双向链表的存储方式
双向链表跟链表差不多,只是它每个结点都含有两个链——一个指向下一结点,另一个指向前一结点。此外,它还能直接访问第一个和最后一个结点。
单链表只能向后操作,不可以向前操作。为了向前、向后操作方便,可以给每个元素附加两个指针域,一个存储前一个元素的地址,另一个存储下一个元素的地址。这种链表称为双向链表,如图
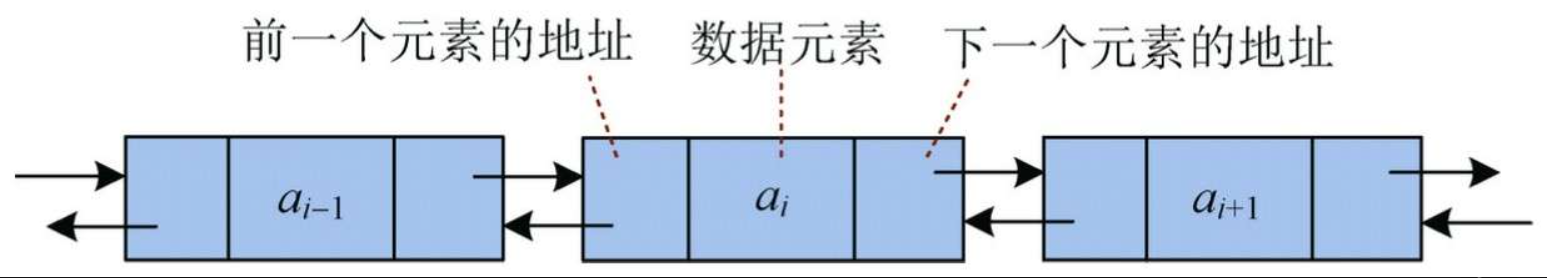
从图中可以看出,双向链表每个节点包含3个域:数据域和两个指针域。两个指针域分别存储前后两个元素节点的地址,即前驱和后继,因此指针指向的类型也是节点类型。
Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
}
双向链表的基本操作
下面以带头节点的双向链表为例,讲解双向链表的初始化、创建、取值、查找、插入、删除操作。
1.初始化
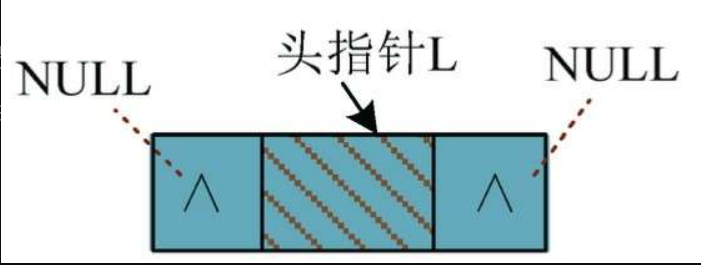
双向链表初始化是指构建一个空表。先创建一个头节点,不存储数据,然后令其前后两个指针域均为空,如图
2.创建
创建双向链表也可以用头插法和尾插法。头插法创建的链表和输入顺序正好相反,称为逆序建表;尾插法创建的链表和输入顺序一致,称为正序建表。
头插法建双向链表的过程如下。
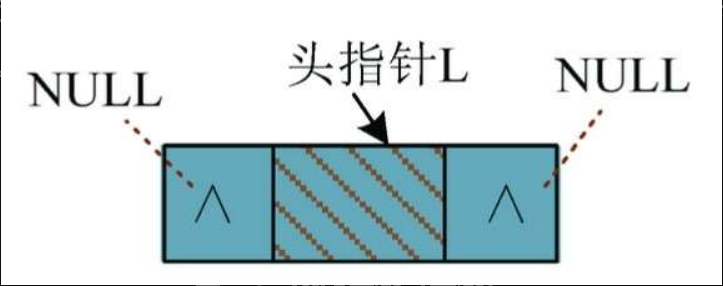
1)初始状态是指初始化后的空表,只有一个头节点,前后两个指针域均为空,如图
2)输入数据元素1,创建新节点,把元素1放入新节点数据域,如图

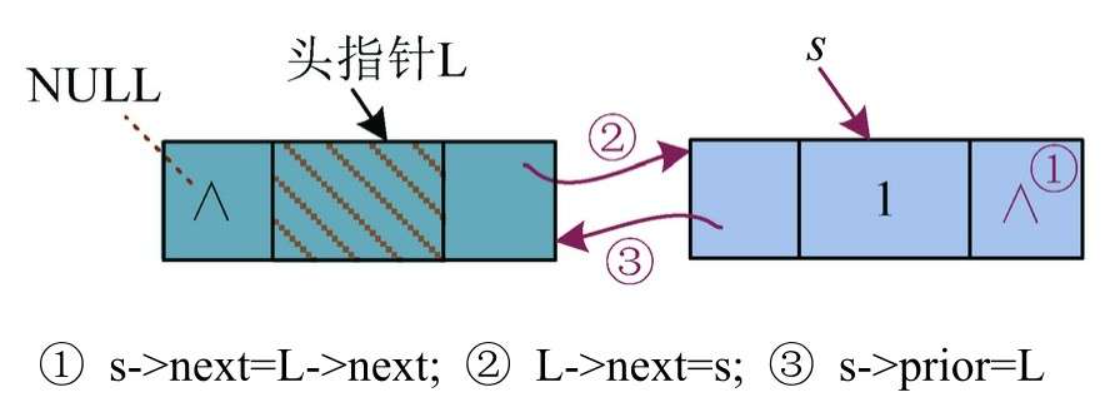
3)头插操作,插入头节点的后面,如图
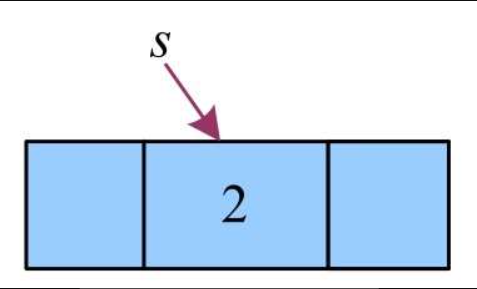
4)输入数据元素2,创建新节点,把元素2放入新节点数据域,如图
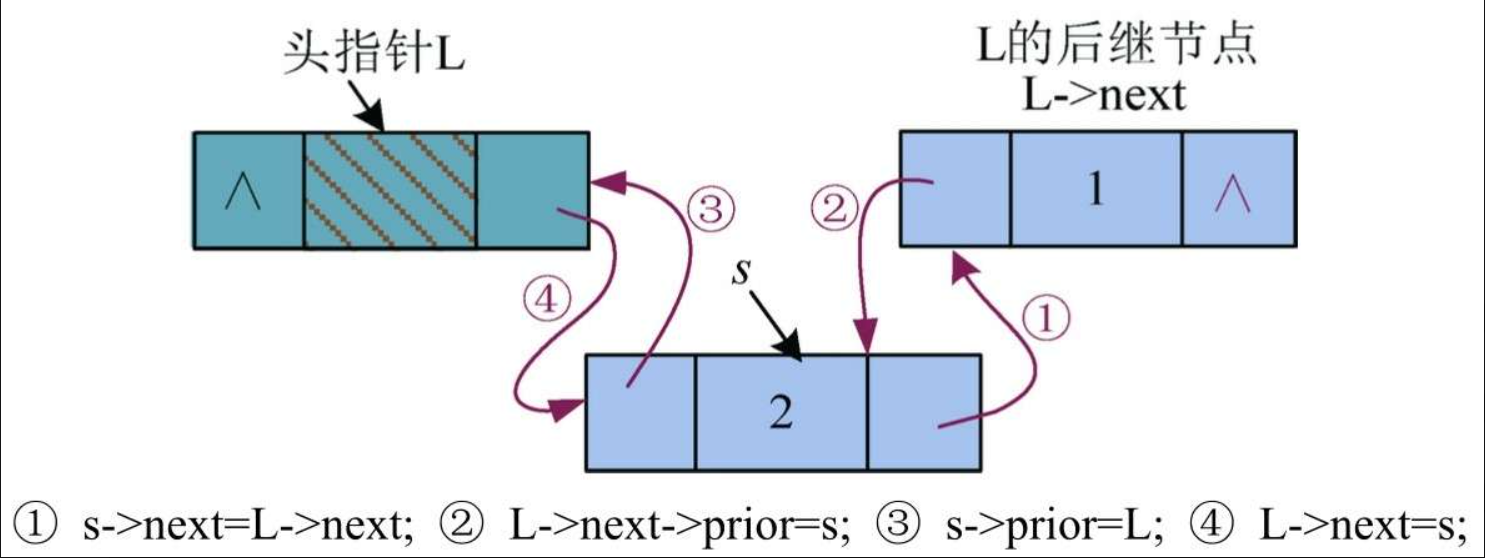
5)头插操作,插入头节点的后面,如图
赋值解释
① s->next=L->next:将L节点后面的节点(后继)地址赋值给s节点的指针域,即s节点的next指针指向L的后继节点。
② L->next->prior=s:将s节点的地址赋值给L的后继节点的prior指针域,即L的后继节点的prior指针指向s节点。
③ s->prior=L:将L节点的地址赋值给s节点的prior指针域,即s节点的prior指针指向L节点。
④ L->next=s:将s节点的地址赋值给L节点的指针域,即L节点的next指针指向s节点。
注意:赋值语句的右侧是一个地址,左侧是一个节点的指针域。
修改指针顺序的原则:先修改没有指针标记的那一端
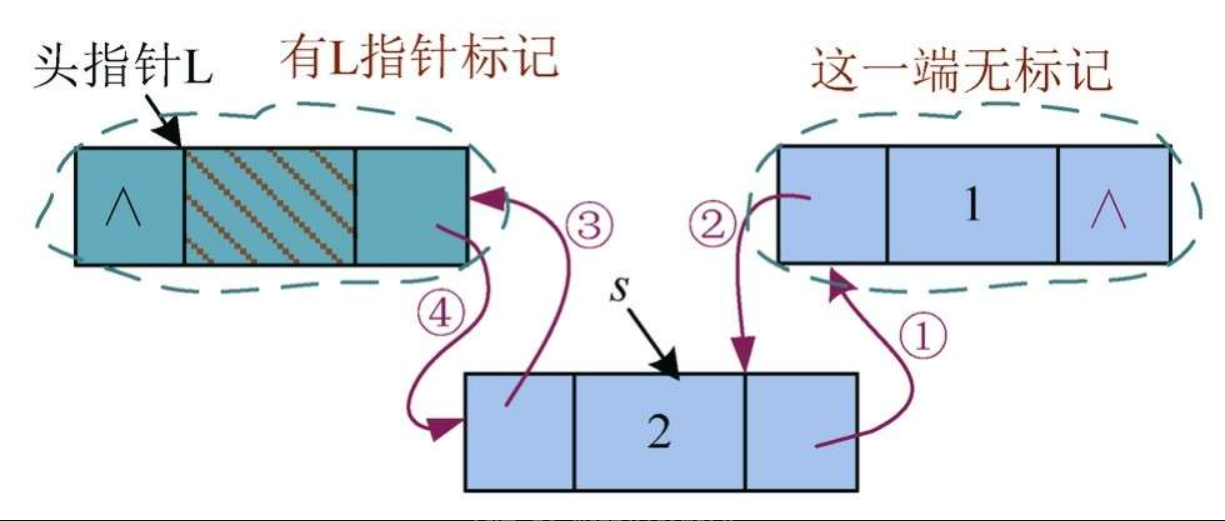
