512); //剩余待写入的大小
int need_block_size = last_size / 512; //待分配的空闲块数
int need_offset_size = last_size % 512; //偏移量
if (need_offset_size > 0)
need_block_size++; //总共需要这么磁盘块
// 7.3 判断磁盘剩余空间是否足够
int unused_block_size = 0; //记录没有使用过的磁盘块的个数
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++)
{
if (fat[i].used == 0)
{
unused_block_size++;
}
}
if (unused_block_size < need_block_size)
{
cout << "磁盘没有空间存放了" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 7.4 磁盘还有足够的空间:分配空闲块,
else
{
int item = cur_opentable->uof[fd].addr;
for (int p = 0; p < need_block_size; p++) //执行多次寻找空闲磁盘的操作,
{
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++)
{
if (fat[i].used == 0) //没有被使用
{
first = fdisk + i * 512; //当前要写入的磁盘块的起始地址
fat[i].used = 1; //标记被使用
fat[item].next = i; //标记下一个磁盘
item = i;
break;
}
}
if (p == need_block_size - 1)
{
for (int k = 0; k < need_offset_size; k++) //将文件的偏移量写入最后一个文件中
first[k] = buf[k];
//更新最后一个磁盘块的next值
fat[i].next = -1;
}
else //如果不是最后一个空闲块
{ //待解决问题,就是如果更新fat的next值
for (int k = 0; k < 512; k++)
first[k] = buf[k];
}
}
//更新文件打开表
cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer = cur_opentable->uof[fd].pointer + last_size;
//更新用户目录文件表
cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length = cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[temp].length + last_size;
}
}
cout << "文件写入成功" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
// 列文件目录
void dir()
{
int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个
for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname)
{
break;
}
}
if (path == "") //表示此时路径在用户的目录表,显示文件目录
{
cout << "\t" << "目录名" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++)
{
cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << endl;
}
}
else //显示目录下的文件
{
cout << "\t" << "文件名" << "\t" << "文件保护码" << "\t" << "文件长度" << "\t" << "文件起始盘块号" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; i++) //输出文件的信息
{
cout << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].filename
<< "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].protect_code
<< "\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].length
<< "\t" << "\t" << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[i].addr << endl;
}
}
}
//登录 @
int login()//分析@
{/*判断你输入的用户和密码在系统中是否真实存在,使用for循环进行遍历实现,提前退出循环说明用户与密码存在,执行到最后没跳出循环说明用户密码不匹配*/
//用户名
string name;
//密码
string password;
cout << "请输入你的姓名:" << endl; //用户输入
cin >> name;
cout << "请输入你的密码:" << endl;
cin >> password;//---让用户输入密码和姓名
int i; // 用户目录循环变量
for (i = 0; i < cur_user_size; i++)//---使用循环可以产生多次创建,但要小于16
//遍历用户目录mfd
{
if (mfd[i].username == name && mfd[i].password == password)//---当用户名与密码都对时
{
break;
}
}
//如果遍历一遍之后,没有任何一项匹配成功,给出提示信息并返回
if (i >= cur_user_size)
{
cout << "没有这个用户或者用户名密码错误" << endl;
return -1;
}
//信息验证成功,分配内存
mfd[i].next = &(cur_all_direct[i]); //用户指向自己的所有目录的结构
//初始化当前用户的信息
cur_user = mfd[i];
cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size = mfd[i].next->cur_user_direct_size; //当前用户的文件夹数量
cur_user_size++; //用户人数++?
cur_opentable = &openfile[cur_user_size]; //指针指向文件打开表对象
cur_opentable->cur_openfilesize = 0; //设初始值(初始打开的文件数为0)
path = ""; //指定当前路径为用户的全部目录处
login_or = true; //当前有用户登录
return 1;
}
void cd()
{
string temp_path;
cin >> temp_path;
if (temp_path == "..") //两级目录,等价于返回到根目录
{
path = "";
return;
}
int i; //遍历文件目录
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断path是否存在
{
if (temp_path == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname) //根据文件夹名称 与 路径名称 判断是否存在
break;
}
if (i >= cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size)
{
cout << "没有这个目录" << endl;
return;
}
path = temp_path;
return;
}
// 创建目录
void mkdir(string name)
{
//判断当前用户的文件目录的数目是否达到最大值
if (cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size == 16)
{
cout << "用户目录已经达到最大值,不能在创建目录了" << endl;
return;
}
//遍历目录
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //判断创建的目录是否存在
{
if (cur_user.next->direct[i].directname == name)
break;
}
if (i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size) //找到同名后代表已经存在
{
cout << "该目录已经存在了" << endl;
return;
}
//如果文件夹可以创建,最后一个下标位置下,创建新的目录
cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].directname = name; //目录名
cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size].cur_file_size = 0; //新创建的目录里面的文件个数为0
cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size++; //用户的目录数加1
cout << "创建目录成功" << endl;
return;
}
// 检测登录状态 @
bool login_or_not()//伴随着必要功能的一起判断使用
{
if (!login_or)//判断没有处于登录状态时
{
cout << "当前没有登录,请使用login进行登录" << endl;
return 0;
}
else
return 1;
}
// 显示用户创建的文件
void ls()
{
if (path == "") //如果是根目录
{
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++) //遍历创建的目录
{
cout << cur_user.next->direct[i].directname << "\t";
}
}
int index1; //标识当前目录在direct数组中第几个-----找当前文件夹对应的下标
