部分内容图片from
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37550986/article/details/125230667
1、构造方法
构造方法一共有5个
1.1、空参构造
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
什么都没干,内部的所有属性均没有实例化
1.2、传入数组初始容量
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
- 传入了初始数组容量,容量小于0直接报错
- 始数组容量大于2的29次幂(536870912),直接赋值2的30幂
- tableSizeFor
- 之前HashMap是把初始容量变化为大于等于initialCapacity的2的最小次幂
- ConcurrentHashMap则变成大于initialCapacity的2的最小次幂(猜测是扩容引起的代价变大,所以适当加大初始容量)
- sizeCtl此时代表ConcurrentHashMap内部数组长度
1.3、传入已有的Map
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
此时的sizeCtl默认为16,将所有的元素放入ConcurrentHashMap
1.4、传入初始容量,扩容阈值
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
直接调用另一个方法
1.5、传入初始容量,扩容阈值,并发线程数量
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
- concurrencyLevel实际并没有使用, 可以看到ConcurrentHashMap的注释说明

- long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
- tableSizeFor( (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor)) 等价与
- tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1))
- 目的还是找到大于initialCapacity的最小2的幂(不含包等于,跟HashMap的区别)
2、初始化方法
2.1、先补一下sizeCtl的含义
- sizeCtl为0,代表数组未初始化,且数组的初始容量为16
- sizeCtl为正数,如果数组未初始化,纪录数组的初始容量,如果已初始化,纪录的是数组的扩容阈值
- sizeCtl为-1表示正在进行初始化
- sizeCtl小于0但不是-1表示数组正在扩容,其中低16位表示并发扩容的线程数,具体为(rs << 16) + n +1
2.1、initTable方法
第一次进行put元素时,会触发initTable方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 第一次put元素时,会触发initTable方法
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
- 以上看代码主要还是利用CAS进行初始化Map内部数组
- 先是一个死循环,判断数组是null或者数组的长度==0
- 接着判断sizeCtl是否小于0,sizeCtl的含义看上述,小于0表示正在初始化或扩容,那么线程yield
- CAS进行初始化,将SIZECTL标志位设置为-1
- 先双重判断数组是null或者数组的长度==0
- 数组初始化长度是否已经赋值,没有复制默认给16
- 设置阈值 n - (n >>> 2) 其实就是数组的长度乘以0.75
3、put方法
put上来就是一个死循环然后各个分支请看以下
3.1、正常put
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
- 第1次for循环,如果table没有初始化那么执行初始化逻辑initTable
- 第2次for循环,tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash))肯定是没有元素的,所以
- tabAt其实就是CAS包装了一层 get(1)
- casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)) 将元素放置在(n - 1) & hash位置上
3.2、hash碰撞put
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
- synchronized (f),f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash),首先对当前冲突节点进行加锁
- 双重判断tabAt(tab, i) == f,防止节点数据已经被替换掉
- fh = f.hash,如果fh>0表示当前节点是一个链表
