文章简介
论文链接 代码链接
Accepted at ECCV2020
Main contribution: mutli-modal distillation unit & feature propagation module; 可以结合多个任务在不同scale下的特点结果.
任务:(室内)场景理解 scene parsing; 辅助任务: depth, semantic segmentation
Background & motivation
- 多任务相比于Single task的优越性:相对于single task,更节省memory;因为减少了重复的feature计算所以有increased speed;如果有complementary information会效果更好
-
First, due to their layer sharing, the resulting memory footprint is substantially reduced. Second, as they explicitly avoid to repeatedly calculate the features in
the shared layers, once for every task, they show increased inference speeds. Most importantly, they have the potential for improved performance if the associated tasks share complementary information, or act as a regularizer for one another. - 但是也会出现unrelated tasks在一起训练结果反而更差的情况(negative transfer),为了解决这一问题,也有一些聚焦于loss function的工作,主要是平衡各任务对loss function的影响(task balancing)。
- 之前的一些工作都是经过一次处理,然后得出结果,也就是predict all tasks at once。这样使得某一任务没有办法使用其他任务的互补信息进行预测。
Note that all aforementioned works so far follow a common pattern: they directly predict all task outputs from the same input in one processing cycle (i.e. all predictions are generated once, in parallel or sequentially, and are not refined afterwards). By doing so, they fail to capture commonalities and differences among tasks, that are likely fruitful for one another (e.g. depth discontinuities are usually aligned with semantic edges).
- 直到PAD-net和PAP-net的出现,他们使用循环网络来使用info among tasks。
To alleviate this issue, a few recent works first employed a multi-task network to make initial task predictions, and then leveraged features from these initial predictions in order to further improve each task output – in a one-off or recursive manner.
- 之前的这两个任务也有问题,本文解决的办法是使用multi scale的信息:Multi scale可以保留原图在不同scale下的特点,比如在patch level
如果有不连续的深度变化,那么这个地方可能也有语义的变化,但是事实是可能没有。如果到了global scale就可以解决这种情况。
We conclude that pattern affinities should not be considered at the task level
only, as existing works do [47,50,51], but be conditioned on the scale level too.
方法
Overall pipeline:
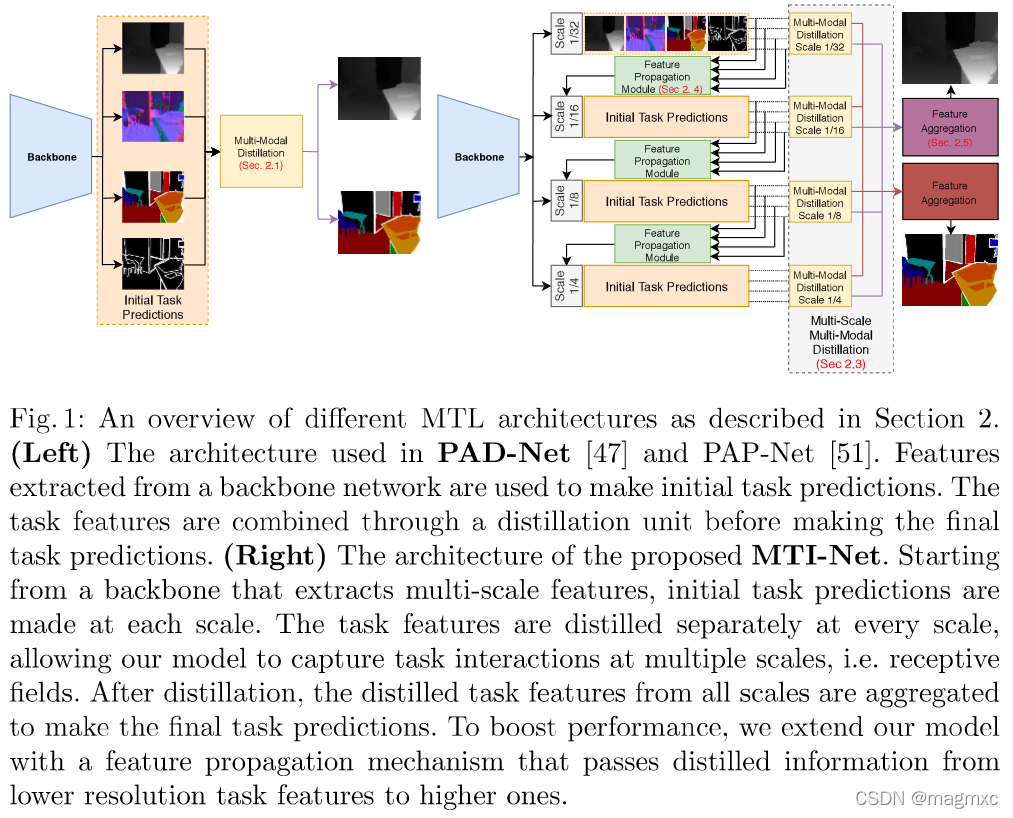
In fact, tasks can influence each other differently for different receptive field sizes.