如果要插入节点的两端都有标记,例如再定义一个指针q指向第1个节点,那么先修改哪个指针都无所谓。实际上,只需要将④语句放在最后修改即可,①②③语句顺序无要求。
拉直链表之后,如图
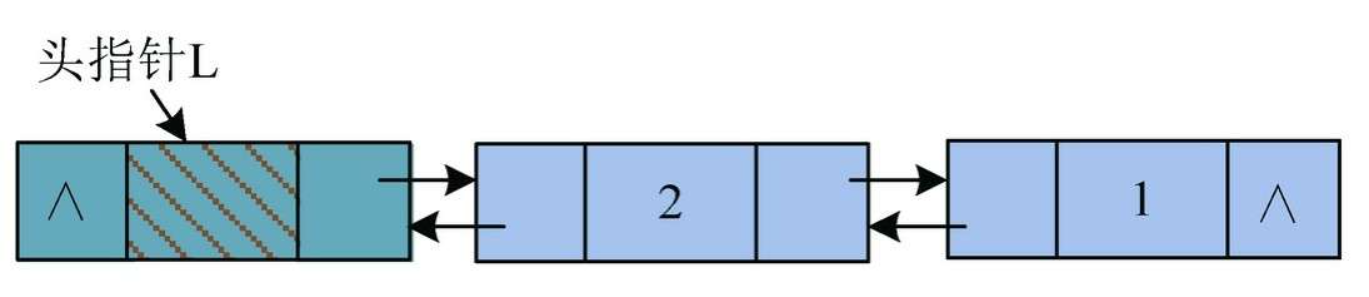
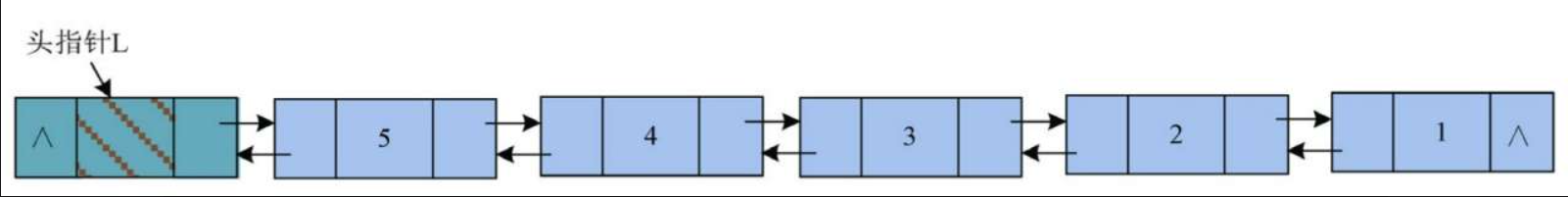
6)继续依次输入数据元素3、4、5,头插法创建的双向链表如图
尾插法建双向链表和尾插法建单链表类似,需要有一个尾指针
/**
* 双向链表节点类
*/
public class Node {
int data; //数据节点
Node prev; //前一个节点
Node next; //后一个节点
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
prev = null;
next = null;
}
}
public class DoublyLinkedList {
//链表的头结点
Node head;
//添加节点到链表的尾部
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//如果链表为空,泽新节点为头结点
if(head == null){
head = newNode;
}else{
//要找到链表的尾部
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null){
current = current.next;
}
//将新节点的前驱指向当前尾部节点
newNode.prev = current;
//将当前尾部节点的后继指向新节点,完成了节点的添加操作
current.next = newNode;
}
}
//打印链表的方法
public void print(){
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
System.out.println(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
public class DoublyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
//添加节点
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.print();
}
}
3.取值和查找
双向链表的取值、查找和单链表的一样
public class DoublyLinkedList {
//链表的头结点
Node head;
//添加节点到链表的尾部
