本章规则:

就是要用所给的木块覆盖阴影区域,而且相邻的木块不能同色
(1)


(2)

(3)
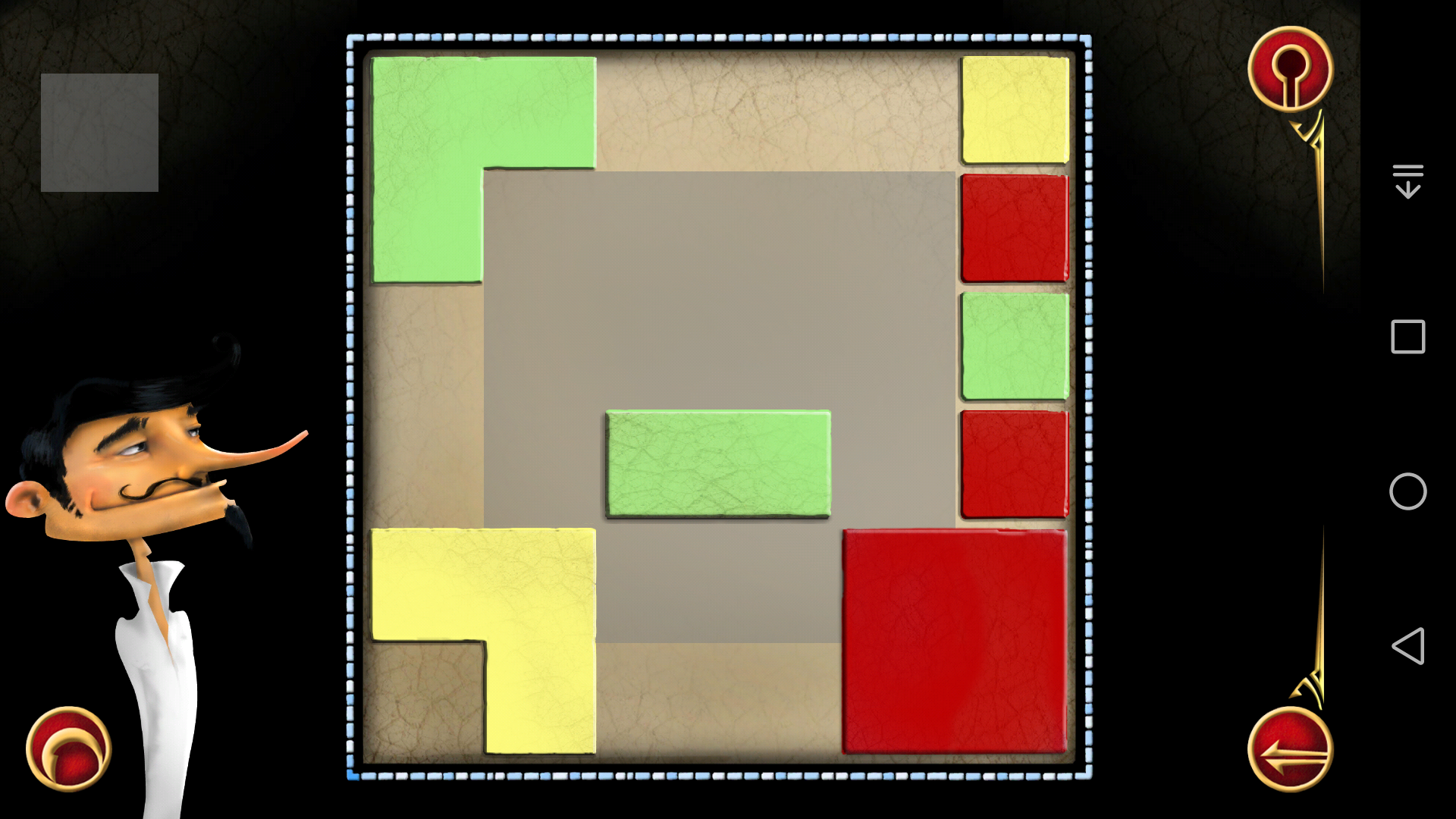


(4)


(5)


(6)


除了第(1)(2)(6)关是只有2种颜色的,其他29个关卡都有3种颜色
(7)


(8)


(9)

(10)
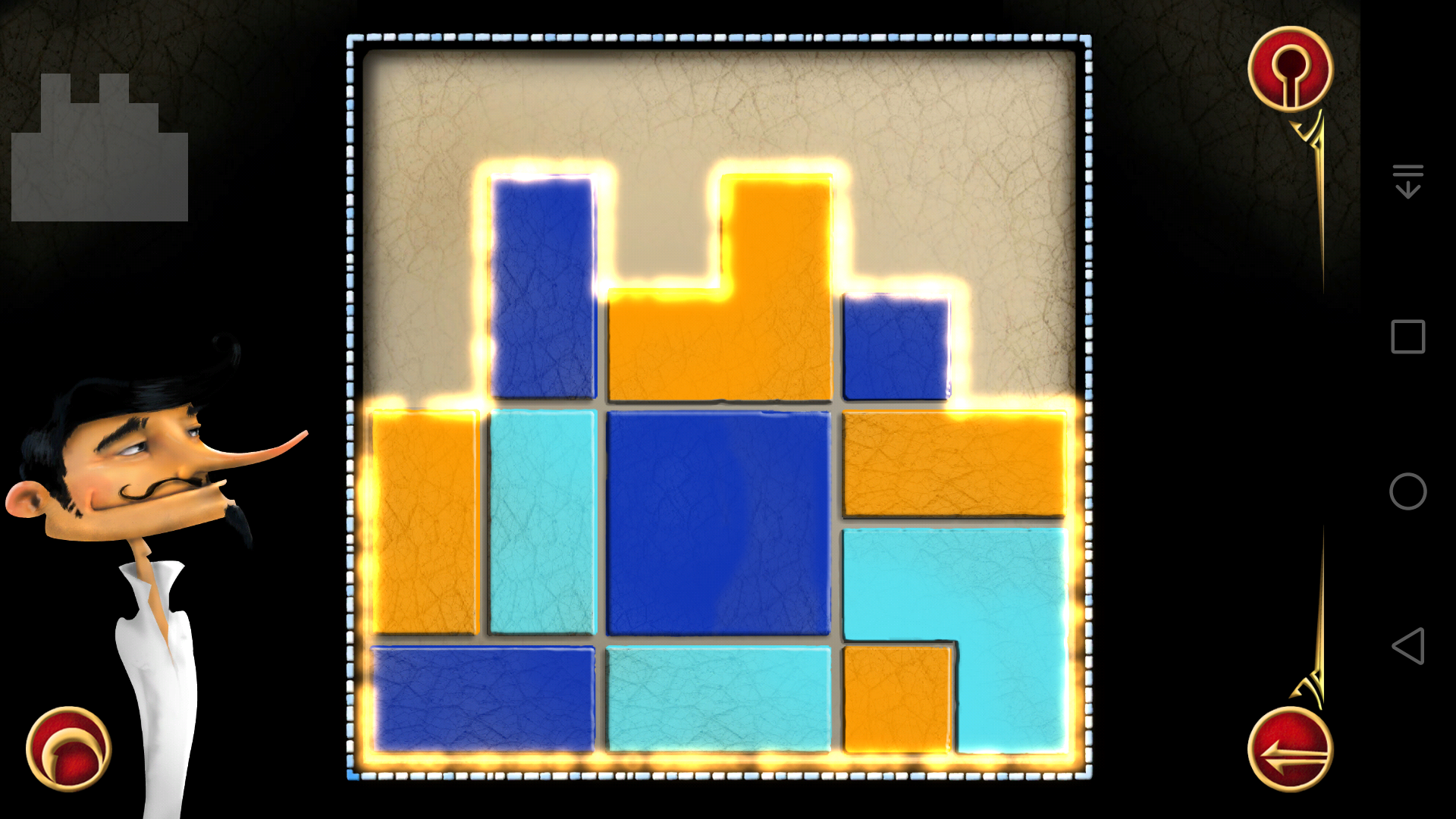
我找到2种解法:


(11)

(12)


(13)


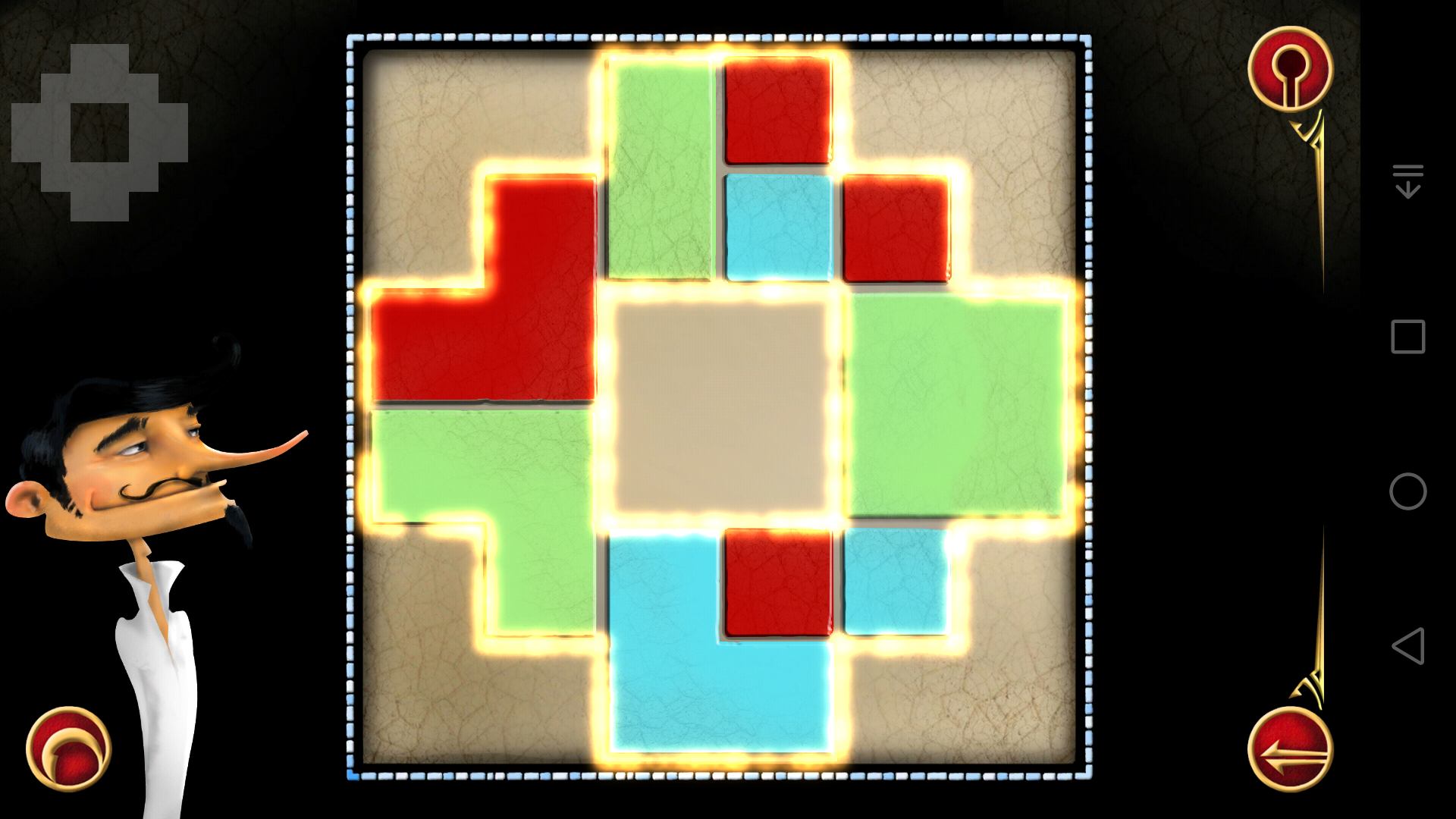
(14)


(15)


