读取Linux服务器硬盘剩余信息并插入Mysql数据库的shell脚本案例
一、分解代码梳理思路
1. 打印信息并获取磁盘分区信息,并获取出容量最大的一个:
一般情况数据库文件或者文件系统都存在最大分区下

echo 'get bigest disk info '
largest_partition="nasen"
# 执行 df -m 命令获取磁盘分区信息
disk_usage=$(df -m)
# 使用 awk 来处理 df 命令的输出,找到容量最大的分区
largest_partition=$(echo "$disk_usage" | awk 'NR>1 {if ($2>=max) {max=$2; part=$1} } END {print part}')
# 输出容量最大的分区名称
echo "容量最大的分区名称是: $largest_partition"
这段代码首先打印出一些信息,然后设置一个变量 largest_partition 为 nasen。接着,它执行 df -m 命令来获取磁盘分区信息,并将结果存储在变量 disk_usage 中。通过 awk 脚本来处理 disk_usage 的输出,找到容量最大的分区,并将其名称存储在变量 largest_partition 中。
2. 创建并清空输出文件:
# 如果需要同时显示最大容量数值和分区名称,可以稍作修改
largest_size_and_partition=$(echo "$disk_usage" | awk 'NR>1 {if ($2>max) {max=$2; part=$1} } END {printf "容量最大的分区名称是: %s, 容量为: %d MB\n", part, max}')
echo "$largest_size_and_partition"
echo 'nasen shell 20240307'
# 检查 output.txt 文件是否存在,如果不存在则创建
if [! -f "output.txt" ]; then
touch output.txt
fi
# 清空 output.txt 文件内容
> output.txt
这里创建了一个名为 largest_size_and_partition 的变量,用于存储同时显示最大容量数值和分区名称的信息。然后,它检查是否存在 output.txt 文件,如果不存在则创建该文件。最后,它清空了 output.txt 文件的内容。
3. 设置外部变量并处理磁盘分区信息:
target_partition="$largest_partition" # 设置外部变量
echo 'system auto get bigest disk:'
echo "$target_partition"
# 执行 df -h 命令获取硬盘分区信息
df -h | awk '{
filesystem = $1
size = $2
used = $3
avail = $4
use_percentage = $5
mounted_on = $6
# 声明变量并赋值
file_system_name = filesystem
total_size = size
used_capacity = used
available_space = avail
usage_percentage = use_percentage
mount_point = mounted_on
# 只匹配文件系统名称为 /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home 的数据
if (filesystem == "'$target_partition'") {
total_size = substr(total_size, 0, length(total_size) - 1)
available_space = substr(available_space, 0, length(available_space) - 1)
used_capacity = substr(used_capacity, 0, length(used_capacity) - 1)
usage_percentage = substr(usage_percentage, 0, length(usage_percentage) - 1)
host="192.168.1.44"
# 输出变量值到文件
print file_system_name, total_size, used_capacity, available_space, usage_percentage, mount_point, host >> "output.txt"
}
}'
echo 'nasen told you system info get success!'
这段代码将外部变量 largest_partition 设置为目标分区。然后,它再次执行 df -h 命令获取硬盘分区信息,并通过 awk 脚本来处理这些信息。它声明了一些变量并赋值,然后只匹配文件系统名称为 target_partition 的数据。对于匹配的行,它进行了一些数据处理,并将变量值输出到 output.txt 文件中。
4. 读取输出文件并插入数据库:
# 读取文件并输出变量值
while IFS= read -r line; do
fields=($line)
file_system_name="${fields[0]}"
total_size="${fields[1]}"
used_capacity="${fields[2]}"
available_space="${fields[3]}"
usage_percentage="${fields[4]}"
mount_point="${fields[5]}"
host="${fields[6]}"
host=`/sbin/ifconfig -a|grep inet|grep -v 127.0.0.1|grep -v inet6|awk '{print $2}'|tr -d "addr:"`
echo "文件系统名称:$file_system_name"
echo "总大小:$total_size"
echo "已使用:$used_capacity"
echo "可用空间:$available_space"
echo "使用率:$usage_percentage"
echo "挂载点:$mount_point"
echo "主机地址:$host"
TABLE="diskcheck_fb"
SQL_LIST="use monitor"
mysql -h 192.168.1.225 -P 3306 -uroot -p123456 << EOF
$SQL_LIST
INSERT INTO diskcheck_fb (avail,used,size,host,mounted,cpu,date) VALUES('$available_space','$usage_percentage','$total_size','$host','$mount_point',"$usage_percentage",NOW());
EOF
echo 'nasen told you insert db success!'