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//如果链表为空,泽新节点为头结点
if(head == null){
head = newNode;
}else{
//要找到链表的尾部
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null){
current = current.next;
}
//将新节点的前驱指向当前尾部节点
newNode.prev = current;
//将当前尾部节点的后继指向新节点,完成了节点的添加操作
current.next = newNode;
}
}
//打印链表的方法
public void print(){
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
System.out.println(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
//在链表中查找节点
public Node find(int data){
//从链表的头结点开始查找
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
//如果找到了节点数据与目标数据匹配,则返回该节点
if(current.data == data){
return current;
}
current = current.next; //否则,继续查找下一个节点
}
return null;
}
}
public class DoublyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
//添加节点
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
// list.print();
// //查找节点
Node foundNode = list.find(5);
if(foundNode != null){
System.out.println("找到了节点: "+ foundNode.data);
}else{
System.out.println("未找到节点");
}
}
4.指定位置插入
单链表只有一个指针域,是向后操作的,不可以向前处理,因此单链表如果在第i个节点之前插入一个元素,就必须先找到第i-1个节点。在第i个节点之前插入一个元素相当于把新节点放在第i-1个节点之后。而双向链表不需要,因为有两个指针,可以向前后两个方向操作,直接找到第i个节点,就可以把新节点插入第i个节点之前。注意:这里假设第i个节点是存在的,如果第i个节点不存在,而第i-1个节点存在,还是需要找到第i-1个节点,将新节点插入第i-1个节点之后,如图