- binCount = 1,对当前冲突节点的链接长度进行统计,用于后面的链表转红黑树
- 从头遍历链表,判断要存储的节点和当前循环节点key的hash和equals都一致,并且onlyIfAbsent=false,直接替换节点的value
- 如果遍历之后,所有节点key的hash和equals和要存储的都不一致,直接插入到尾部
- else if (f instanceof TreeBin),如果当前是树节点,那么执行以下逻辑
3.2.1、putTreeVal方法
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if (p == null) {
first = root = new TreeNode<K,V>(h, k, v, null, null);
break;
}
else if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) {
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
TreeNode<K,V> x, f = first;
first = x = new TreeNode<K,V>(h, k, v, f, xp);
if (f != null)
f.prev = x;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
if (!xp.red)
x.red = true;
else {
lockRoot();
try {
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
} finally {
unlockRoot();
}
}
break;
}
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
return null;
}
- 首先上来一个死循环,从root节点开始遍历
- root==null,表示树是空的,直接把要插入的节点赋值给root,first
- (ph = p.hash) > h,确定dir的值,确定插入元素在tree的左侧还是右侧
- (pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk)), hash值和equals,直接返回旧的value值,根据onlyIfAbsent,直接替换成新的
- 开始递归遍历树的左侧和右侧,如果找到hash值和equals一致,直接返回旧的value值,根据onlyIfAbsent,直接替换成新的
- 根据dir的值,决定将元素插入树的左侧还是右侧,并且重新平衡红黑树
3.2.2、treeifyBin方法
链表插入元素之后的逻辑,需要判断是否树化
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
- binCount!=0 说明该节点有hash碰撞,要么是链表,要是是红黑树
- binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(8),binCount>=8,只能是链表(红黑树固定赋值2),走树化逻辑
3.2.2.1、treeifyBin
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;
if (tab != null) {
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
tryPresize(n << 1);
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
synchronized (b) {
if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {
TreeNode<K,V> p =
new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,
null, null);
if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));
}
}
}
}
}
- if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64),如果数组的长度小于64,那么走tryPresize扩容逻辑
- 数组长度>=64, synchronized该节点,遍历该节点,形成红黑树,并CAS下挂到数组
3.2.2.2、tryPresize
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1);
int sc;
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table; int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
}
}