done < output.txt
这段代码使用一个 while 循环来读取 output.txt 文件的每一行,并将每行分割成字段。然后,它将字段的值分别存储在变量中,并通过一些命令和脚本来获取主机地址。最后,它使用 mysql 命令将这些信息插入到数据库中,并打印出一些信息表示插入成功。
5.mysql监控数据库的监控表DEMO
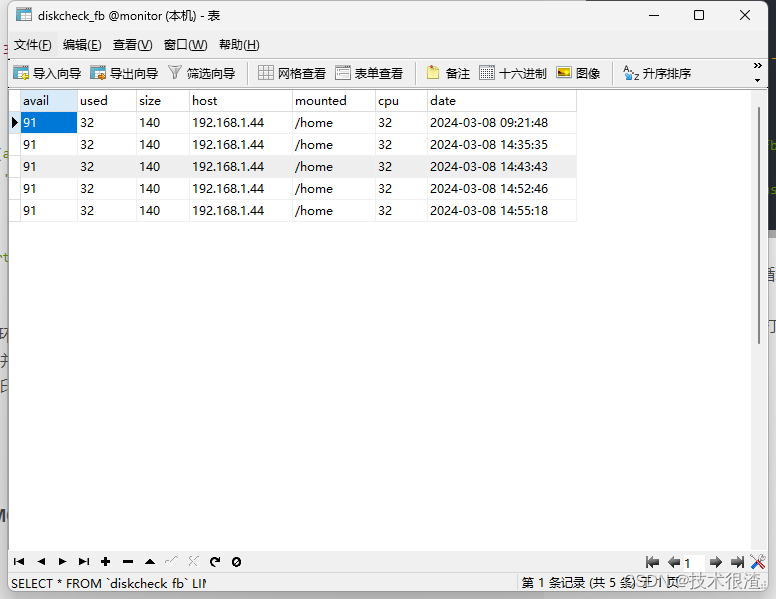
CREATE TABLE `diskcheck_fb` (
`avail` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '硬盘空余空间',
`used` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '硬盘已用空间',
`size` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '硬盘空间大小',
`host` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '所检查主机ip',
`mounted` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '所检查硬盘目录',
`cpu` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'cpu使用率',
`date` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间'
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC;
二、完整shell脚本代码
#!/bin/bash
echo 'get bigest disk info '
largest_partition="nasen"
# 执行 df -m 命令获取磁盘分区信息
disk_usage=$(df -m)
# 使用 awk 来处理 df 命令的输出,找到容量最大的分区
largest_partition=$(echo "$disk_usage" | awk 'NR>1 {if ($2>=max) {max=$2; part=$1} } END {print part}')
# 输出容量最大的分区名称
echo "容量最大的分区名称是: $largest_partition"
# 如果需要同时显示最大容量数值和分区名称,可以稍作修改
largest_size_and_partition=$(echo "$disk_usage" | awk 'NR>1 {if ($2>max) {max=$2; part=$1} } END {printf "容量最大的分区名称是: %s, 容量为: %d MB\n", part, max}')
echo "$largest_size_and_partition"
echo 'nasen shell 20240307'
# 检查 output.txt 文件是否存在,如果不存在则创建
if [ ! -f "output.txt" ]; then
touch output.txt
fi
# 清空 output.txt 文件内容
> output.txt
target_partition="$largest_partition" # 设置外部变量
echo 'system auto get bigest disk:'
echo "$target_partition"
# 执行 df -h 命令获取硬盘分区信息
df -h | awk '{
filesystem = $1
size = $2
used = $3
avail = $4
use_percentage = $5
mounted_on = $6
# 声明变量并赋值
file_system_name = filesystem
total_size = size
used_capacity = used
available_space = avail
usage_percentage = use_percentage
mount_point = mounted_on
# 只匹配文件系统名称为 /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home 的数据
if (filesystem == "'$target_partition'") {
total_size = substr(total_size, 0, length(total_size) - 1)
available_space = substr(available_space, 0, length(available_space) - 1)
used_capacity = substr(used_capacity, 0, length(used_capacity) - 1)
usage_percentage = substr(usage_percentage, 0, length(usage_percentage) - 1)
host="192.168.1.44"
# 输出变量值到文件
print file_system_name, total_size, used_capacity, available_space, usage_percentage, mount_point, host >> "output.txt"
}
}'
echo 'nasen told you system info get success!'