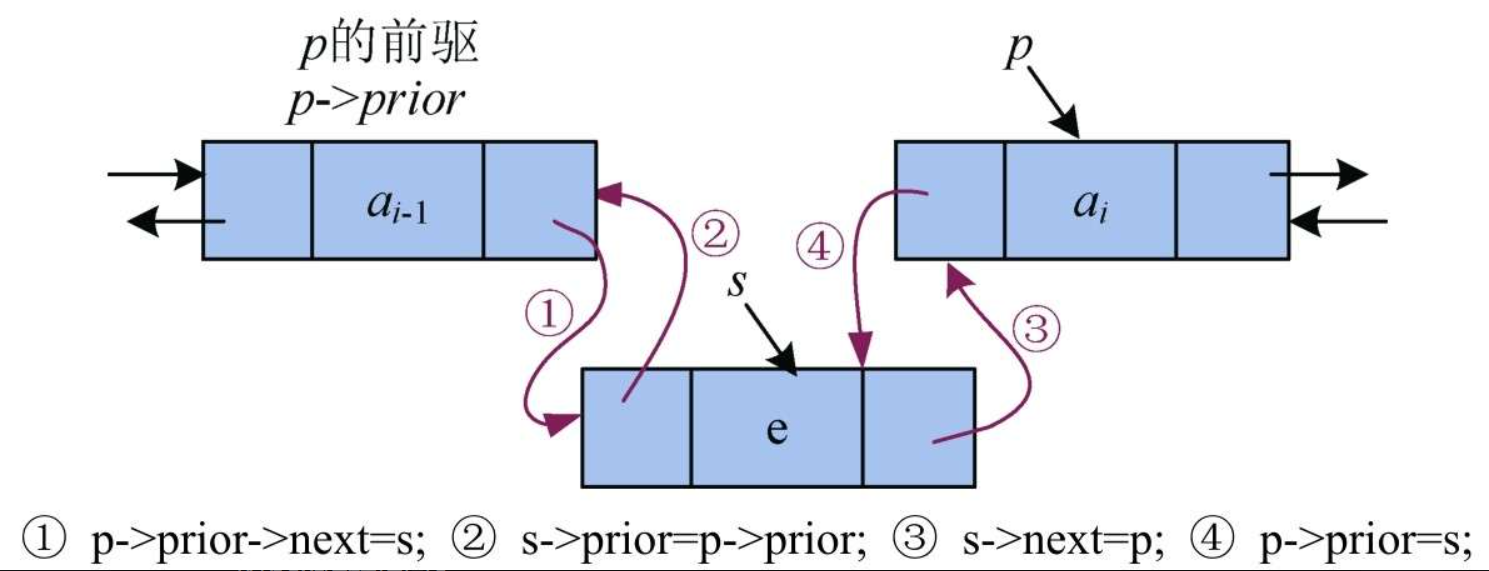
赋值解释
① p->prior->next=s:s节点的地址赋值给p的前驱节点的next指针域,即p的前驱的next指针指向s。
② s->prior=p->prior:p的前驱的地址赋值给s节点的prior指针域,即s节点的prior指针指向p的前驱。
③ s->next=p:p节点的地址赋值给s节点的next指针域,即s节点的next指针指向p节点。
④ p->prior=s:s节点的地址赋值给p节点的prior指针域,即p节点的prior指针指向s节点。
因为p的前驱无标记,一旦修改了p节点的prior指针,p的前驱就找不到了,因此,最后修改这个指针。实际上,只需要将④语句放在最后修改即可,①②③语句顺序无要求。
修改指针顺序的原则:先修改没有指针标记的那一端。
package com.maweiqi.DoublyLindked;
/**
* 双向链表类
*/
public class DoublyLinkedList {
//链表的头结点
Node head;
//添加节点到链表的尾部
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//如果链表为空,泽新节点为头结点
if(head == null){
head = newNode;
}else{
//要找到链表的尾部
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null){
current = current.next;
}
//将新节点的前驱指向当前尾部节点
newNode.prev = current;
//将当前尾部节点的后继指向新节点,完成了节点的添加操作
current.next = newNode;
}
}
//在制定节点后面插入新节点
public void insertAfter(Node node , int data){
if(node == null){
System.out.println("指定节点为空,插入失败");
return;
}
//创建新节点
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//将新节点的前驱指向指定节点
newNode.prev = node;
//将新节点的后继指向指定节点的后继
newNode.next = node.next;
//如果指定节点有后继,则将后继节点的前驱指向新节点
if(node.next != null){
node.next.prev = newNode;
}
