霍夫变换是一种无需图像内容先验知识的特征提取技术,可以广泛的应用图像中直线、圆、椭圆等形状的识别。本文主要基于opencv源代码实现经典的线性霍夫变换。
在直角坐标系下,直线被定义为:
y=mx+b (1)
其中, m为斜率,b为与y轴的截距,只要确定了m和b,一条直线就可以被唯一地确定下来。如果用ρ0表示原点到该直线的代数距离,θ0表示该直线的正交线与x轴的夹角,则:
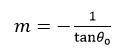
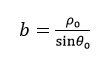
则该直线又可表示为:
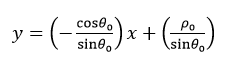
简化成一般式,即:
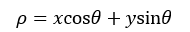
很容易想到,(ρ,θ)是极坐标的表示形式。但如果把(ρ,θ)也用直角坐标的形式表示,即把ρ和θ做正交处理,则(ρ,θ)就被称为霍夫空间。
在直角坐标系中的一点,对应于霍夫空间的一条正弦曲线。直线是由无数个点组成的,在霍夫空间就是无数条正弦曲线,但这些正弦曲线会相交于一点(ρ0,θ0),把该点带入公式2和公式3就得了直线的斜率和截距,这样一条直线就被确定了下来。因此在用霍夫变换识别直线时,霍夫空间中的极大值就有可能对应一条直线。
则霍夫线性变换算法实现步骤主要有:
1、对边缘图像进行霍夫空间变换;
2、在4邻域内找到霍夫空间变换的极大值;
3、对这些极大值安装由大到小顺序进行排序,极大值越大,越有可能是直线;
4、输出直线。
基于opencv实现的源代码如下:
void FindLinesByHough(const BYTE* const* binaryImg, int M, int N, float rho, float theta, int threshold, LineNode* &pLines, int &linesMax)
{
//tho表示距离刻度,theta表示角度刻度,pLines表示返回的直线数组指针,threshold表示直线的最少像素值,linesMax表示要返回的最大边数目。
int* pAccm = NULL;
KVNode* pKVNodeSort = NULL;
float* tabSin = NULL;
float* tabCos = NULL;
int total = 0;
int numAngle, numRho;
int i, j;
double scale = 0.0;
float iRho = 1 / rho;
int width = M;
int height = N;
numAngle = Round(PI / theta);
numRho = Round(((width + height) * 2 + 1) / rho);
pAccm = new int[(numAngle + 2)*(numRho + 2)]{0};
pKVNodeSort = new KVNode[numAngle*numRho];
tabSin = new float[numAngle]{0.0f};
tabCos = new float[numAngle]{0.0f};
float ang = 0;//避免重复计算角度,事先计算好sinθi/ρ和cosθi/ρ
for (int n = 0; n < numAngle; ang += theta, n++)
{
tabSin[n] = sinf(ang)*iRho;
tabCos[n] = cosf(ang)*iRho;
}
//第一步:逐点进行或霍夫空间变换,并将结果写入累加器数组内
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
if (0 != (int)binaryImg[j][i])
{
for (int n = 0; n < numAngle; n++)
{
int r = Round(j*tabCos[n] + i*tabSin[n]);
r += (numRho - 1) / 2;
++pAccm[(n + 1)*(numRho + 2) + r + 1];
}
}
}
}
//第二步:找到局部极大值,即做四方向的非极大值抑制
for (int r = 0; r < numRho; ++r)
{
for (int n = 0; n < numAngle; ++n)
{
int base = (n + 1)*(numRho + 2) + r + 1;
if (pAccm[base]>threshold && pAccm[base]>pAccm[base - 1] && pAccm[base] > pAccm[base + 1] && pAccm[base] > pAccm[base - numRho - 2] && pAccm[base] > pAccm[base + numRho + 2])
{
KVNode tempKVNode;
tempKVNode.index = base;
tempKVNode.pixelSum = pAccm[base];
pKVNodeSort[total++] = tempKVNode;
}
}
}
//第三步:对累加器值按由大到小排序
sort(pKVNodeSort, pKVNodeSort + total, Compare);
//第四步:输出linesMax条直线,如果linesMax等于total,则输出所有直线
linesMax = (linesMax <= total) ? linesMax : total;
pLines = new LineNode[linesMax];
scale = 1.0 / (numRho + 2);
for (int i = 0; i < linesMax; ++i)
{
LineNode tempLineNode;
int index = pKVNodeSort[i].index;//分离出该极大值在霍夫空间中的位置
int n = floor(index*scale) - 1;
int r = index - (n + 1)*(numRho + 2) - 1;
tempLineNode.rho = (r - (numRho - 1)*0.5f)*rho;
tempLineNode.angle = n*theta;
pLines[i] = tempLineNode;
}
}
bool Compare(KVNode& aNode, KVNode& bNode)
{
return (aNode.pixelSum > bNode.pixelSum);
}struct LineNode
{
float rho;
float angle;
};
struct KVNode
{
int index;
int pixelSum;
};
























 5959
5959

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