# 读取文件并输出变量值
while IFS= read -r line; do
fields=($line)
file_system_name="${fields[0]}"
total_size="${fields[1]}"
used_capacity="${fields[2]}"
available_space="${fields[3]}"
usage_percentage="${fields[4]}"
mount_point="${fields[5]}"
host="${fields[6]}"
host=`/sbin/ifconfig -a|grep inet|grep -v 127.0.0.1|grep -v inet6|awk '{print $2}'|tr -d "addr:"`
echo "文件系统名称:$file_system_name"
echo "总大小:$total_size"
echo "已使用:$used_capacity"
echo "可用空间:$available_space"
echo "使用率:$usage_percentage"
echo "挂载点:$mount_point"
echo "主机地址:$host"
TABLE="diskcheck_fb"
SQL_LIST="use monitor"
mysql -h 192.168.1.225 -P 3306 -uroot -p123456 << EOF
$SQL_LIST
INSERT INTO diskcheck_fb (avail,used,size,host,mounted,cpu,date) VALUES('$available_space','$used_capacity','$total_size','$host','$mount_point',"$usage_percentage",NOW());
EOF
echo 'nasen told you insert db success!'
done < output.txt
三、代码实际验证
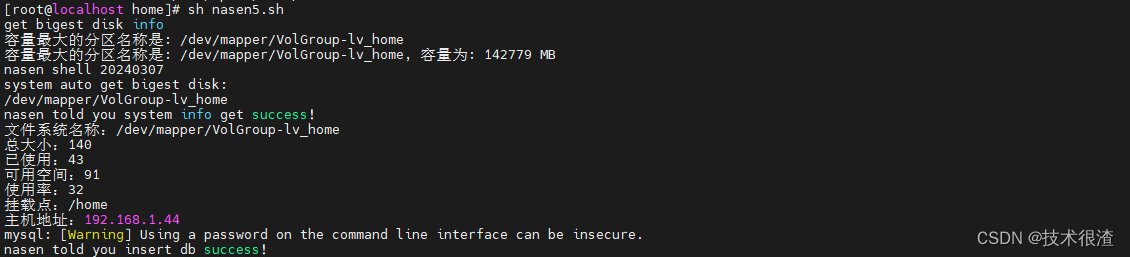
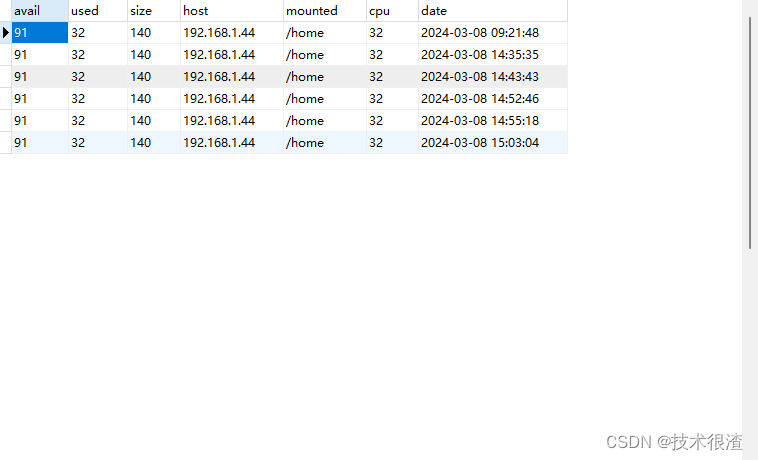
亲测有效,同学们可以自己试试!