(16)
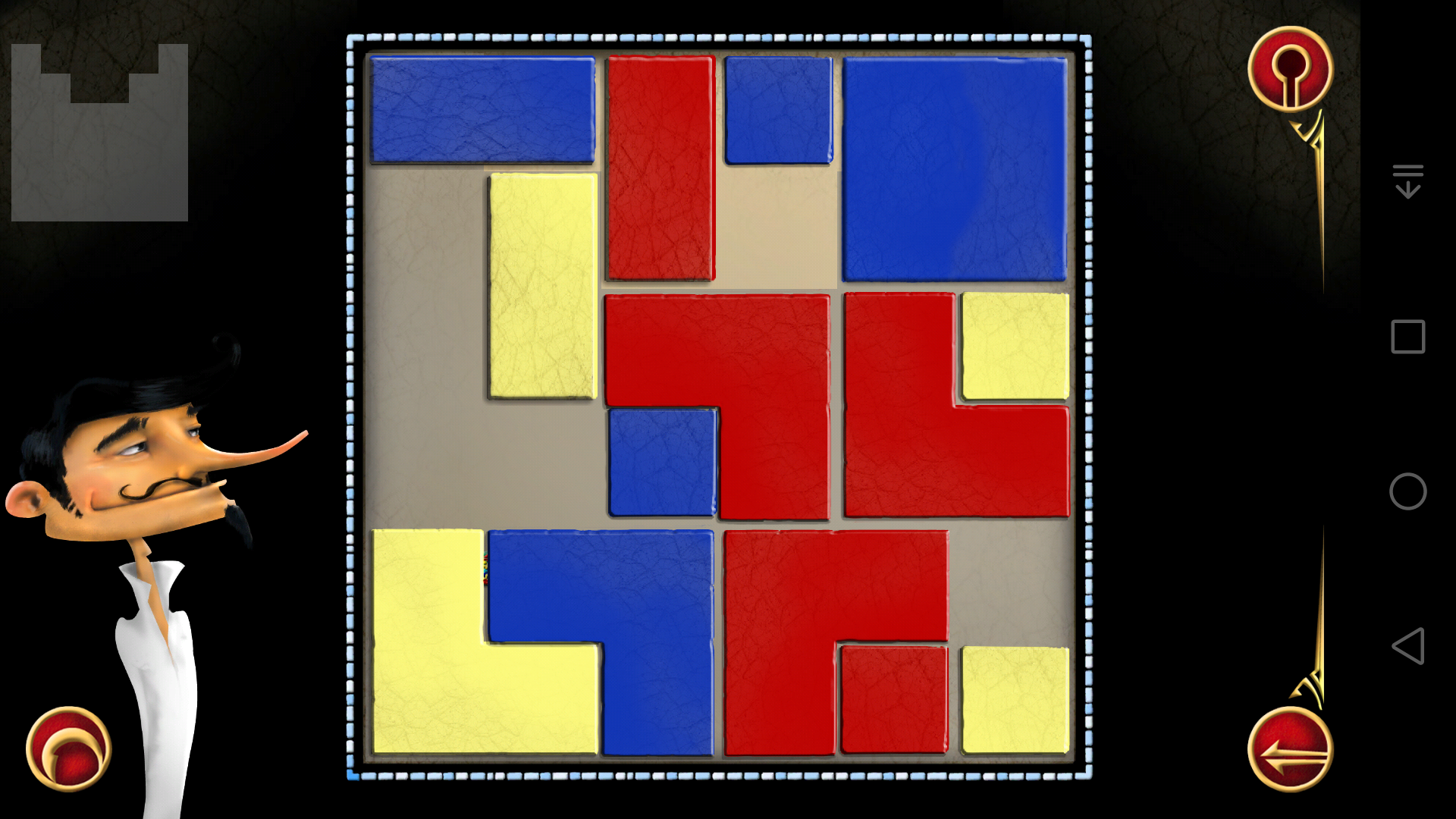

(17)
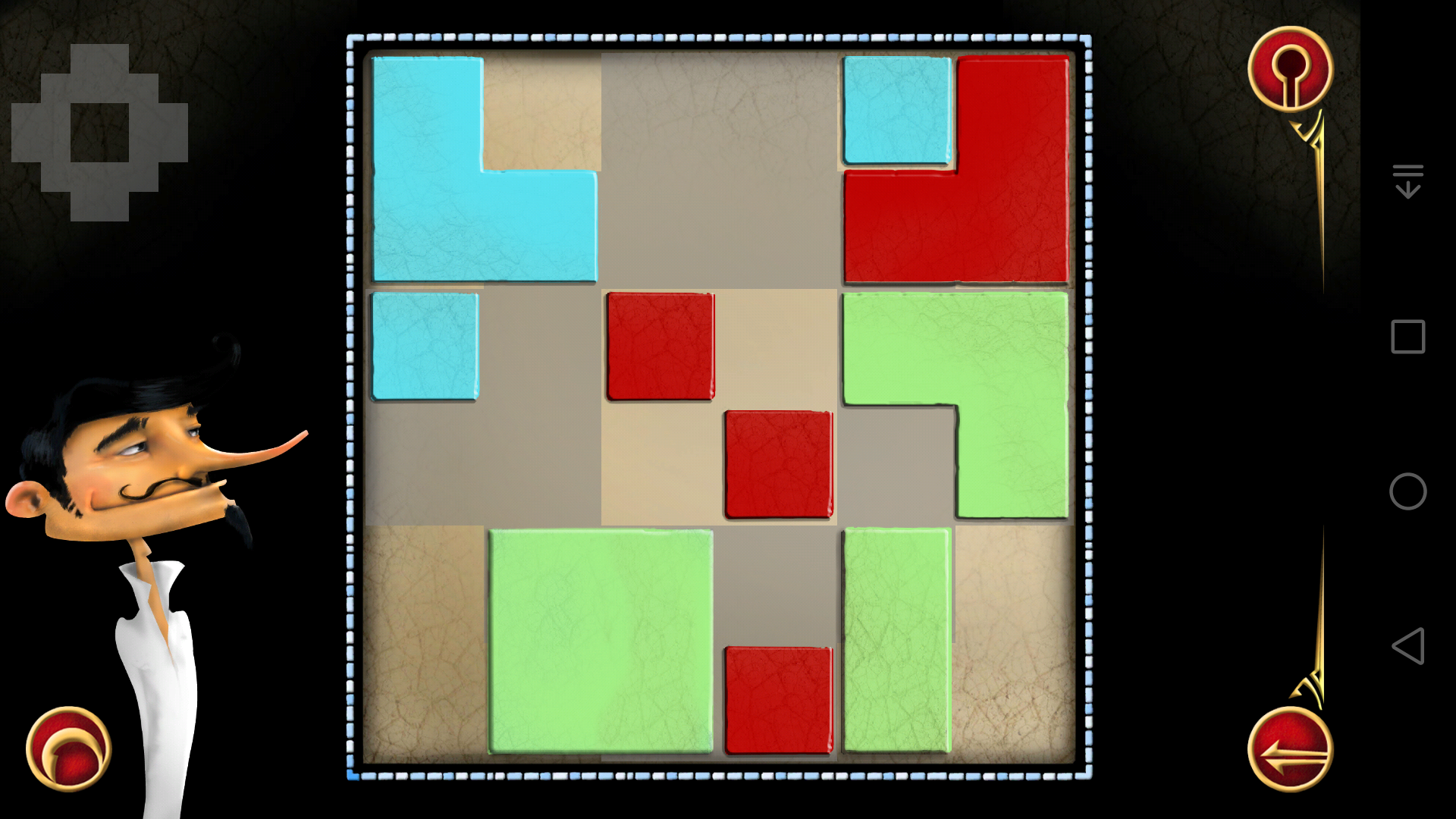

