shell
参考文章:
https://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-shell-variable.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44099163/article/details/123354242
1、变量
- 变量名和等号之间不能有空格
- 命名只能使用英文字母,数字和下划线,首个字符不能以数字开头
- 中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线 _
- 不能使用标点符号
- 不能使用bash里的关键字(可用help命令查看保留关键字)
1、定义和使用变量
#定义变量
test="hello shell"
echo ${test}
#等同echo $test

变量名外面的花括号是可选的,加不加都行,加花括号是为了帮助解释器识别变量的边界。
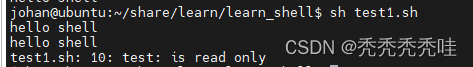
2、只读变量
#!/bin/bash
#定义变量
test="hello shell"
echo ${test}
#只读变量
readonly test
echo $test
test="revise"
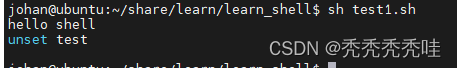
3、删除变量
#!/bin/bash
#定义变量
test="hello shell"
echo ${test}
#s删除变量
echo "unset test"
unset test
echo ${test}
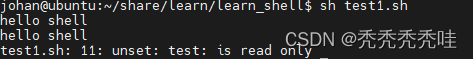
- 变量被删除后不能再次使用
- unset 命令不能删除只读变量。
#!/bin/bash
#定义变量
test="hello shell"
echo ${test}
#只读变量
readonly test
echo $test
#test="revise"
unset test
4、变量类型
- 局部变量 局部变量在脚本或命令中定义,仅在当前shell实例中有效,其他shell启动的程序不能访问局部变量。
- 环境变量 所有的程序,包括shell启动的程序,都能访问环境变量,有些程序需要环境变量来保证其正常运行。必要的时候shell脚本也可以定义环境变量。
- shell变量 shell变量是由shell程序设置的特殊变量。shell变量中有一部分是环境变量,有一部分是局部变量,这些变量保证了shell的正常运行
2、Shell 字符串
1、单引号和双引号
字符串可以用单引号,也可以用双引号,也可以不用引号。
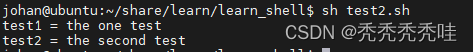
#!/bin/bash
test1="the one test"
echo "test1 = "$test1
test2='the second test'
echo "test2 = "$test2
单引号字符串的限制:
- 单引号里的任何字符都会原样输出,单引号字符串中的变量是无效的;
- 单引号字串中不能出现单独一个的单引号(对单引号使用转义符后也不行),但可成对出现,作为字符串拼接使用。
#!/bin/bash
test1="the one test"
echo "test1 = "$test1
test2='the second test'
echo "test2 = "$test2
test3='the third $test2'
echo "test3 = "$test3

双引号的优点:
- 双引号里可以有变量
- 双引号里可以出现转义字符

2、获取字符串长度
#!/bin/bash
string="abcd"
echo ${#string} # 输出 4
3、提取子字符串
#!/bin/bash
#从字符串第 2 个字符开始截取 6 个字符
string="this is a test of string"
echo ${string:1:6}
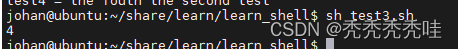
sh出现错误:

用下面命令替换sh
bash -x test3.sh
4、查找子字符串
查找字符 i 或 s 的位置(哪个字母先出现就计算哪个)
#!/bin/bash
string="this is a test of string"
echo `expr index "$string" is`

3、shell数组
bash支持一维数组(不支持多维数组),并且没有限定数组的大小。
类似于 C 语言,数组元素的下标由 0 开始编号。获取数组中的元素要利用下标,下标可以是整数或算术表达式,其值应大于或等于 0。
1、定义和读取数组
用括号来表示数组,数组元素用"空格"符号分割开。
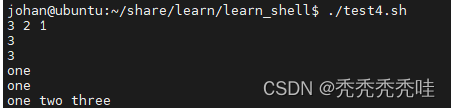
#!/bin/bash
test_array1=(3 2 1)
echo ${test_array1[@]}
echo $test_array1
echo ${test_array1[0]}
test_array2=(one two three)
echo ${test_array2[0]}
echo $test_array2
echo ${test_array2[@]}
- List item
sh执行脚本会出问题

2、获取数组的长度
获取数组长度的方法与获取字符串长度的方法相同
# 取得数组元素的个数
length=${#array_name[@]}
# 或者
length=${#array_name[*]}
# 取得数组单个元素的长度
length=${#array_name[n]}
#!/bin/bash
test_array1=(333 2 1)
# 取得数组元素的个数
length1=${#test_array1[@]}
echo "length1 = $length1"
# 或者
length2=${#test_array1[*]}
echo "length2 = $length2"
# 取得数组单个元素的长度
length3=${#test_array1[0]}
echo "length3 = $length3"