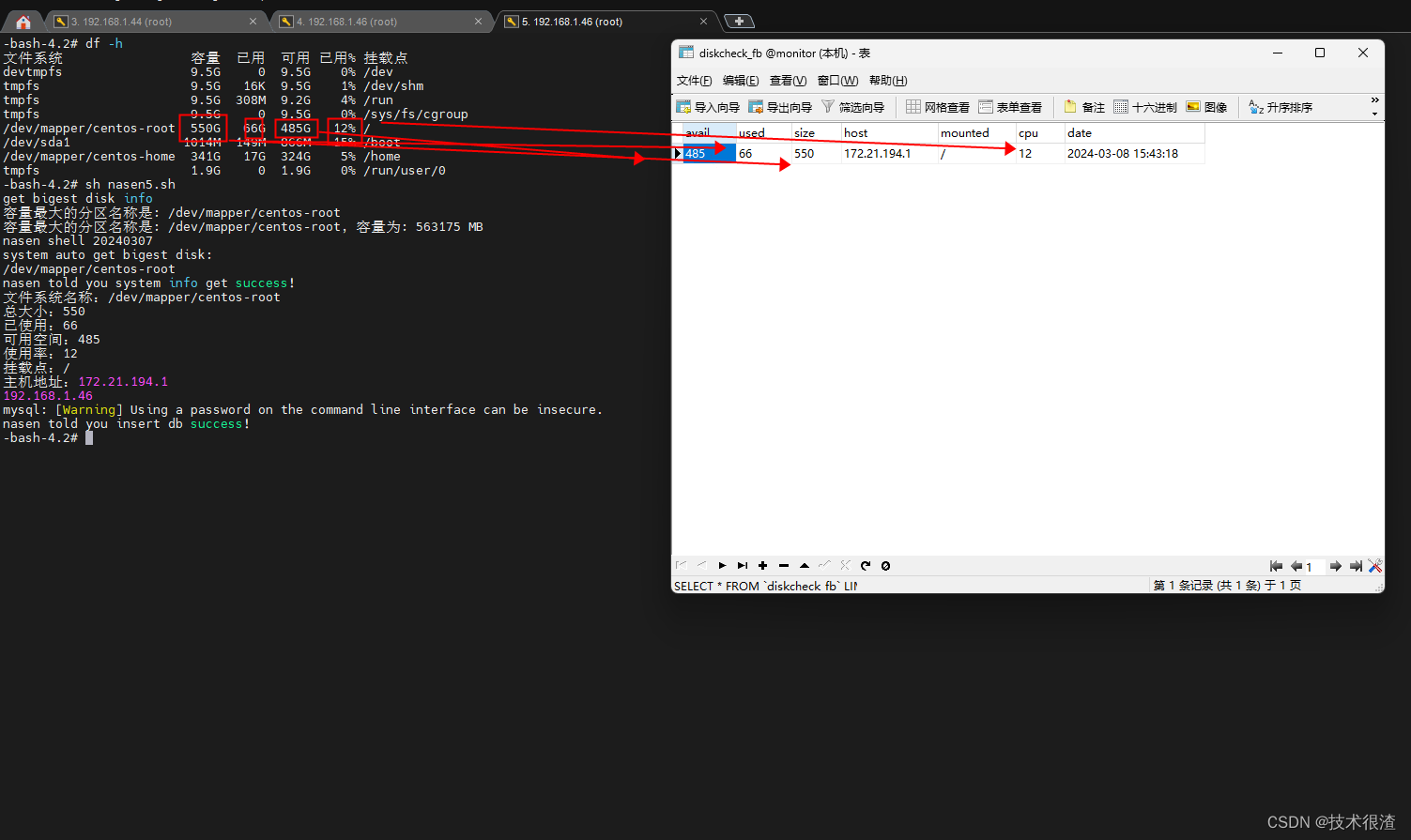
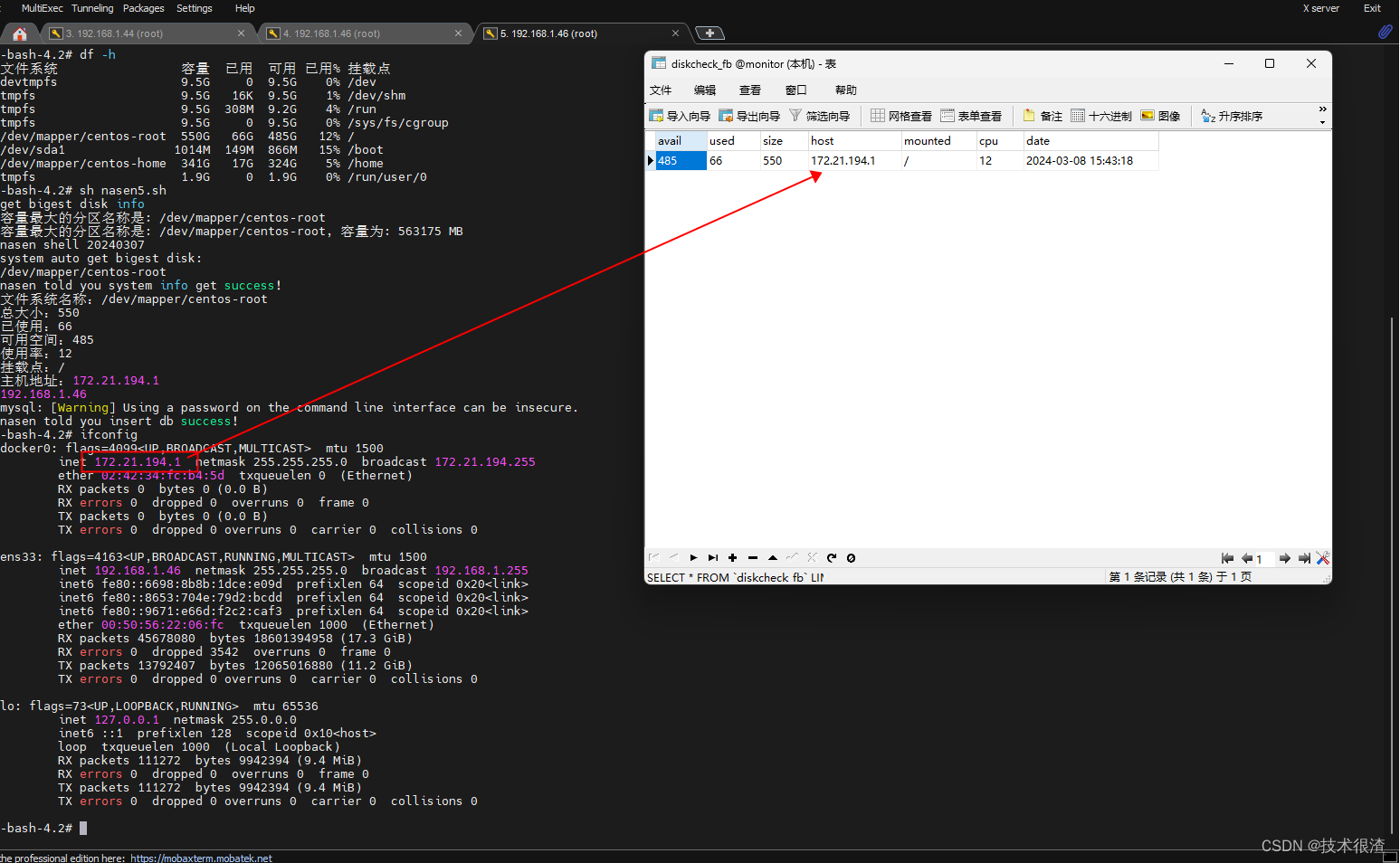
网卡IP可以自己改一下匹配逻辑
host=`/sbin/ifconfig -a|grep inet|grep -v 127.0.0.1|grep -v inet6|awk '{print $2}'|tr -d "addr:"`
四、其他思路的实现代码案例
#!/bin/sh
# check_disk status
# author yang
datetime=`date +"%Y-%m-%d/%H:%M:%S"` #获取当前时间
avail=`df -h | awk '{print $4}' | grep -v 已用 | tail -1| cut -d "G" -f1 -`
used=`df -h | awk '{print $3}' | tail -1| cut -d "G" -f1 -`
host=`/sbin/ifconfig -a|grep inet|grep -v 127.0.0.1|grep -v inet6|awk '{print $2}'|tr -d "addr:"`
mounted=`df -h | awk '{print $6}' | tail -1`
# zyl=`df -h | awk '{print $5}' | tail -1| cut -d "%" -f 1`
size=`df -h | awk '{print $2}' | tail -1| cut -d "G" -f1 -`