for (index1 = 0; index1 < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; index1++)
{
if (path == cur_user.next->direct[index1].directname)
{
break;
}
}
for (int a = 0; a < cur_user.next->direct[index1].cur_file_size; a++) //遍历文件
{
cout << cur_user.next->direct[index1].ufd[a].filename << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
//功能派发处@
void input_operation() //用户输入命令
{
if (cur_user.username == "")//---如果用户输入的为空---一定条件下执行的if语句
cout << "localhost :";
else
cout << cur_user.username << "用户登录成功,请执行功能" << path << ">";
string operation;
cin >> operation;//将用户输入的值存储起来,方便向下的进行
if (operation == "login")///登录功能的实现
{
login();
}
else if (operation == "dir" && login_or_not())//创建目录功能的实现
dir();
else if (operation == "create" && login_or_not())//创建文件
{
string filename;
printf("请输入你要创建的文件名:\n");
cin >> filename;
create(filename);
}
else if (operation == "del" && login_or_not())//删除文件
{
string filename;
cin >> filename;
del(filename);
}
else if (operation == "open" && login_or_not())//打开文件
{
string name;
printf("请输入你要打开的文件名:");
cin >> name;
open(name);
}
else if (operation == "close" && login_or_not())//关闭文件
{
string name;
cin >> name;
close(name);
}
else if (operation == "read" && login_or_not())//读文件
{
string name;
cin >> name;
read(name);
}
else if (operation == "write" && login_or_not())//写文件
{
string content;
string name;
cout << "请输入要写入的文件:";
cin >> name;
cin.ignore(); //清空缓冲区的内容,不然getline读到上一个回车直接结束。。。
cout << "请输入文件要写入的内容: " << endl;;
getline(cin, content); //读入一整行内容
char buf[512];
int times = content.length() / 512;
int offset = content.length() % 512;
if (offset != 0)
times++;
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
if (i == times - 1) //注意这里不能写成times--
{
for (int j = 0; j < offset; j++)
buf[j] = content[j];
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < 512; j++)
buf[j] = content[j];
}
write(name, buf, content.length());
}
}
else if (operation == "ls" && login_or_not())//列出文件
{
ls();
}
else if (operation == "exit")//退出系统
{
exit(0);
}
else if (operation == "cd" && login_or_not())//切换目录
{
cd();
}
else if (operation == "mkdir" && login_or_not())//创建目录
{
string name;
printf("请输入创建的目录名:\n");
cin >> name;
mkdir(name);
}
else if (operation == "register")//注册
{
register_user();
}
else if (operation == "remove" && login_or_not())//删除目录
{
string name;
printf("请输入你要删除的目录名:");
cin >> name;
remove(name);
}
else if (operation == "change" && login_or_not())//更改文件属性
{
string name;
cin >> name;
change(name);
}
else if (operation == "help" && login_or_not())//显示命令
{
display();
}
else if (operation == "clear" && login_or_not())//清屏
{
system("cls");//windows下
cout << endl << "\t" << "*------------------文件系统-命令菜单--------------------*" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << "\t" << "命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "功能" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|-------------------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 1 << "\t" << "register" << "\t" << "注册" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 2 << "\t" << "login" << "\t" << "\t" << "登录" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 3 << "\t" << "mkdir (name)" << "\t" << "创建目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 4 << "\t" << "remove(name)" << "\t" << "删除目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 5 << "\t" << "cd" << "\t" << "\t" << "切换目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 6 << "\t" << "dir" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 7 << "\t" << "create (name)" << "\t" << "创建文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 8 << "\t" << "open (name)" << "\t" << "打开文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 9 << "\t" << "close (name)" << "\t" << "关闭文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 10 << "\t" << "read (name)" << "\t" << "读文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 11 << "\t" << "del (name)" << "\t" << "删除文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 12 << "\t" << "ls" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 13 << "\t" << "write" << "\t" << "\t" << "写文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 14 << "\t" << "change(name)" << "\t" << "改文件属性" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 15 << "\t" << "clear" << "\t" << "\t" << "清屏" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 16 << "\t" << "help" << "\t" << "\t" << "显示命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 17 << "\t" << "exit" << "\t" << "\t" << "退出系统" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "*-------------------------------------------------------*" << endl << endl;
//system("clear");//linux下
}
else//输入其他的东西
{
cout << "你的命令错误,重新输入" << endl;
