Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with ‘debug’ enabled
在启动springboot项目,突然报以下错误:
2020-08-10 15:54:41.570 WARN 16212 --- [ restartedMain] ConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext : Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'customerServiceImpl': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'baseMapper'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.huang.layuimcsmb.bus.mapper.CustomerMapper' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
2020-08-10 15:54:41.573 INFO 16212 --- [ restartedMain] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Stopping service [Tomcat]
2020-08-10 15:54:41.606 INFO 16212 --- [ restartedMain] ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener :
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled.
2020-08-10 15:54:41.765 ERROR 16212 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Application run failed
org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'customerServiceImpl': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'baseMapper'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.huang.layuimcsmb.bus.mapper.CustomerMapper' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:643) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.inject(InjectionMetadata.java:130) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:399) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1422) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:594) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:517) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.lambda$doGetBean$0(AbstractBeanFactory.java:323) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:226) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:321) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:202) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:893) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:879) ~[spring-context-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:551) ~[spring-context-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java:143) ~[spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:758) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:750) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:397) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:315) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1237) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1226) [spring-boot-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
at com.huang.layuimcsmb.LayuimcsMbApplication.main(LayuimcsMbApplication.java:11) [classes/:na]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) ~[na:1.8.0_131]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) ~[na:1.8.0_131]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[na:1.8.0_131]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[na:1.8.0_131]
at org.springframework.boot.devtools.restart.RestartLauncher.run(RestartLauncher.java:49) [spring-boot-devtools-2.3.1.RELEASE.jar:2.3.1.RELEASE]
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.huang.layuimcsmb.bus.mapper.CustomerMapper' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1714) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1270) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1224) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:640) ~[spring-beans-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar:5.2.7.RELEASE]
... 25 common frames omitted
因为我自己用的是mabatisplus的自动生成代码一键生成的。总体结构如下:
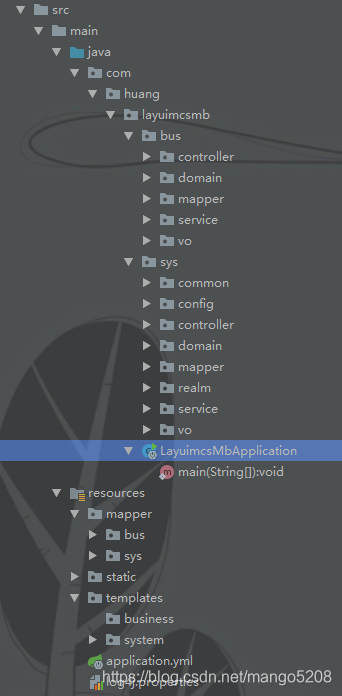
错误说的我 ‘customerServiceImpl’ 出错了,我去检查,并未出现任何错误,与我之前的几乎一样(之前并没有出错),因为刚生成,未写任何代码。

多次检查发现,说我并没有满足
unsatisfied dependency expressed through field ‘baseMapper’;
字段“baseMapper”表示的不满足的依赖关系;
随后检查启动类的mapper.发现了问题,我们常常喜欢将所有的层级都放在一个包下,所有启动类扫描包时,由于我个人将系统模块和业务模块分不同的包,所以没有扫描到。

解决办法






 在启动Spring Boot应用时遇到ApplicationContext启动错误,提示需在调试模式下重新运行以显示条件报告。错误涉及'customerServiceImpl'的依赖问题,具体为'baseMapper'字段的不满足。问题源于mapper扫描未包含所有层级,通过调整启动类扫描配置,确保扫描到主路径下的所有mapper,从而解决问题。
在启动Spring Boot应用时遇到ApplicationContext启动错误,提示需在调试模式下重新运行以显示条件报告。错误涉及'customerServiceImpl'的依赖问题,具体为'baseMapper'字段的不满足。问题源于mapper扫描未包含所有层级,通过调整启动类扫描配置,确保扫描到主路径下的所有mapper,从而解决问题。
















 2158
2158

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