# use=$(($used/$size))
# echo $use
TIME_INTERVAL=5
time=$(date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
LAST_CPU_INFO=$(cat /proc/stat | grep -w cpu | awk '{print $2,$3,$4,$5,$6,$7,$8}')
LAST_SYS_IDLE=$(echo $LAST_CPU_INFO | awk '{print $4}')
LAST_TOTAL_CPU_T=$(echo $LAST_CPU_INFO | awk '{print $1+$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7}')
sleep ${TIME_INTERVAL}
NEXT_CPU_INFO=$(cat /proc/stat | grep -w cpu | awk '{print $2,$3,$4,$5,$6,$7,$8}')
NEXT_SYS_IDLE=$(echo $NEXT_CPU_INFO | awk '{print $4}')
NEXT_TOTAL_CPU_T=$(echo $NEXT_CPU_INFO | awk '{print $1+$2+$3+$4+$5+$6+$7}')
#系统空闲时间
SYSTEM_IDLE=`echo ${NEXT_SYS_IDLE} ${LAST_SYS_IDLE} | awk '{print $1-$2}'`
#CPU总时间
TOTAL_TIME=`echo ${NEXT_TOTAL_CPU_T} ${LAST_TOTAL_CPU_T} | awk '{print $1-$2}'`
CPU_USAGE=`echo ${SYSTEM_IDLE} ${TOTAL_TIME} | awk '{printf "%.2f", 100-$1/$2*100}'`
TABLE="diskcheck_fb"
SQL_LIST="use monitor"
mysql -h 192.168.1.255 -P 3306 -u root -p123456 << EOF
$SQL_LIST
INSERT INTO diskcheck_fb (avail,used,size,host,mounted,cpu,date) VALUES('$avail','$used','$size','$host','$mounted',"${CPU_USAGE}%",NOW());
EOF
笔者简介
国内某一线知名软件公司企业认证在职员工:任JAVA高级研发工程师,大数据领域专家,数据库领域专家兼任高级DBA!10年软件开发经验!现任国内某大型软件公司大数据研发工程师、MySQL数据库DBA,软件架构师。直接参与设计国家级亿级别大数据项目!并维护真实企业级生产数据库300余个!紧急处理数据库生产事故上百起,挽回数据丢失所造成的灾难损失不计其数!并为某国家级大数据系统的技术方案(国家知识产权局颁布)专利权的第一专利发明人!


























 226
226











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