//将指定节点的后继指向新节点,完成插入操作
node.next = newNode;
}
//在链表中查找节点
public Node find(int data){
//从链表的头结点开始查找
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
//如果找到了节点数据与目标数据匹配,则返回该节点
if(current.data == data){
return current;
}
current = current.next; //否则,继续查找下一个节点
}
return null;
}
//打印链表的方法
public void print(){
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
System.out.println(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
package com.maweiqi.DoublyLindked;
/**
*/
public class DoublyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
//添加节点
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
// list.print();
// //查找节点
Node foundNode = list.find(5);
if(foundNode != null){
System.out.println("找到了节点: "+ foundNode.data);
}else{
System.out.println("未找到节点");
}
//
// //在指定节点后插入新节点
list.insertAfter(foundNode,5);
System.out.println("插入节点后的链表为:");
list.print();
}
}
5.删除
删除一个节点,实际上是把这个节点跳过去。在单向链表中,必须先找到第i-1个节点,才能把第i个节点跳过去。双向链表不必如此,只要直接找到第i个节点,然后修改指针即可,如图
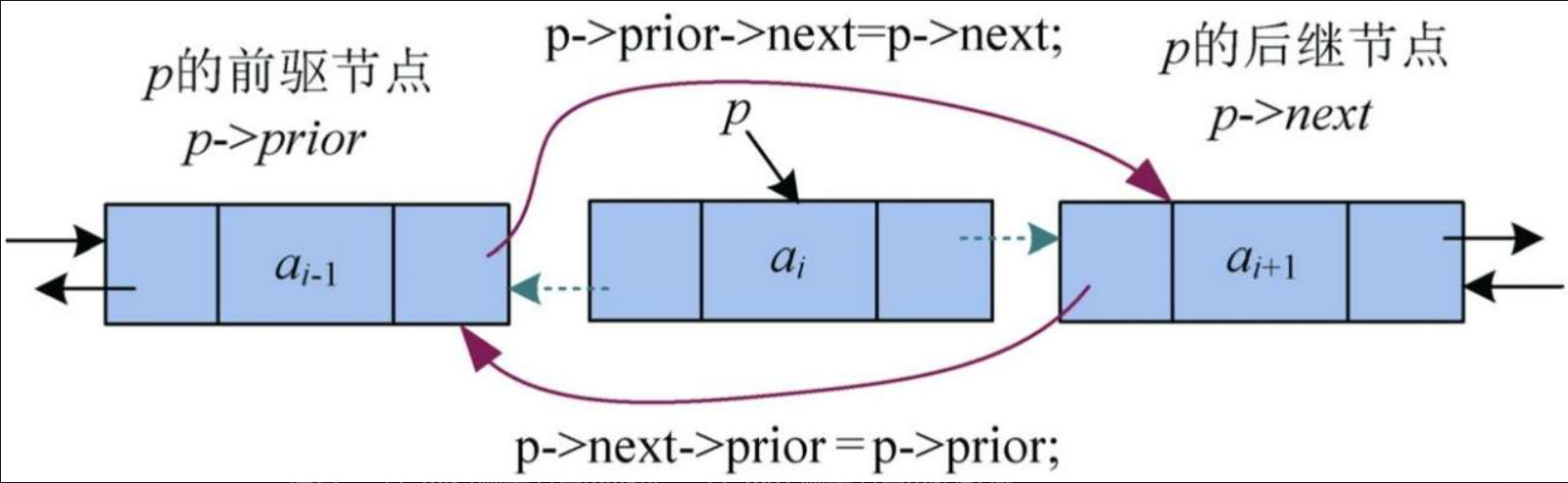
p->prior->next=p->next:将p的后继节点的地址赋值给p的前驱节点的next指针域。即p的前驱节点的next指针指向p的后继节点。
注意:等号的右侧是节点的地址,等号的左侧是节点的指针域。
p->next->prior =p->prior:将p的前驱节点的地址赋值给p的后继节点的prior指针域,即p的后继节点的prior指针指向p的前驱节点。此项修改的前提是p的后继节点存在,如果不存在,则不需要此项修改。