4、Shell 注释
1、单行注释
以 # 开头的行就是注释,会被解释器忽略。
2、多行注释
使用以下格式:
:<<EOF
注释内容...
注释内容...
注释内容...
EOF
#!/bin/bash
test_array1=(333 2 1)
echo "start EOF"
:<<EOF
# 取得数组元素的个数
length1=${#test_array1[@]}
echo "length1 = $length1"
# 或者
length2=${#test_array1[*]}
echo "length2 = $length2"
# 取得数组单个元素的长度
length3=${#test_array1[0]}
echo "length3 = $length3"
EOF
echo "end EOF"

还可以使用以下格式(把EOF替换为!):
:<<!
注释内容...
注释内容...
注释内容...
!
# : + 空格 + 单引号
: '
这是注释的部分。
可以有多行内容。
'
5、Shell 流程控制
1、if 语句语法
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
fi
2、if else 语法格式
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
else
command
fi
3、if else-if else 语法格式
if condition1
then
command1
elif condition2
then
command2
else
commandN
fi
#!/bin/bash
a=10
b=8
if [ $a == $b ];then #[与$a之间要有空格
echo "a=b"
elif [ $a -gt $b ];then #gt greater than
echo "a > b"
else
echo "a < b"
fi

如果使用 ((…)) 作为判断语句,大于和小于可以直接使用 > 和 <
if (( a > b )); then
...
fi
if (( $a == $b ));then
echo "a == b"
elif (( $a < $b ));then
echo "a < b"
elif (( $a > $b ));then
echo "a > b"
else
echo "no one match"
fi

4、for 循环
for循环一般格式为:
for var in item1 item2 ... itemN
do
command1
command2
...
commandN
done
#!/bin/bash
for loop in 1 2 3 4 5
do
echo "The value is: $loop"
done

5、while 语句
语法格式为:
while condition
do
command
done
#!/bin/bash
int=1
while(( $int<=5 ))
do
echo $int
let "int++"
done

6、case … esac
case … esac 为多选择语句,与其他语言中的 switch … case 语句类似,是一种多分支选择结构,每个 case 分支用右圆括号开始,用两个分号 ;; 表示 break,即执行结束,跳出整个 case … esac 语句,esac(就是 case 反过来)作为结束标记。
case … esac 语法格式如下:
case 值 in
模式1)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
模式2)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
esac
#!/bin/bash
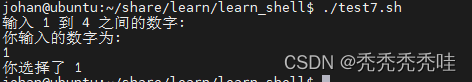
echo '输入 1 到 4 之间的数字:'
echo '你输入的数字为:'
read aNum
case $aNum in
1) echo '你选择了 1'
;;
2)echo '你选择了 2'
;;
3) echo '你选择了 3'
;;
4)echo '你选择了 4'
;;
*)echo '你没有输入 1 到 4 之间的数字'
;;
esac
7、跳出循环
1、break 命令
break 命令允许跳出所有循环(终止执行后面的所有循环)。
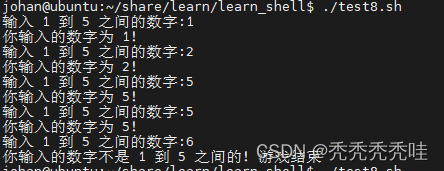
#!/bin/bash
while :
do
echo -n "输入 1 到 5 之间的数字:"
read aNum
case $aNum in
1|2|3|4|5) echo "你输入的数字为 $aNum!"
;;
*) echo "你输入的数字不是 1 到 5 之间的! 游戏结束"
break
;;
esac
done
2、continue
continue 命令与 break 命令类似,只有一点差别,它不会跳出所有循环,仅仅跳出当前循环。
#!/bin/bash
while :
do
echo -n "输入 1 到 5 之间的数字:"
read aNum
case $aNum in
1|2|3|4|5) echo "你输入的数字为 $aNum!"
;;
*) echo "你输入的数字不是 1 到 5 之间的! 游戏结束"
#break
continue
;;
esac
done

6、shell echo命令
echo -n 不换行输出
#!/bin/bash
echo -n "this is a test"
echo "this is a test1"

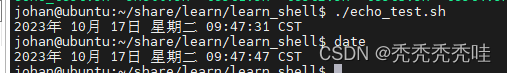
1、显示日期
echo `date`#反引号
2、显示变量
#!/bin/bash
string="hello shell"
echo $string