- (之前的实验都是基于performing multi-modal distillation at a fixed scale)事实上,不同的任务会因不同的接受域大小而产生不同的影响。
实验设计和结果
We measure the pixel affinity in local patches on the label space of each task, using kernels of fixed size.
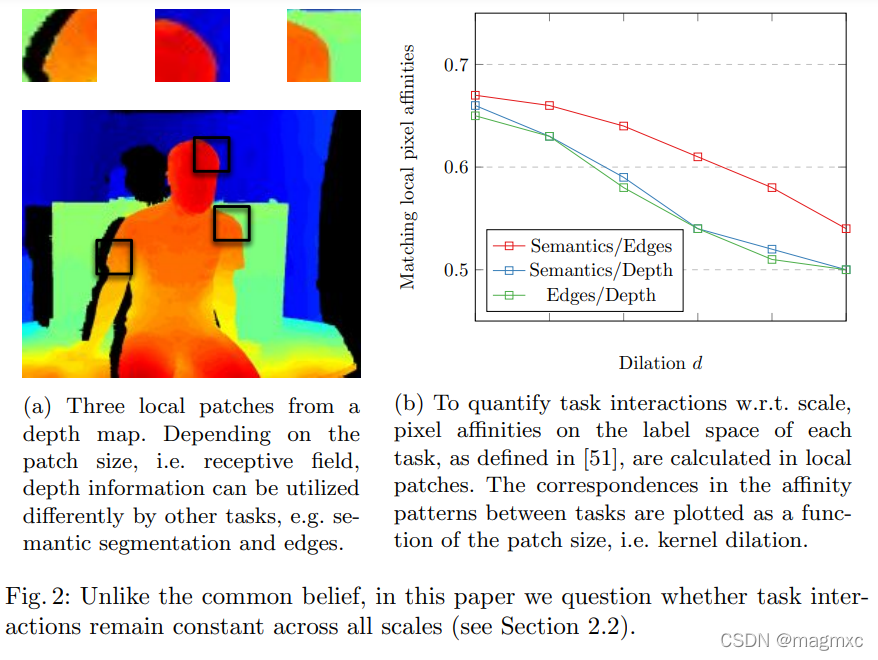
a) 解释不同scale的prediction效果区别(为什么要同时有local和global的scale)
b) 不同task和 d(dilation of kernel)的affinity关系(affinity详见PAD net)
Multi-scale multi-modal distillaion
- 定义详见文章 2.3
- 模块设计参考了PAD net
- 提取feature among tasks
Feature propagation across scales
- 定义详见文章 2.4
- 将feature从前一个scale到后一个scale
实验结果
提供的代码只有MTI-net在HRNet框架下PASCAL数据集的实现。
review总结
本文主要关注文章idea形成的过程,对方案的实现和实验的结果关注较少.




















 1156
1156











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