(18)
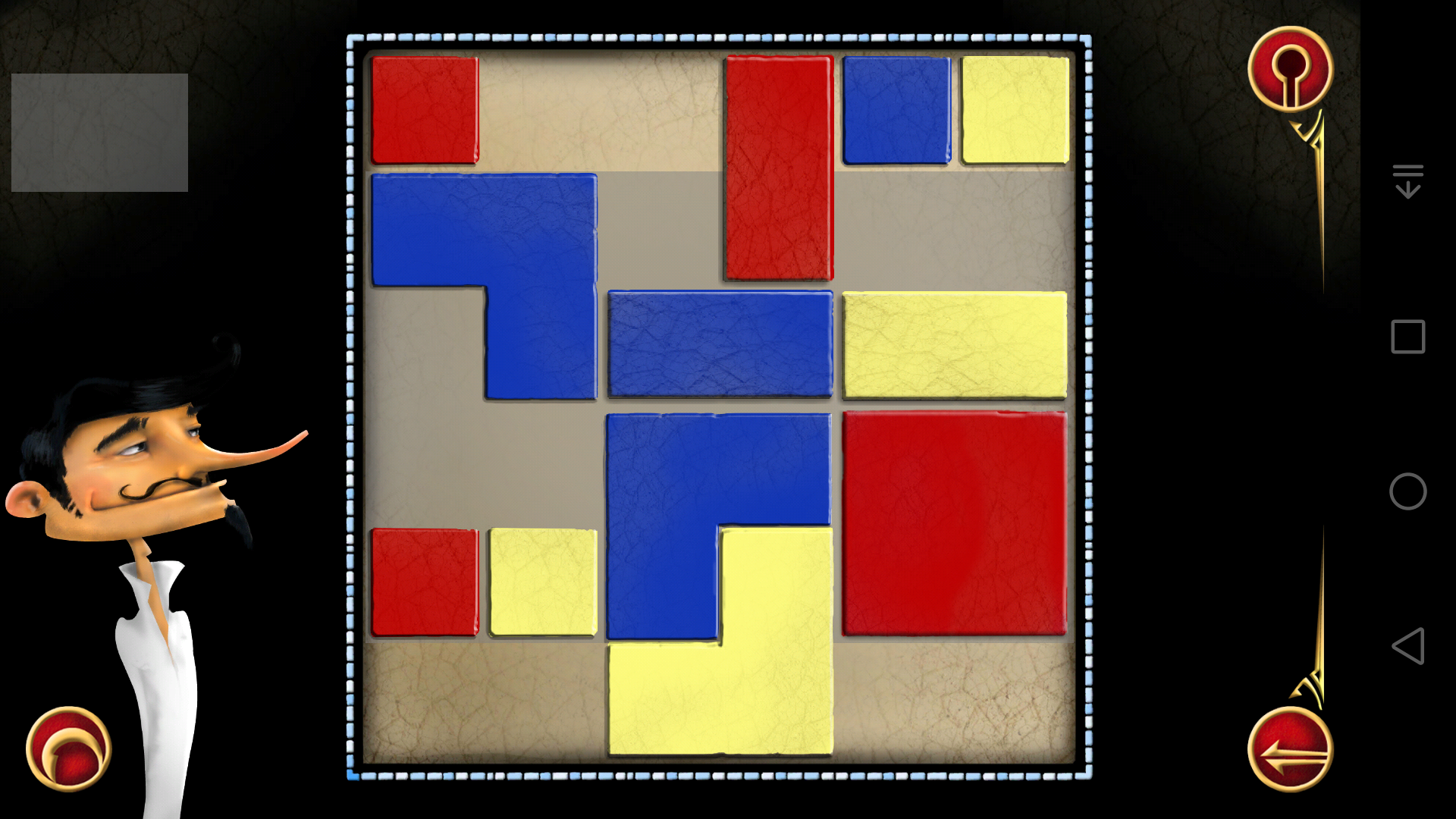

(19)


