解题报告 之 HDU5335 Walk Out
Description
In an


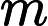 maze, the right-bottom corner is the exit (position
maze, the right-bottom corner is the exit (position



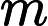
 is the exit). In every position of this maze, there is either a
is the exit). In every position of this maze, there is either a
 or a
or a
 written on it.
written on it.
An explorer gets lost in this grid. His position now is



 , and he wants to go to the exit. Since to arrive at the exit is easy for him, he wants to do something more difficult. At first, he'll write down the number on position
, and he wants to go to the exit. Since to arrive at the exit is easy for him, he wants to do something more difficult. At first, he'll write down the number on position




 . Every time, he could make a move to one adjacent position (two positions are adjacent if and only if they share an edge). While walking, he will write down the number on the position he's on to the end of his number. When finished, he will get a binary number. Please determine the minimum value of this number in binary system.
. Every time, he could make a move to one adjacent position (two positions are adjacent if and only if they share an edge). While walking, he will write down the number on the position he's on to the end of his number. When finished, he will get a binary number. Please determine the minimum value of this number in binary system.


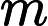 maze, the right-bottom corner is the exit (position
maze, the right-bottom corner is the exit (position



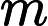
 is the exit). In every position of this maze, there is either a
is the exit). In every position of this maze, there is either a
 or a
or a
 written on it.
written on it.
An explorer gets lost in this grid. His position now is




 , and he wants to go to the exit. Since to arrive at the exit is easy for him, he wants to do something more difficult. At first, he'll write down the number on position
, and he wants to go to the exit. Since to arrive at the exit is easy for him, he wants to do something more difficult. At first, he'll write down the number on position




 . Every time, he could make a move to one adjacent position (two positions are adjacent if and only if they share an edge). While walking, he will write down the number on the position he's on to the end of his number. When finished, he will get a binary number. Please determine the minimum value of this number in binary system.
. Every time, he could make a move to one adjacent position (two positions are adjacent if and only if they share an edge). While walking, he will write down the number on the position he's on to the end of his number. When finished, he will get a binary number. Please determine the minimum value of this number in binary system.
Input
The first line of the input is a single integer
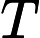


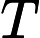



 , indicating the number of testcases.
, indicating the number of testcases.
For each testcase, the first line contains two integers and
and
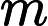






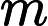





 . The
. The
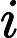 -th line of the next
-th line of the next
 lines contains one 01 string of length
lines contains one 01 string of length
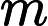 , which represents
, which represents
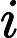 -th row of the maze.
-th row of the maze.


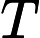



 , indicating the number of testcases.
, indicating the number of testcases.
For each testcase, the first line contains two integers
 and
and
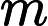






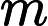





 . The
. The
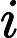 -th line of the next
-th line of the next
 lines contains one 01 string of length
lines contains one 01 string of length
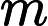 , which represents
, which represents
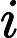 -th row of the maze.
-th row of the maze.
Output
For each testcase, print the answer in binary system. Please eliminate all the preceding
 unless the answer itself is
unless the answer itself is
 (in this case, print
(in this case, print
 instead).
instead).
 unless the answer itself is
unless the answer itself is
 (in this case, print
(in this case, print
 instead).
instead).
Sample Input
2
2 2
11
11
3 3
001
111
101
Sample Output
111
101
题目大意:给你一个n
*m
的格子图,每个格子要么是1,要么是0。起点在(1,1),终点在(n,m)。让你找一条路,让途中经过的数字按先后顺序排列组成的二进制数最小。
分析:很容易想到,如果起点是1,那么后面一定只能向右下走了,不然数位多了是第一致命的,然后考虑每一次走优先走0,没有0再走1。所以此时直接广搜到终点就是最短的答案。那么如果起点不是1呢?那么我们就可以先让前面有一些0,直到找到一个1之后又重复第一种情况。所以我们要找的是x+y最大位置1,因为找到1之后我们就要开始优先考虑数位最小了,只能向右下走,所以找到x+y最大的1是保证了位数最小。所以这里需要进行第二次bfs,去将所有(x+y)max的点找到,并依次从这些点开始出发重复第一种情况。
上代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1000 + 10;
struct Node
{
int x, y;
Node()
{
}
Node( int x, int y )
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
};
int vis[MAXN][MAXN];
int zero[MAXN * 4]; //所有x+y的位置上是否存在为0的点
char map[MAXN][MAXN];
int Move[MAXN][MAXN]; //记录路经,方便输出
vector<Node> bg; //所有x+y最大的点
int n, m;
int dir[4][2] = { { 0,1 }, { 1,0 }, { -1,0 }, { 0,-1 } }; //移动方向,注意1和4为一对,2和3为一对
void ini()
{
memset( vis, 0, sizeof vis );
memset( zero, 0, sizeof zero );
memset( Move, -1, sizeof Move );
}
bool inline check( int x, int y )
{
if(x <= 0 || x > n || y <= 0 || y > m)
return false;
return true;
}
void bfs()
//找到x+y最远的点
{
bg.clear();
bg.push_back( Node (1, 1) );
//此时(1,1)为0,先假设为最远的点
queue<Node> q;
q.push( Node( 1, 1 ) );
vis[1][1] = 1;
int dis = 1; //最小距离
int x, y;
while(!q.empty())
{
Node tem = q.front();
q.pop();
x = tem.x;
y = tem.y;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int temx = x + dir[i][0];
int temy = y + dir[i][1];
if(!check( temx, temy ) || map[temx][temy] == '1' || vis[temx][temy]) //如果越界或者是1或者已经找过了就不找了
continue;
vis[temx][temy] = 1;
q.push( Node( temx, temy ) );
if(temx + temy > dis) //发现更远的点
{
dis = temx + temy;
bg.clear();
}
if(temx + temy == dis) //发现了最远点
{
bg.push_back( Node( temx, temy ) );
}
}
}
}
void bfs2()
//找到从x出发小的数
{
queue<Node> q;
if(map[1][1] == '1') //如果起点是1,也优先保证数位最短
{
q.push( Node( 1, 1 ) );
}
else //如果起点是0,则找到第一个1的最远点
{
bfs();
for(int i = 0; i < bg.size(); i++)
q.push( bg[i] );
}
while(!q.empty()) //从第一个1开始,只向右下走
{
Node tem = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = tem.x;
int y = tem.y;
if(map[x][y] == '1'&&zero[x + y]) //如果当前格子为1,但距离同为 x+y 的点有为0的
{
continue;//则跳过
}
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
int temx = x + dir[i][0];
int temy = y + dir[i][1];
if(!check( temx, temy )) continue;
Move[temx][temy] = 3 - i; //记录反方向,方便输出
if(map[temx][temy] == '0') //x+y的点有为0的
zero[temx + temy] = 1;
if(!vis[temx][temy])
{
vis[temx][temy] = 1;
q.push( Node( temx, temy ) );
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int kase;
scanf( "%d", &kase );
while(kase--)
{
ini();
scanf( "%d%d", &n, &m );
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf( "%s", map[i] + 1 );
}
bfs2();
int x = n, y = m;
int mtem, cnt = 0;
char ans[MAXN * 4];
while(true) //方向走,构造结果
{
ans[cnt++] = map[x][y];
mtem = Move[x][y];
if(mtem == -1) break;
x = x + dir[mtem][0];
y = y + dir[mtem][1];
}
while(cnt&&ans[cnt - 1] == '0') //删除前导〇
cnt--;
if(!cnt)
{
printf( "0\n" );
continue;
}
for(int i = cnt - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf( "%c", ans[i] );
}
printf( "\n" );
}
return 0;
}

























 858
858

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