这样就把p节点跳过去了,然后用delete p释放被删除节点的空间。删除节点修改指针没有顺序,先修改哪个都可以。
package com.maweiqi.DoublyLindked;
/**
* 双向链表类
*/
public class DoublyLinkedList {
//链表的头结点
Node head;
//添加节点到链表的尾部
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//如果链表为空,泽新节点为头结点
if(head == null){
head = newNode;
}else{
//要找到链表的尾部
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null){
current = current.next;
}
//将新节点的前驱指向当前尾部节点
newNode.prev = current;
//将当前尾部节点的后继指向新节点,完成了节点的添加操作
current.next = newNode;
}
}
//在制定节点后面插入新节点
public void insertAfter(Node node , int data){
if(node == null){
System.out.println("指定节点为空,插入失败");
return;
}
//创建新节点
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//将新节点的前驱指向指定节点
newNode.prev = node;
//将新节点的后继指向指定节点的后继
newNode.next = node.next;
//如果指定节点有后继,则将后继节点的前驱指向新节点
if(node.next != null){
node.next.prev = newNode;
}
//将指定节点的后继指向新节点,完成插入操作
node.next = newNode;
}
//在链表中查找节点
public Node find(int data){
//从链表的头结点开始查找
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
//如果找到了节点数据与目标数据匹配,则返回该节点
if(current.data == data){
return current;
}
current = current.next; //否则,继续查找下一个节点
}
return null;
}
//从链表中删除节点
public void delete(int data){
//从链表的头结点开始查找
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
//如果我们找到删除的节点
if(current.data == data){
//如果是非头节点
if(current.prev != null){
//将要删除的节点的前驱的后继指向要删除节点的后继
current.prev.next = current.next;
}else{
//如果是头节点,则更新头结点为要删除节点的后继
head = current.next;
}
if(current.next != null){
//将要删除节点的后继的前驱指向要删除节点的前驱
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
return;
}
current = current.next; //每次循环寻找下一个元素
}
}
//打印链表的方法
public void print(){
Node current = head;
while (current != null){
System.out.println(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
package com.maweiqi.DoublyLindked;
/**
*/
public class DoublyLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
//添加节点
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
// list.print();
// //查找节点
// Node foundNode = list.find(5);
// if(foundNode != null){
// System.out.println("找到了节点: "+ foundNode.data);
// }else{
// System.out.println("未找到节点");
// }
//
// //在指定节点后插入新节点
// list.insertAfter(foundNode,5);
// System.out.println("插入节点后的链表为:");
// list.print();
//
// //删除节点
list.delete(2);
System.out.println("删除节点后的链表");
list.print();
}
}





















 1195
1195











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