(20)
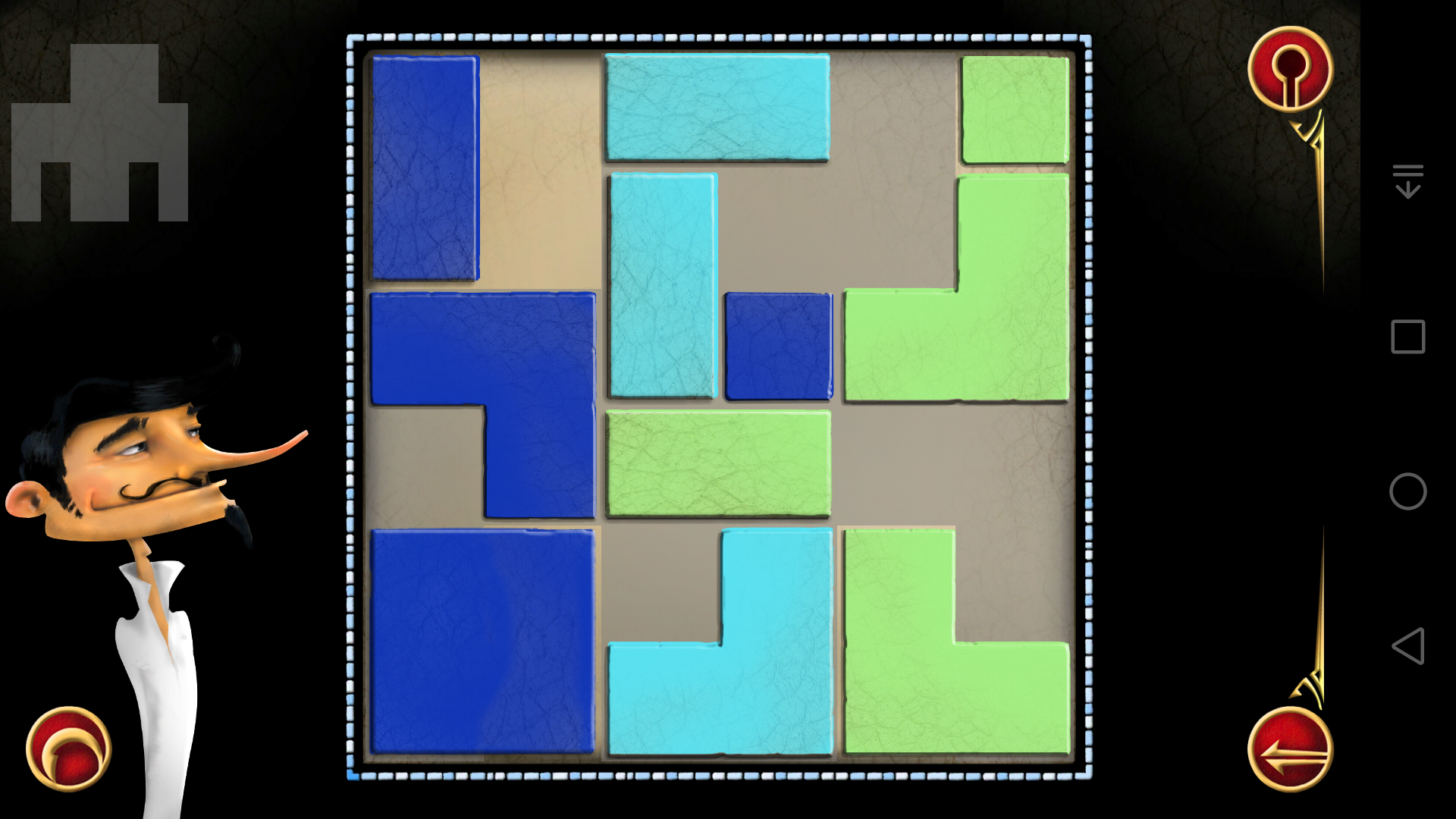
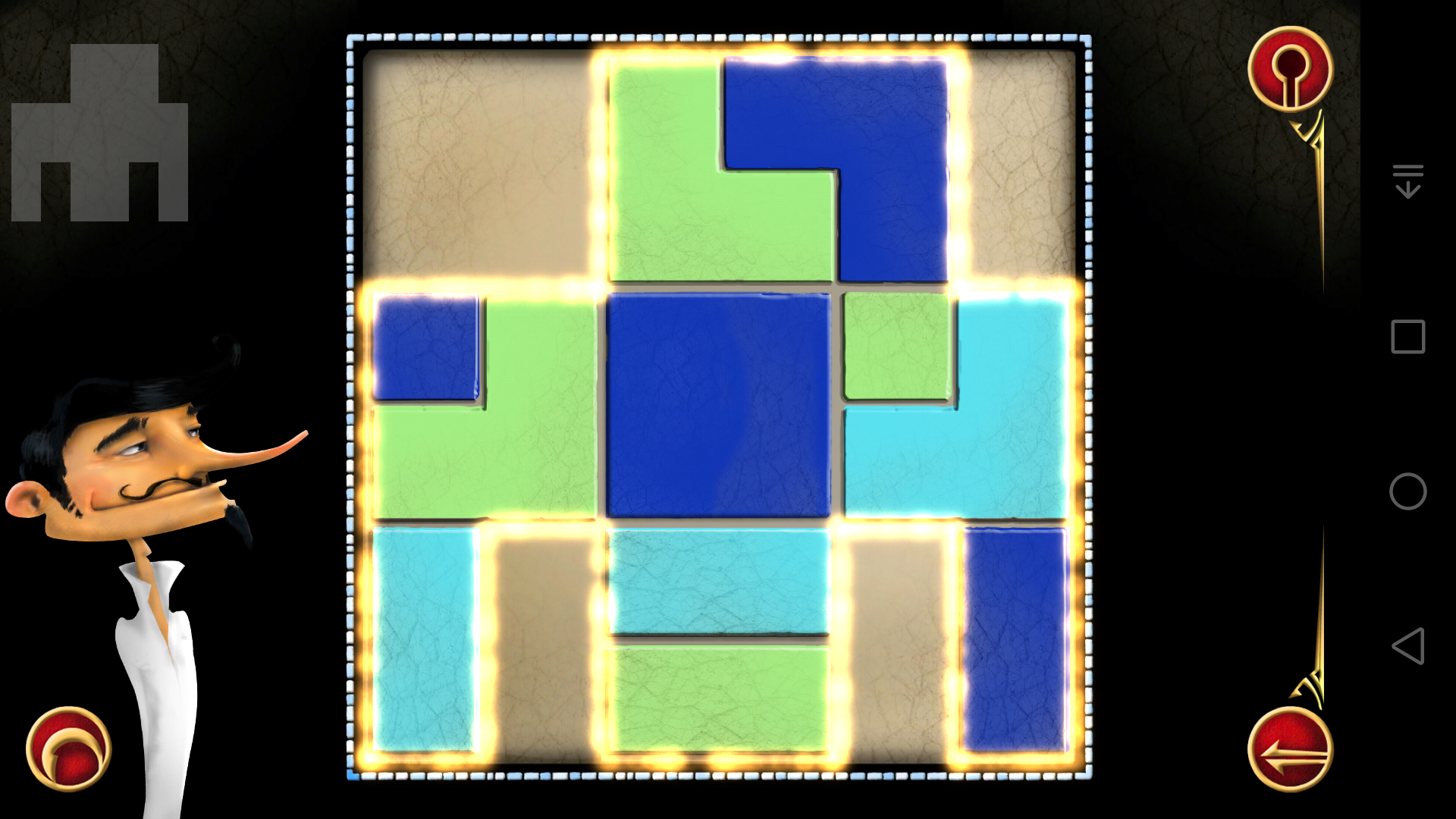
(21)
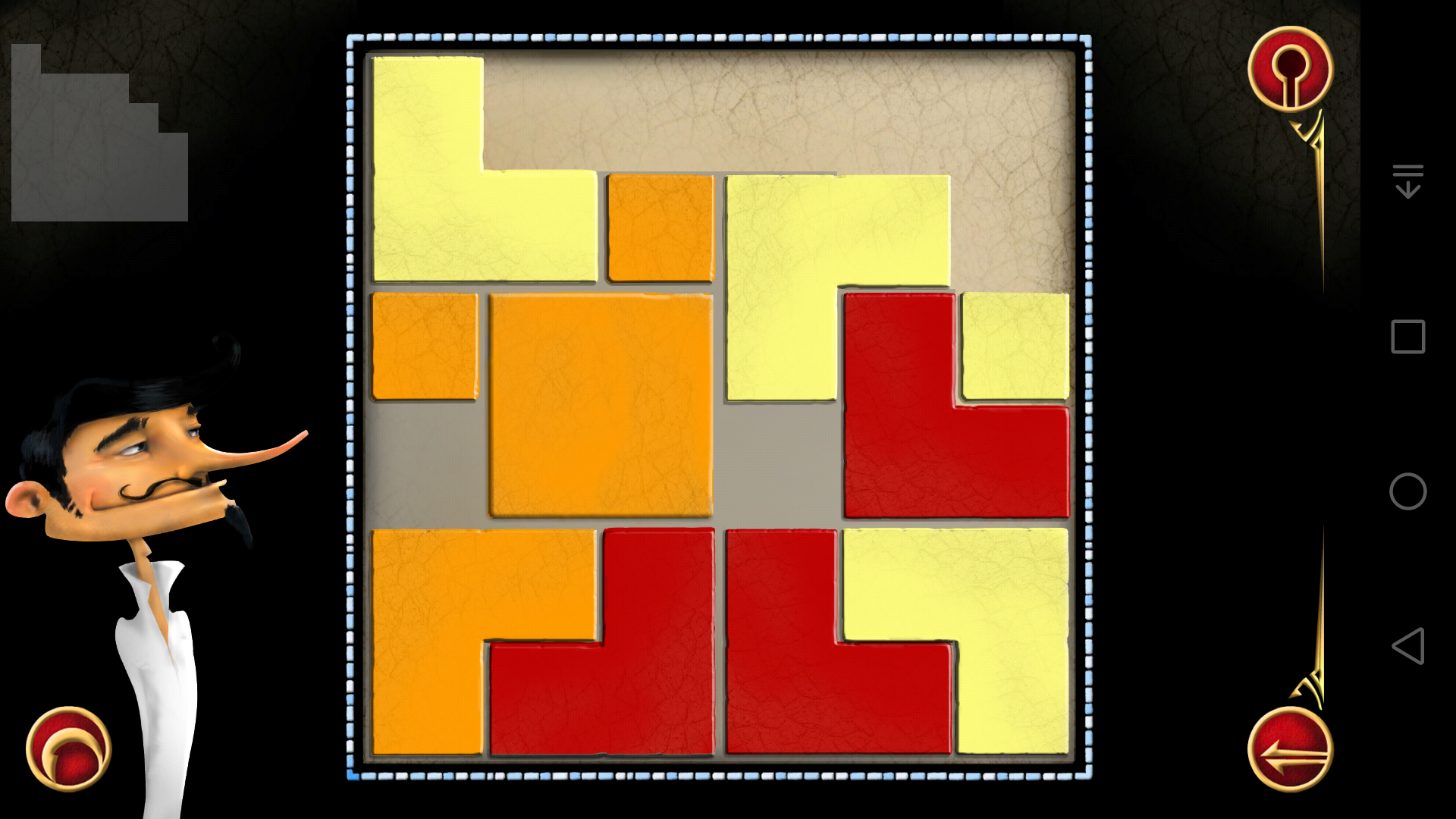
说实话这一关难到我了,虽然找到了可以把木块都放进阴影区域的方法,但是却没法使得相邻色块不同色。
所以我怀疑可能是因为惯性思维,所以我才想不到答案,只好借助我的编程能力来解决。
程序说明:
6*6的正方形分为目标阴影区域和非阴影区域,色块有3种颜色,8种形状,除了1*1的小正方形和2*2的大正方形之外,还有4个L型的块,以及1*2的横块和竖块,依次编号1-8。
给每个块标记一个核心点,用来表示块的位置:
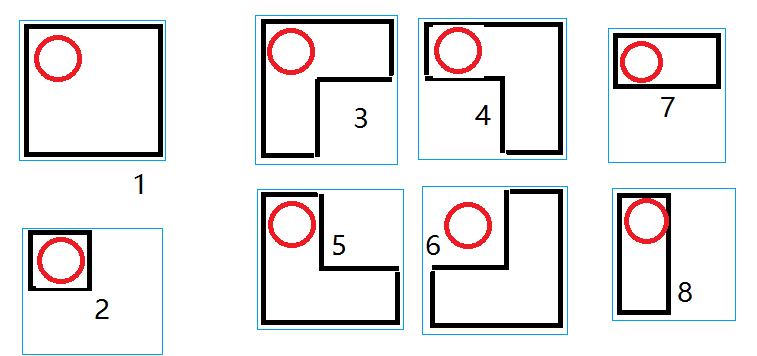
其中数字表示对形状的编号
每个块的位置用4个数字表示,空格用0表示,8个块依次是
1,2,3,4
1,0,0,0
1,2,3,0
1,2,0,4
1,0,3,4
0,2,3,4
1,2,0,0
1,0,3,0
如此便记录了每个块的形状,至于颜色就比较简单了,用1,2,3表示3种颜色就可以了
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;//一共n个块,n<20
int color[20]; //block[i]=1、2、3,表示3种颜色
int shape[20];//shape[i]=1、2、3、4、5、6,表示6种颜色
int list[6][6];//0是阴影区域,-1不是
int di[5] = { -1,0, 0, 1, 1 };//行偏移
int dj[5] = { -1,0, 1, 0, 1 };//列偏移
int dx[5] = { -1, 0, 0, -1, 1 };//行偏移
int dy[5] = { -1, 1, -1, 0, 0 };//列偏移
int p[9][4] = //指向di和dj
{
0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 3, 4,
1, 0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 3, 0,
1, 2, 0, 4,
1, 0, 3, 4,
0, 2, 3, 4,
1, 2, 0, 0,
1, 0, 3, 0
};
bool ok(int i, int j,int k) //能否在(i,j)放第k个块
{
int t[4], x, y;
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)t[a] = p[shape[k]][a];
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
if (x<0 || x>5 || y<0 || y>5)return false;
if (list[x][y])return false; //此处实际上是数组的四层嵌套
for (int b = 1; b <= 4; b++)
{
x = i + di[t[a]] + dx[b], y = j + dj[t[a]] + dy[b];
if (x<0 || x>5 || y<0 || y>5)continue;
if (list[x][y] == color[k])return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool trys(int k) //第k个块能否放下去
{