else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break;
else if (tab == table) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt;
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
}
}
}
- 首先确认扩容的大小就是翻个倍,tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1 )
- 死循环判断 while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) ,sizeCtl大于0表示当前数组没有正在扩容,没有正在协助转移
- if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0),走数组初始化逻辑,CAS将标志位设置为-1
- else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY),如果扩容之后的数组长度小于等于sc,说明已经扩容过了,直接打断
- else if (tab == table)双重判断,确保table没有被扩容掉
- rs = resizeStamp(n) < 0,表示当前有线程正在扩容,那么执行协助扩容
- rs = resizeStamp(n) > 0,表示当前没有线程扩容,对rs左移16位然后+2,表示正有一个线程进行扩容
- resizeStamp详解释请看以下
分支1:rs = resizeStamp(n) > 0时,表示目前还没有线程进行扩容,直接执行transfer方法
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
- CAS对rs左移16位+2
- 高16位就表示扩容的标记,能还原出是多少扩多少
- 低16位表示当前扩容的线程是一个
- 为啥是+2,后面补充,1是起始位,应该是有作用的
- transfer(tab, null),null=nextTable,因为是第一个线程进行扩容的,所以不需要协助扩容的nextTable
分支2:rs = resizeStamp(n) < 0时,表示已经有n-1个线程进行扩容中,CAS对sc+1,直接执行transfer方法
- CAS对sc+1,直接执行transfer方法
- transfer(tab, nextTable),因为是不是第一个线程进行扩容的,所以是协助扩容
3.2.2.2.1、resizeStamp
/**
* Returns the stamp bits for resizing a table of size n.
* Must be negative when shifted left by RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT.
*/
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
- 找到还未扩容前的数组长度
- 找到长度二进制最高位1前不包括符号位0的个数
- 1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1 = 1000000000000000
- Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1)) 就是对Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n)高位变成1,表示已经有线程在做扩容操作
4、transfer核心扩容
transfer被很多地方调用,比如转红黑树的时候,比如put完毕之后
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
4.1、stride
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
- stride表示每个线程负责迁移数组分片的长度
- stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n
- cpu核心大于1, stride=数组长度/8/cpu的核心数,否则就是整个数组的长度
- stride不能小于16,小于重新设置为16
4.2、nextTab
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
- nextTab,是要迁移的新的数组,新的数组长度是老的2倍,n << 1= n*2
- transferIndex,我们要确定一个线程的数据迁移区域,一个长度是不行的;还必须要知道一个数据迁移的起始的位置,这样才能通过:起始位置+长度;来确定迁移的范围;而transferIndex 就是确定线程迁移的起始位置;每个线程的起始位肯定都不同,因此这个变量会随着协助扩容的线程增加而不断的变化;
