题目
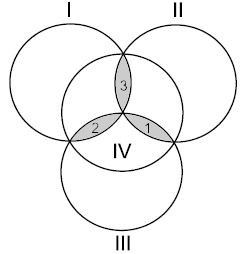
Let us consider four disks intersecting as in the figure. Each of the three shapes formed by the intersection of three disks will be called a petal.
Write zero or one on each of the disks. Then write on each petal the remainder in the division by two of the sum of integers on the disks that contain this petal.
For example, if there were the integers 0, 1, 0, and 1 written on the disks, then the integers written on the petals will be 0, 1, and 0 (the disks and petals are given in the order shown in the figure).
This scheme is called a Hamming code. It has an interesting property: if you enemy changes secretely any of the seven integers, you can determine uniquely which integer has been changed. Solve this problem and you will know how this can be done.
Problem illustration
Input
The only line contains seven integers separated with a space, each of them being zero or one. The first four integers are those written on the disks in the order shown in the figure. The following three integers are those written on the petals in the order shown in the figure
Output
Output one line containing seven integers separated with a space. The integers must form a Hamming code. The set of integers may differ from the input set by one integer at most. It is guaranteed that either the input set is a Hamming code or a Hamming code can be obtained from it by changing exactly one integer.
Example
题目大意:
一共七个区域

如果1 3 4区域的数相加%2!=6区域,那就不是汉明码;
1 2 4
2 3 4 同理;
(本质是二进制)
题目重点理解
For example, if there were the integers 0, 1, 0, and 1 written on the disks, then the integers written on the petals will be 0, 1, and 0 (the disks and petals are given in the order shown in the figure).
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[20];
bool judge(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e,int f,int g)
{
if((a+c+d)%2!=f) return false;
if((a+b+d)%2!=g) return false;
if((b+c+d)%2!=e) return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=7;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
if(judge(a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])!=0)
{
for(i=1;i<=7;i++)
{
if(i>1)
cout<<" ";
cout<<a[i];
}
}
for(i=1;i<=7;i++)
{
a[i]=1^a[i];
if(judge(a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])!=0)
{
cout<<a[1]<<" "<<a[2]<<" "<<a[3]<<" "<<a[4]<<" "<<a[5]<<" "<<a[6]<<" "<<a[7];
break;
}
a[i]=1^a[i];
}
return 0;
}
新学会的 ^
这个是异或
1^1=0
0^0=0
1^0=1
0^1=1
相同为0
不同为1
我忘记是不是离散数学提到的了0.0






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