if (k > n)
{
cout << "答案(颜色)如下:\n";
for (int i = 0; i<6; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
if (list[i][j] == -1)cout << " ";
else cout << list[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return true;
}
int t[4], x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)if (ok(i, j, k))
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)t[i] = p[shape[k]][i];
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
list[x][y] = color[k];
}
if (trys(k + 1))return true; //深度优先搜索
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)//回溯
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
list[x][y] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
n = 0;
cout << "依次输入各个块的颜色,用1或2或3表示,以0结束\n";
while (cin >> color[++n])if (color[n] == 0)break;
n--;
cout << "依次输入各个块的形状,用1-8表示\n";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> shape[i];
cout << "依次输入36个格子各自是否属于目标阴影区域,0表示是,-1表示不是\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)cin >> list[i][j];
trys(1);
return 0;
}<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;//一共n个块,n<20
int color[20]; //block[i]=1、2、3,表示3种颜色
int shape[20];//shape[i]=1、2、3、4、5、6,表示6种颜色
int list[6][6];//0是阴影区域,-1不是
int di[5] = { -1,0, 0, 1, 1 };//行偏移
int dj[5] = { -1,0, 1, 0, 1 };//列偏移
int dx[5] = { -1, 0, 0, -1, 1 };//行偏移
int dy[5] = { -1, 1, -1, 0, 0 };//列偏移
int p[9][4] = //指向di和dj
{
0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 3, 4,
1, 0, 0, 0,
1, 2, 3, 0,
1, 2, 0, 4,
1, 0, 3, 4,
0, 2, 3, 4,
1, 2, 0, 0,
1, 0, 3, 0
};
bool ok(int i, int j,int k) //能否在(i,j)放第k个块
{
int t[4], x, y;