7、Shell test 命令
1、数值测试

代码中的 [] 执行基本的算数运算
#!/bin/bash
num1=$1
num2=$2
echo "num1= $num1"
echo "num2= $num2"
if test $[num1] -eq $[num2];then
echo "two nums are equal"
else
echo "two nums are not equal"
fi

2、字符串测试
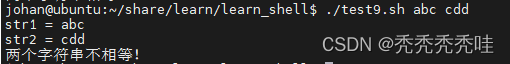
str1=$1
str2=$2
echo "str1 = $str1"
echo "str2 = $str2"
if test $str1 = $str2
then
echo '两个字符串相等!'
else
echo '两个字符串不相等!'
fi
8、Shell 基本运算符
1、算术运算符

注意:条件表达式要放在方括号之间,并且要有空格,例如: [
a
=
=
a==
a==b] 是错误的,必须写成 [ $a == $b ]。
#!/bin/bash
a=100
b=20
var=`expr $a + $b`
echo "a + b = $var"
var=`expr $a - $b`
echo "a - b = $var"
var=`expr $a \* $b`
echo "a * b = $var"
var=`expr $a / $b`
echo "a / b = $var"
var=`expr $a % $b`
echo "a % b = $var"
if [ $a == $b ];then
echo "a,b equal"
else
echo "a,b not equal"
fi

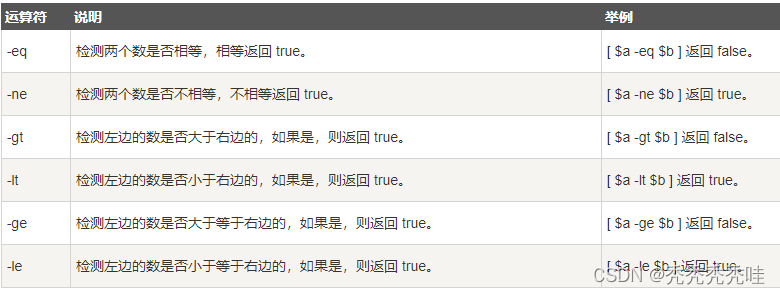
2、关系运算符
3、布尔运算符

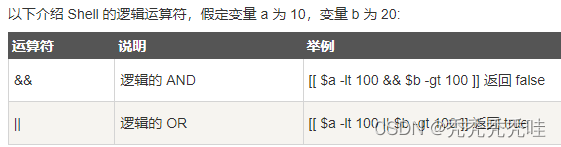
4、逻辑运算符
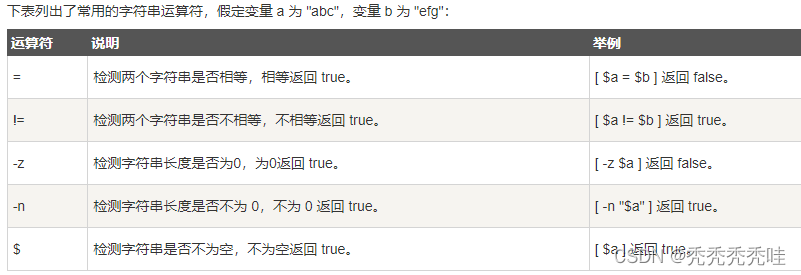
5、字符串运算符
6、文件测试运算符

9、shell函数
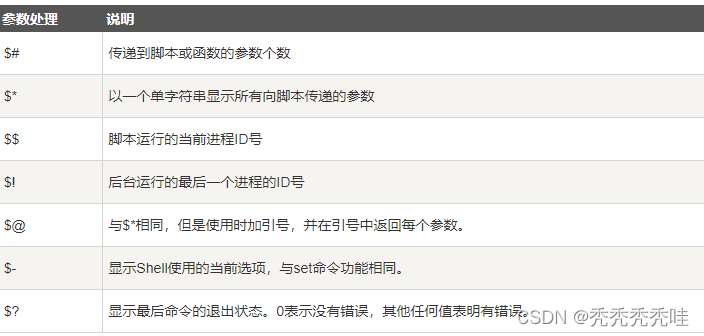
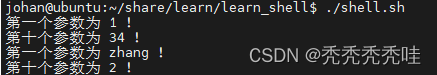
#!/bin/bash
#函数
funWithParam()
{
echo "第一个参数为 $1 !"
echo "第十个参数为 ${10} !"
}
funWithParam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 34 73
fun1()
{
echo "第一个参数为 $1 !"
echo "第十个参数为 ${3} !"
}
fun1 "zhang" 1212 2 32 322























 1474
1474











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










