1、创建编号为ABC三个线程,三个线程循环打印自己的编号,要求打印出来的结果必须是ABC;
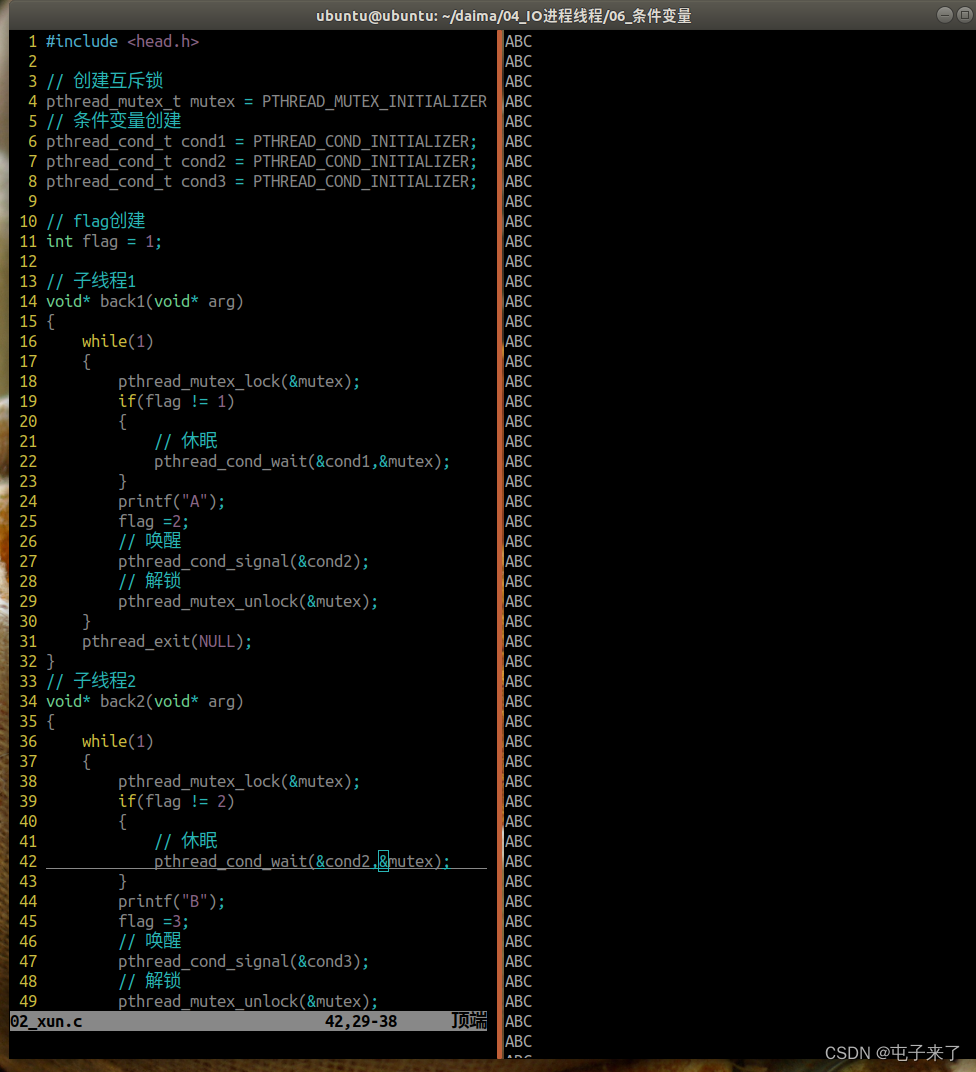
代码:
#include <head.h>
//创建互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
//条件变量创建
pthread_cond_t cond1 =PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond2 =PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond3 =PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
//限制访问机制
int flag=1;
void* callback1(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
/*************临界区**************/
//上锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(flag != 1)
{
//休眠 解锁
pthread_cond_wait(&cond1,&mutex);
}
printf("A");
flag=2;
//唤醒
pthread_cond_signal(&cond2);
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
/*************临界区**************/
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* callback2(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
/*************临界区**************/
//上锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(flag != 2)
{
//休眠 解锁
pthread_cond_wait(&cond2,&mutex);
}
printf("B");
flag=3;
//唤醒
pthread_cond_signal(&cond3);
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
/*************临界区**************/
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* callback3(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
/*************临界区**************/
//上锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(flag != 3)
{
//休眠 解锁
pthread_cond_wait(&cond3,&mutex);
}
printf("C\n");
flag=1;
//唤醒
pthread_cond_signal(&cond1);
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
/*************临界区**************/
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//练习1.创建三个线程id号为ABC,要求三个线程循环打印自己的ID号, 运行顺序为ABCAB.....