}
}
//用户注册
void register_user()
{
cout << "请输入用户名:";
string username; //用户名
cin >> username;
cout << "请输入密码:";
string password; //密码
cin >> password;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) //判断用户名是否存在
{
if (mfd[i].username == username) //如果已经存在
{
cout << "该用户已经存在" << endl;
return;
}
}
mfd[cur_user_size].username = username; //保存在mfd中(第一级目录)
mfd[cur_user_size].password = password;
cur_user_size++; //用户人数加1
cout << "用户注册成功!" << endl;
}
//删除目录
void remove(string name)
{
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size; i++)
{
if (name == cur_user.next->direct[i].directname)
{
index = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size; i++) //删除目录里面的文件
{//直接释这些文件所占的磁盘块
fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].used = 0; //没有使用
int temp = fat[cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr].next;
while (temp != -1)
{
fat[temp].used = 0;
temp = fat[temp].next;
}
}
//删除目录项,就是将两个目录项的内容进行交换
cur_user.next->direct[index].cur_file_size = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].cur_file_size; //注意这里需要减一,由于本身结构的限制
cur_user.next->direct[index].directname = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].directname;
for (int i = 0; i < cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].cur_file_size; i++) //注意这里的减一
{
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].addr = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].ufd[i].addr;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].filename = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].ufd[i].filename;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].length = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].ufd[i].length;
cur_user.next->direct[index].ufd[i].protect_code = cur_user.next->direct[cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size - 1].ufd[i].protect_code;
}
cur_user.next->cur_user_direct_size--; //目录数量减1
cout << "删除目录成功" << endl;
return;
}
///菜单@
void display() //展示命令
{
cout << endl << "\t" << "*------------------文件系统-命令菜单--------------------*" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << "\t" << "命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "功能" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|-------------------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 1 << "\t" << "register" << "\t" << "注册" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 2 << "\t" << "login" << "\t" << "\t" << "登录" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 3 << "\t" << "mkdir (name)" << "\t" << "创建目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 4 << "\t" << "remove(name)" << "\t" << "删除目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 5 << "\t" << "cd" << "\t" << "\t" << "切换目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 6 << "\t" << "dir" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出目录" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 7 << "\t" << "create (name)" << "\t" << "创建文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 8 << "\t" << "open (name)" << "\t" << "打开文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 9 << "\t" << "close (name)" << "\t" << "关闭文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 10 << "\t" << "read (name)" << "\t" << "读文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 11 << "\t" << "del (name)" << "\t" << "删除文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 12 << "\t" << "ls" << "\t" << "\t" << "列出文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 13 << "\t" << "write" << "\t" << "\t" << "写文件" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 14 << "\t" << "change(name)" << "\t" << "改文件属性" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 15 << "\t" << "clear" << "\t" << "\t" << "清屏" << "\t" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 16 << "\t" << "help" << "\t" << "\t" << "显示命令" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "|" << "\t" << 17 << "\t" << "exit" << "\t" << "\t" << "退出系统" << "\t" << "\t" << "|" << endl;
cout << "\t" << "*-------------------------------------------------------*" << endl << endl;
}
//主函数@
int main()
{
system("color F0"); //系统背景色
cur_user.username = ""; //初始化当前用户的用户名为空
path = ""; //文件路径
fdisk = (char*)malloc(1024 * 1024 * sizeof(char)); //用内存模拟外存,申请内存空间,初始化
display();///菜单调用
while (true)
input_operation();//功能的实现
free(fdisk); //程序结束,释放资源
return 0;
}
三.功能实现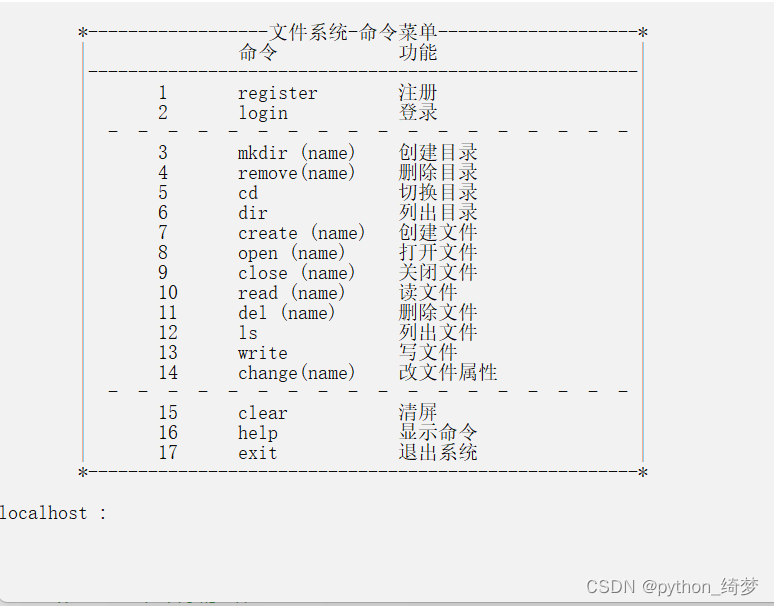
1.注册用户
在localhost:后面输入"register"+回车,再输入用户名与密码。
2.登录用户
在localhost:后面输入"login"+回车,再输入用户名与密码。
3.执行功能
推荐首次执行顺序:
mkdir---创建目录
cd+空格+创建的目录名---从用户中进入到目录中
create---创建文件
write+空格+文件名---写入指定文件
read+空格+文件名---读文件
close+空格+文件名---关闭文件
4.退出系统
输入exit退出






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