- 在ConcurrentHashMap中,分配区域是从数组的末端开始,从后往前配分区域,第一个线程起始迁移数据的下标:transferIndex -1(数组最大下标),分配区域:[transfer-1,transfer-stride],第二线程的起始位置:(transferIndex - stride-1),分配区域:[transferIndex - stride-1,transferIndex - 2 * stride],依次类推。
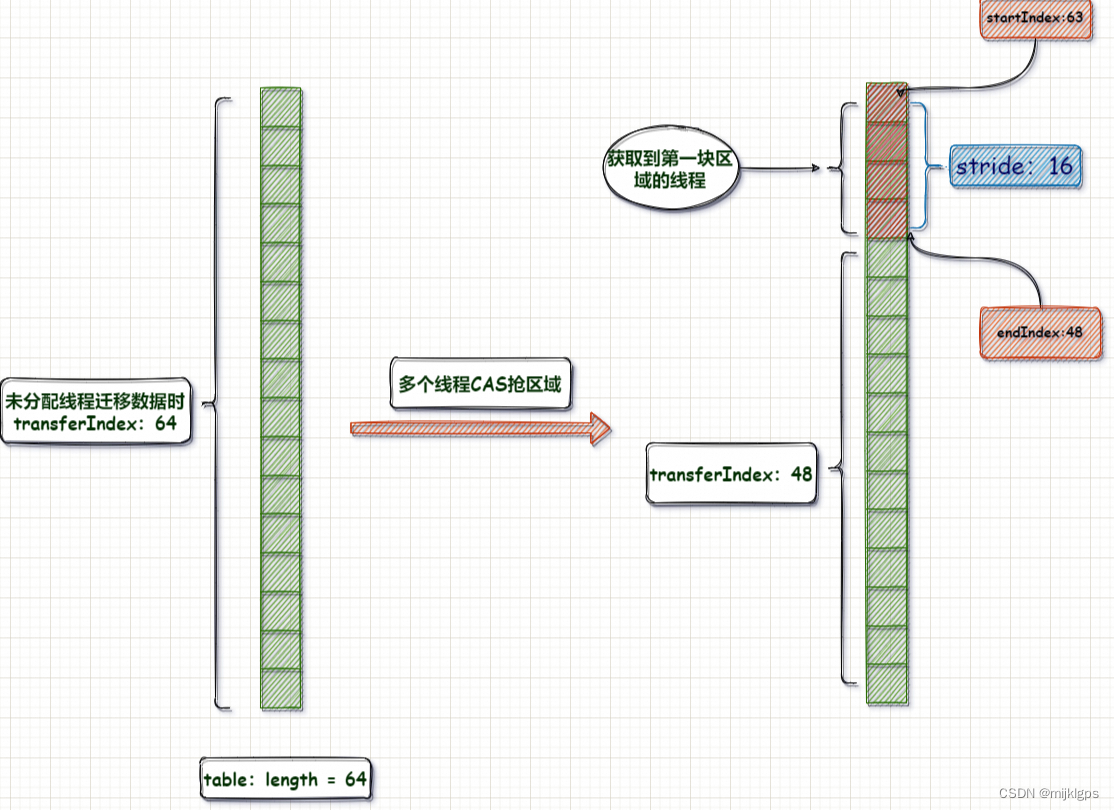
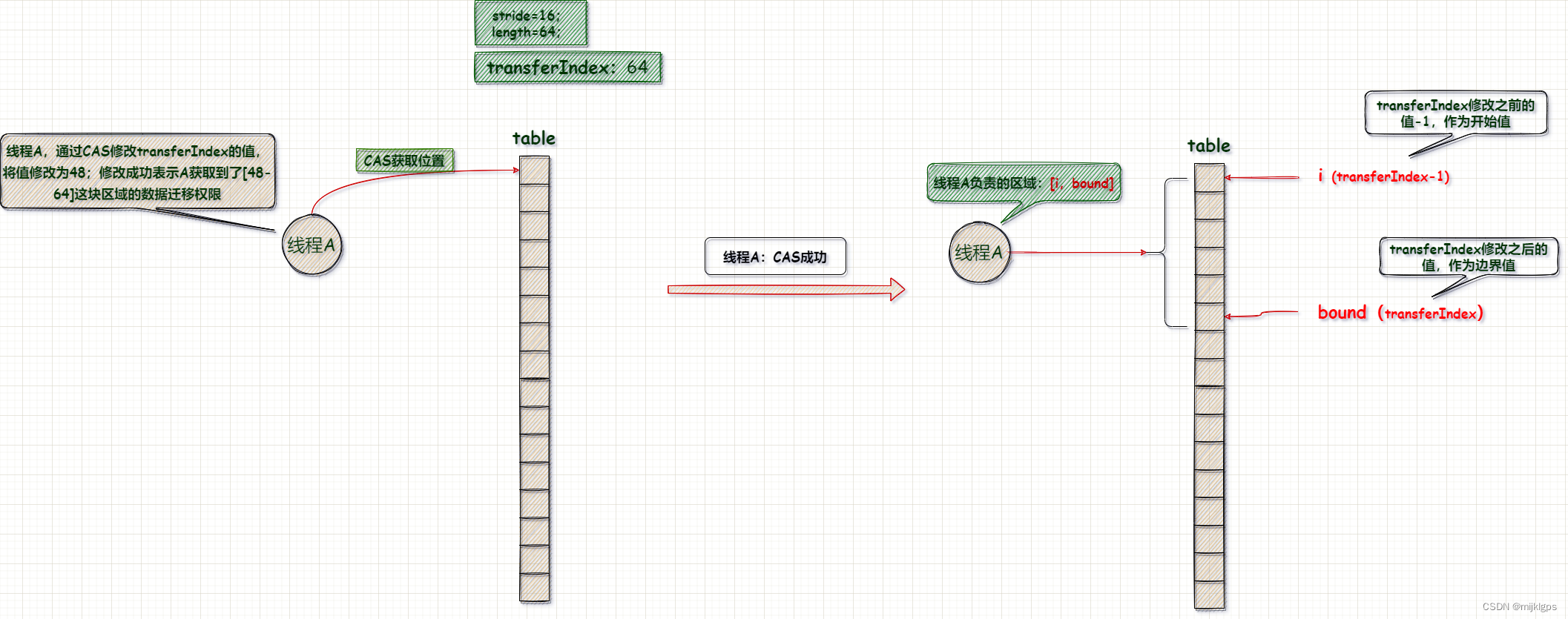
4.3、计算当前线程负责迁移的数组起始位置
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
- if (–i >= bound || finishing),
- 获得了起始位置之后,会将i的值修改为线程迁移数据的起始位置
- bound是线程迁移数据的结束位置
- 满足这两个条件说明扩容已经完成了
- else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0)
- 当同时由多个线程,协助扩容时,可能被前面的线程将区域抢完了;导致后面线程没法获取迁移区域
- else if (U.compareAndSwapInt…
- CAS竞争获取起始位置;竞争成功,修改TRANSFERINDEX的值
- transferIndex修改之前的值是迁移数据的起始位置,修改之后的值是结束位置;也作为下一个线程的迁移数据的起始位置;
- 当前线程的开始坐标,i=(nextIndex=transferIndex)-1,坐标变化
- 当前线程的结束坐标,nextBound = nextIndex > stride ? nextIndex - stride : 0
4.4、判断数据迁移是否结束
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
- i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn,这几个条件表示扩容完毕了
- i当前指针已经到数组结尾了
- i >= n达到了数组的长度
- i+原数组n达到了nextn
- if (finishing) ,判断结束标志,然后对一些变量做赋值处理
- nextTable置空
- table赋值成nextTable
- sizeCtl赋值为扩容后数组长度的0.75
- if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1))
- 说明当前线程迁移完毕了,但是其他线程还没有结束,SIZECTL减去1,表示当前的线程迁移完毕
- ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) ,resizeStamp左移16位等于sc-2,初始值是1,本身的线程是1,所以是减去2。表示所有的线程都完成迁移,那么finishing迁移结束标志true,advance自旋设置true等待下次循环设置其他变量位默认值,i设置为n,走默认值逻辑
4.5、数据迁移
节点是null或者节点的key的hash=-1表示正在迁移,直接再次自选等待迁移结束
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
正在迁移的节点ForwardingNode的hash是-1表示正在迁移
4.5.1、链表或普通节点的迁移
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
- 普通节点也是链表
- 链表需要拆分成2份,一个在原位置,一份在i+n位置
- 这里有个小细节,就是为什么数组一定是要是2的幂
- 取决于key的hash高位与上2n-1最高的1位置是否等于0,等于0是原位置,等于n是i+n位置
- 第1次遍历找到与根节点Hash值不一致的子链表头
- 判断runBit=0表示这个链表头,是原来i的链表
- runBit=n表示这个链表头,是要迁移i+n位置的链表
- 第2遍遍历找到确认每个节点的(ph & n)= 0,决定追加到原位置链表,还是i+n链表
- 将原table的i位置,设置位ForwardingNode的hash固定为-1
4.5.2、红黑树迁移
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
- 直接遍历红黑树,利用(ph & n)= 0算法,拆分成2个TreeNode
- 对2个TreeNode长度进行判断,<=6退化成普通的链表,>6包装成TreeBin
- ph & n = 0,迁移到原i位置
- ph & n = 0,迁移到原i位置
5、addCount扩容
在没有产生hash碰撞的前提下,put方法的结尾会计算counterCells是否到扩容的阈值,用来扩容
// 计算扩容逻辑
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
