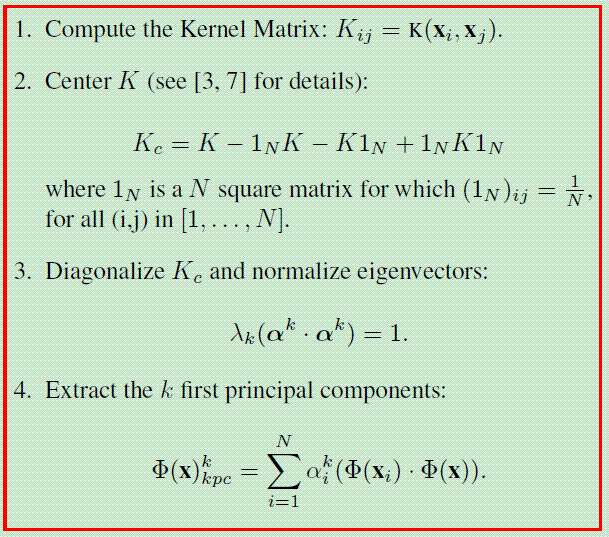
最近准备往核方法方向发展,于是仔细研读了经典的核主成份分析方法。通过参考别人的源代码,自己实现了KPCA,基本了解了核方法的实质。个人体会亲手实现一下还是很有益的。matlab源代码如下:
function [eigvector, eigvalue,Y] = KPCA(X,r,opts)
%
% Kernel Principal Component Analysis
% [eigvector, eigvalue,Y] = KPCA(X,r,opts)
% Input:
% X: d*N data matrix;Each column vector of X is a sample vector.
% r: Dimensionality of reduced space (default: d)
% opts: Struct value in Matlab. The fields in options that can be set:
% KernelType - Choices are:
% 'Gaussian' - exp{-gamma(|x-y|^2)}
% 'Polynomial' - (x'*y)^d
% 'PolyPlus' - (x'*y+1)^d
% gamma - parameter for Gaussian kernel
% d - parameter for polynomial kernel
%
% Output:
% eigvector: N*r matrix;Each column is an embedding function, for a new
% data point (column vector) x, y = eigvector'*K(x,:)'
% will be the embedding result of x.
% K(x,:) = [K(x1,x),K(x2,x),...K(xN,x)]
% eigvalue: The sorted eigvalue of KPCA eigen-problem.
% Y : Data matrix after the nonlinear transform
if nargin<1
error('Not enough input arguments.')
end
[d,N]=size(X);
if nargin<2
r=d;
end
%% Ensure r is not bigger than d
if r>d
r=d;
end;
% Construct the Kernel matrix K
K =ConstructKernelMatrix(X,[],opts);
% Centering kernel matrix
One_N=ones(N)./N;
Kc = K - One_N*K - K*One_N + One_N*K*One_N;
clear One_N;
% Solve the eigenvalue problem N*lamda*alpha = K*alpha
if N>1000 && r
% using eigs to speed up!
opts.disp=0;
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eigs(Kc,r,'la',opts);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
else
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eig(Kc);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
[junk, index] = sort(-eigvalue);
eigvalue = eigvalue(index);
eigvector = eigvector(:,index);
end
if r < length(eigvalue)
eigvalue = eigvalue(1:r);
eigvector = eigvector(:, 1:r);
end
% Only reserve the eigenvector with nonzero eigenvalues
maxEigValue = max(abs(eigvalue));
eigIdx = find(abs(eigvalue)/maxEigValue < 1e-6);
eigvalue (eigIdx) = [];
eigvector (:,eigIdx) = [];
% Normalizing eigenvector
for i=1:length(eigvalue)
eigvector(:,i)=eigvector(:,i)/sqrt(eigvalue(i));
end;
if nargout >= 3
% Projecting the data in lower dimensions
Y = eigvector'*K;
end
function K=ConstructKernelMatrix(X,Y,opts)
%
% function K=ConstructKernelMatrix(X,Y,opts)
% Usage:
% opts.KernelType='Gaussian';
% K = ConstructKernelMatrix(X,[],opts)
% K = ConstructKernelMatrix(X,Y,opts)
%
% Input:
% X: d*N data matrix;Each column vector of X is a sample vector.
% Y: d*M data matrix;Each column vector of Y is a sample vector.
% opts: Struct value in Matlab. The fields in options that can be set:
% KernelType - Choices are:
% 'Gaussian' - exp{-gamma(|x-y|^2)}
% 'Polynomial' - (x'*y)^d
% 'PolyPlus' - (x'*y+1)^d
% gamma - parameter for Gaussian kernel
% d - parameter for polynomial kernel
% Output:
% K N*N or N*M matrix
if nargin<1
error('Not enough input arguments.')
end
if (~exist('opts','var'))
opts = [];
else
if ~isstruct(opts)
error('parameter error!');
end
end
N=size(X,2);
if isempty(Y)
K=zeros(N,N);
else
M=size(Y,2);
if size(X,1)~=size(Y,1)
error('Matrixes X and Y should have the same row dimensionality!');
end;
K=zeros(N,M);
end;
%=================================================
if ~isfield(opts,'KernelType')
opts.KernelType = 'Gaussian';
end
switch lower(opts.KernelType)
case {lower('Gaussian')} % exp{-gamma(|x-y|^2)}
if ~isfield(opts,'gamma')
opts.gamma = 0.5;
end
case {lower('Polynomial')} % (x'*y)^d
if ~isfield(opts,'d')
opts.d = 1;
end
case {lower('PolyPlus')} % (x'*y+1)^d
if ~isfield(opts,'d')
opts.d = 1;
end
otherwise
error('KernelType does not exist!');
end
switch lower(opts.KernelType)
case {lower('Gaussian')}
if isempty(Y)
for i=1:N
for j=i:N
dist = sum(((X(:,i) - X(:,j)).^2));
temp=exp(-opts.gamma*dist);
K(i,j)=temp;
if i~=j
K(j,i)=temp;
end;
end
end
else
for i=1:N
for j=1:M
dist = sum(((X(:,i) - Y(:,j)).^2));
K(i,j)=exp(-opts.gamma*dist);
end
end
end
case {lower('Polynomial')}
if isempty(Y)
for i=1:N
for j=i:N
temp=(X(:,i)'*X(:,j))^opts.d;
K(i,j)=temp;
if i~=j
K(j,i)=temp;
end;
end
end
else
for i=1:N
for j=1:M
K(i,j)=(X(:,i)'*Y(:,j))^opts.d;
end
end
end
case {lower('PolyPlus')}
if isempty(Y)
for i=1:N
for j=i:N
temp=(X(:,i)'*X(:,j)+1)^opts.d;
K(i,j)=temp;
if i~=j
K(j,i)=temp;
end;
end
end
else
for i=1:N
for j=1:M
K(i,j)=(X(:,i)'*Y(:,j)+1)^opts.d;
end
end
end
otherwise
error('KernelType does not exist!');
end
参考文献:
[1]B. Sch¨olkopf, A.J. Smola, and K.-R M¨uller, “Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem,”Neural Computation, vol. 10, pp. 1299–1319, 1998.
[2]KERNEL PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR FEATURE REDUCTION IN HYPERSPECTRALE IMAGES ANALYSIS
[3]http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/homes/dengcai2/Data/data.html
KPCA 算法:
引用地址:http://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-457187-342046.html
注意:
1.如果出现错误:
Undefined function or method 'ConstructKernelMatrix' for input arguments of type 'double'
可以把ConstructKernelMatrix函数另存为一个*.m文件试试。
2.若有其他错误,请回复,共同解决。


























 606
606

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