pthread_t A,B,C;
if(pthread_create(&A,NULL,callback1,NULL)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create faild __%d__\n",__LINE__);
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&B,NULL,callback2,NULL)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create faild __%d__\n",__LINE__);
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&C,NULL,callback3,NULL)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create faild __%d__\n",__LINE__);
return -1;
}
pthread_join(A,NULL);
pthread_join(B,NULL);
pthread_join(C,NULL);
//销毁互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
//销毁条件变量
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond1);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond2);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond3);
return 0;
}
2、实现进程中父子相互通信
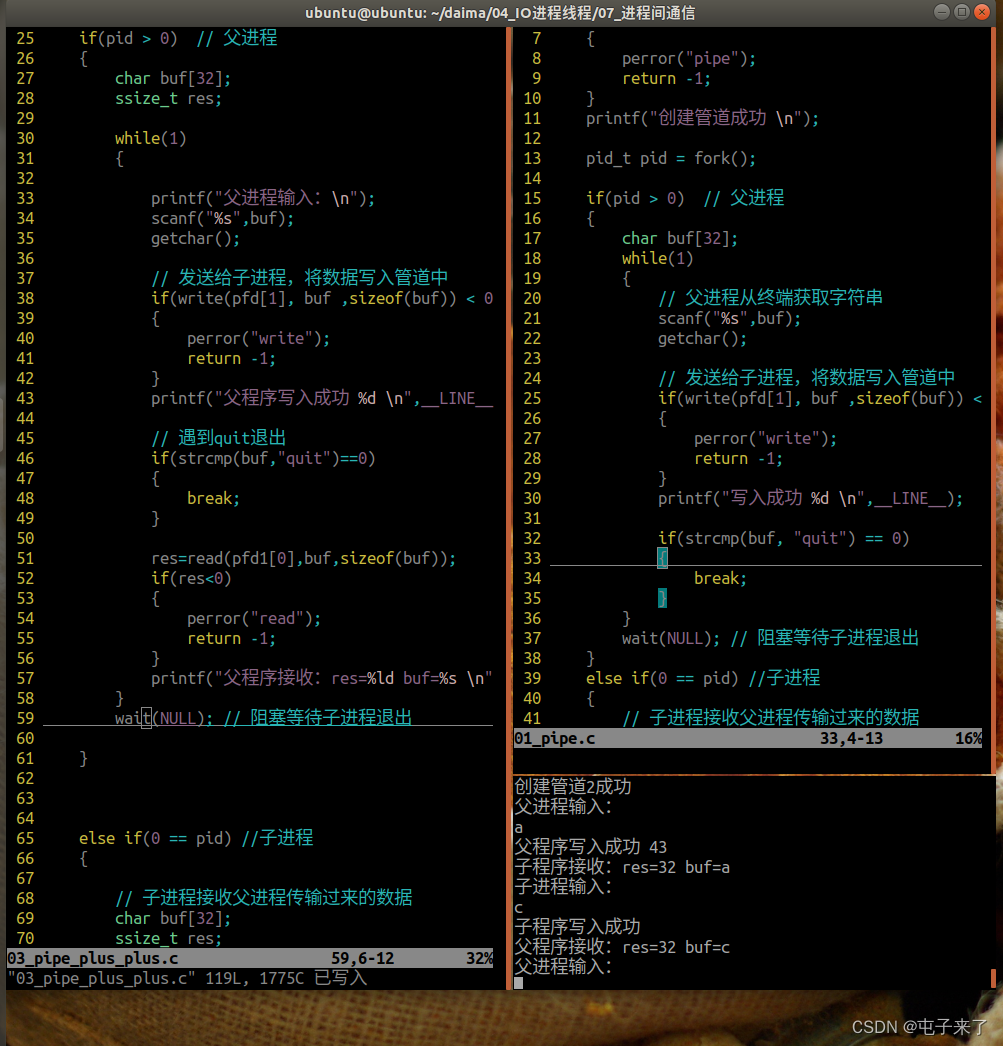
代码:
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int pfd[2]; // 创建一个管道
if(pipe(pfd) < 0)
{
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
printf("创建管道1成功 \n");
int pfd1[2]; // 创建一个管道
if(pipe(pfd1) < 0)
{
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
printf("创建管道2成功 \n");
pid_t pid = fork(); //创建父子进程
if(pid > 0) // 父进程
{
char buf[32];
ssize_t res;
while(1)
{
printf("父进程输入:\n");
scanf("%s",buf);
getchar();
// 发送给子进程,将数据写入管道中
if(write(pfd[1], buf ,sizeof(buf)) < 0)
{
perror("write");
return -1;
}
printf("父程序写入成功 %d \n",__LINE__);
// 遇到quit退出
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
res=read(pfd1[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
if(res<0)
{
perror("read");
return -1;
}
printf("父程序接收:res=%ld buf=%s \n",res,buf);
}
wait(NULL); // 阻塞等待子进程退出
}
else if(0 == pid) //子进程
{
// 子进程接收父进程传输过来的数据
char buf[32];
ssize_t res;
while(1)
{
// 当管道中没有数据的时候,read函数阻塞
res = read(pfd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
if( res < 0)
{
perror("read");
return -1;
}
printf("子程序接收:res=%ld buf=%s \n",res,buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
printf("子进程输入:\n");
scanf("%s",buf);
getchar();
// 将数据写入管道中
if(write(pfd1[1],buf,sizeof(buf)) <0 )
{
perror("write");
return -1;
}
printf("子程序写入成功\n");
}
wait(NULL);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
close(pfd[0]);
close(pfd[1]);
close(pfd1[0]);
close(pfd1[1]);
return 0;
}





















 757
757











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