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)t[a] = p[shape[k]][a];
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
if (x<0 || x>5 || y<0 || y>5)return false;
if (list[x][y])return false; //此处实际上是数组的四层嵌套
for (int b = 1; b <= 4; b++)
{
x = i + di[t[a]] + dx[b], y = j + dj[t[a]] + dy[b];
if (x<0 || x>5 || y<0 || y>5)continue;
if (list[x][y] == color[k])return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool trys(int k) //第k个块能否放下去
{
if (k > n)
{
cout << "答案(颜色)如下:\n";
for (int i = 0; i<6; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
if (list[i][j] == -1)cout << " ";
else cout << list[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return true;
}
int t[4], x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)if (ok(i, j, k))
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)t[i] = p[shape[k]][i];
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
list[x][y] = color[k];
}
if (trys(k + 1))return true; //深度优先搜索
for (int a = 0; a < 4; a++)//回溯
{
if (t[a] == 0)continue;
x = i + di[t[a]], y = j + dj[t[a]];
list[x][y] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
n = 0;
cout << "依次输入各个块的颜色,用1或2或3表示,以0结束\n";
while (cin >> color[++n])if (color[n] == 0)break;
n--;
cout << "依次输入各个块的形状,用1-8表示\n";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> shape[i];
cout << "依次输入36个格子各自是否属于目标阴影区域,0表示是,-1表示不是\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)cin >> list[i][j];
trys(1);
return 0;
}输入:
1 2 1 2 2 3 1 2 3 3 1 0
5 2 3 2 1 5 2 3 6 5 4
0-1-1-1-1-1
0 0 0 0-1-1
0 0 0 0 0-1
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
运行结果:

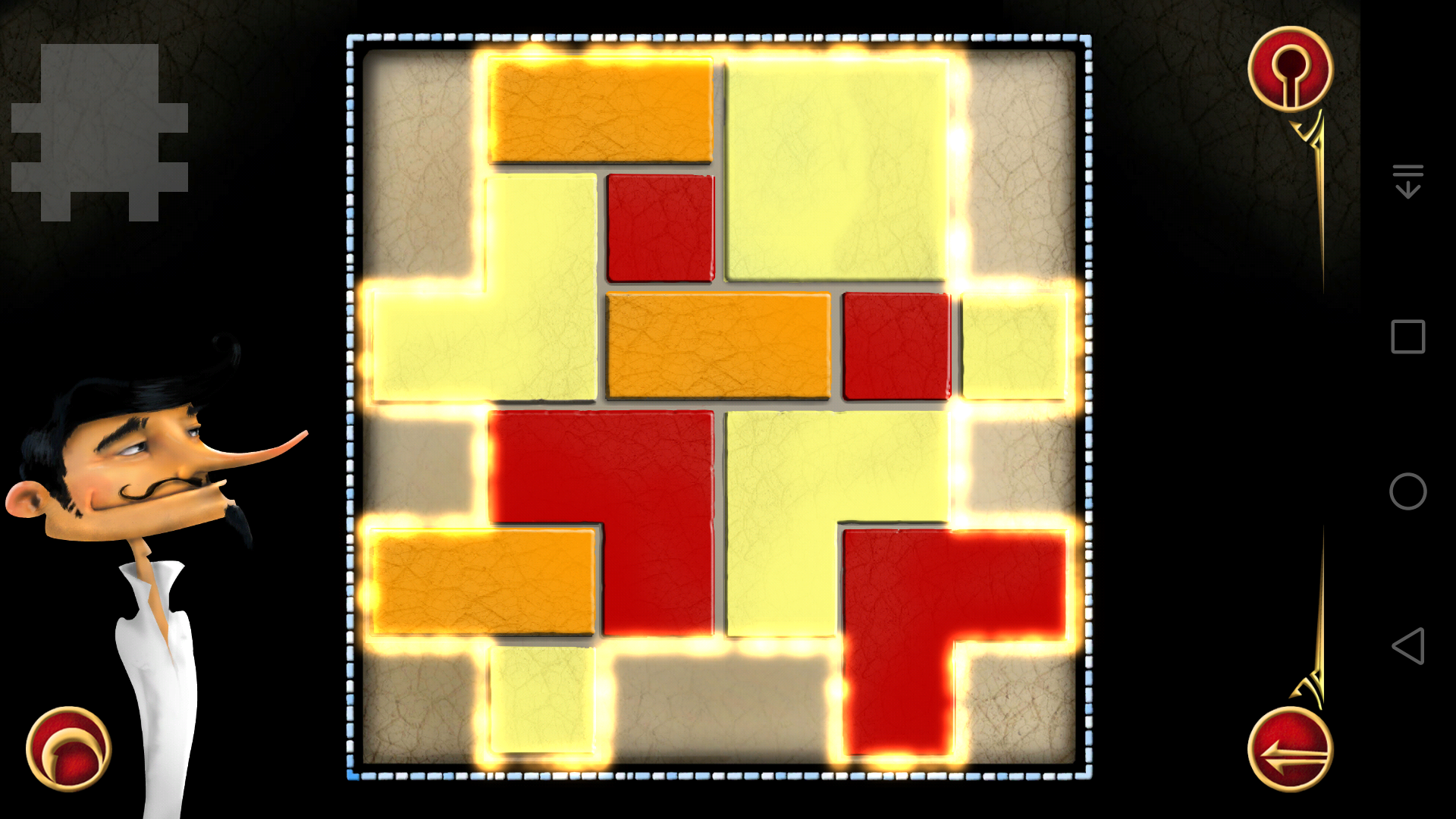
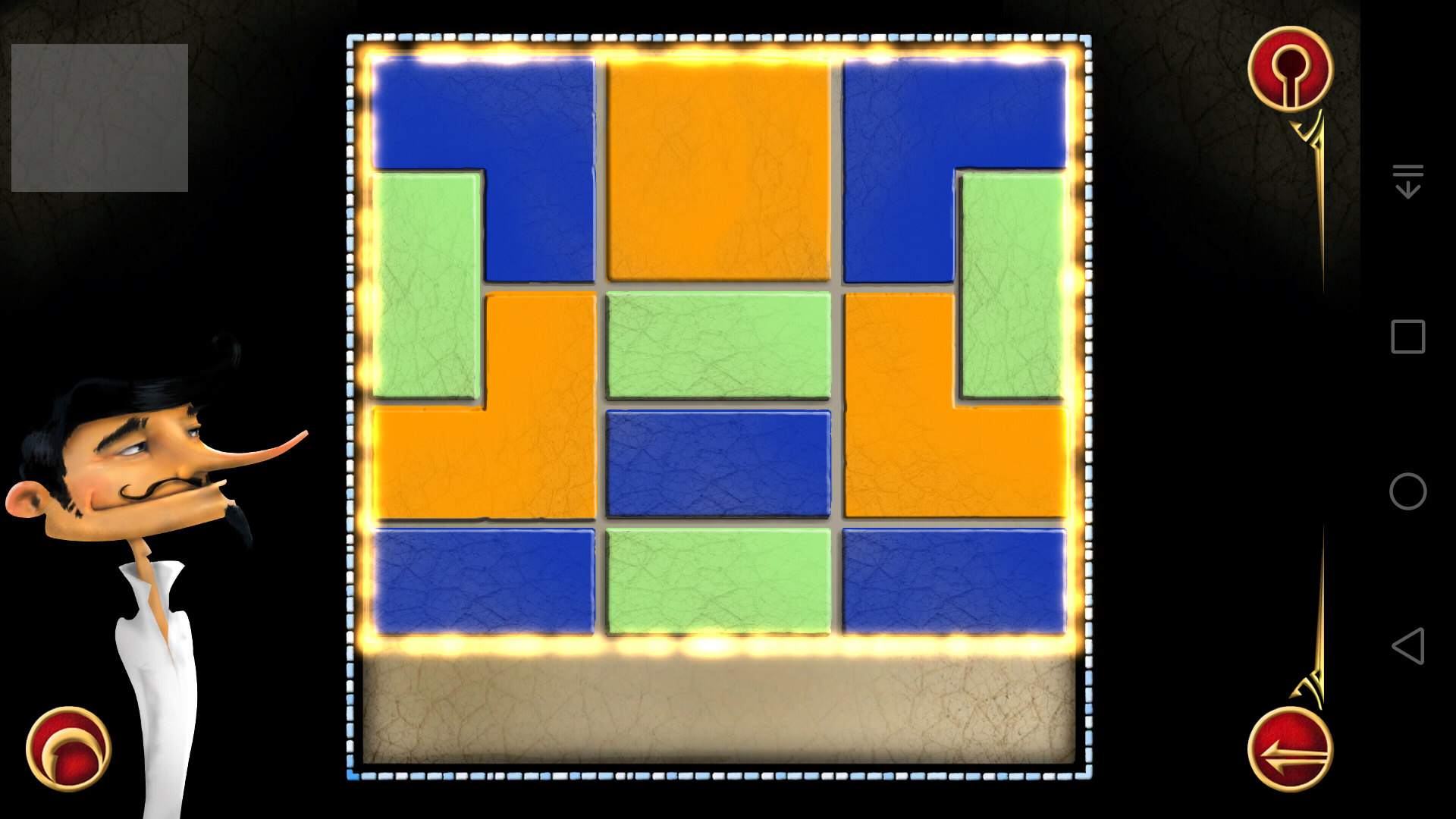
所以对应的答案就是:

从这张图可以看出,在惯性思维的影响下,很难找到这个答案。至于有没有其他答案就不清楚了,可以改一下代码变成求所有答案的程序,不过我认为没必要。
(22)


(23)


(24)

(25)


(26)


(27)


(28)


(29)

(30)

(31)


(32)


成就:

the virtuoso of the mosaic 通关即可
the expert on lizard matters 收集所有隐藏在木块下的蜥蜴(蜥蜴共有5个,分别在第1、5、9、13、16关)
the art of doubleness 用2种解法完成同一关(如上我给出了第10关的2种解法)
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