addCount代码
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
5.1、上半段
5.1.1、counterCells未初始化
(as = counterCells) != null,按假设来说,这个返回 false,看下一个判断。
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)
8个线程同时执行这行,那只有一个线程会执行会成功(取反了),修改baseCount的值,不进入方法体。其它7个线程执行方法体中的方法。
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
按假设来讲,as == null 返回 true,7个线程都会执行 fullAddCount(x, uncontended)
5.1.2、counterCells初始化了,(as = counterCells) != null,则8个线程全部执行下个判断
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null,
- ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() 这个方法是返回一个随机数,彼此之间不同。
- as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m] 这个是得到counterCells数组中的一个元素,与put插入元素位置的算法是一致的
- 假设极端情况下,8个线程计算出的下标是同一个。
- 若该下标处元素为 null,那8个线程,都会执行 fullAddCount
- 若该下标处元素不为null,那 8个线程都执行!(uncontended = U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
- 只有1个线程直接对counterCells对应的下标+1
- 其他7线程直接对执行fullAddCount
5.1.3、总结
- 若counterCells 这个数组未初始化,非竞争条件下,修改 baseCount+1,否则执行 fullAddCount
- 若 counterCells 这个数组已经初始化,非竞争条件下并且对应的counterCells下标有值修改value+1,否则执行 fullAddCount
5.2、fullAddCount
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
初始化让当前线程获取随机数
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as && U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
- counterCells == as双重判断
- cellsBusy,CAS判断只有一个线程可以进入代码
- 初始化CounterCel为长度2的数组,并且h & 1,设置为1
- 结束后cellsBusy标志位0
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
- counterCells不为空,counterCells对应的(m - 1) & h位置是null的话,直接CAS赋值为节点CounterCell(1)
- counterCells对应的节点部位空的话,CASCounterCell的value+1
- 再次没有成功的话走 counterCells扩容逻辑
- 再次没有成功的话走 baseCount+1
5.3、总结
无竞争条件下,执行 put() 方法时,操作baseCount 实现计数
首次竞争条件下,执行 put()方法,会初始化CounterCell ,并实现计数
CounterCell 一旦初始化,计数就优先使用CounterCell
每个线程,要么修改CounterCell 、要么修改baseCount,实现计数
CounterCell 在竞争特别严重时,会扩容。(扩容上限与 CPU 核数有关,不会一直扩容, n >= NCPU会截断扩容)
6、get
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
全程无锁。get操作可以无锁是由于Node元素的val和指针next是用volatile修饰的,在多线程环境下线程A修改结点的val或者新增节点的时候是对线程B可见的。
- 计算hash值,定位到该table索引位置,如果是首节点符合就返回
- 如果遇到扩容的时候,会调用标志正在扩容节点ForwardingNode的find方法,查找该节点,匹配就返回
- 以上都不符合的话,就往下遍历节点,匹配就返回,否则最后就返回null





















 333
333











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








