Java对象的分配,根据其过程,将其分为快速分配和慢速分配两种形式,其中快速分配使用无锁的指针碰撞技术在新生代的Eden区上进行分配,而慢速分配根据堆的实现方式、GC的实现方式、代的实现方式不同而具有不同的分配调用层次。
下面就以bytecodeInterpreter解释器对于new指令的解释出发,分析实例对象的内存分配过程:
一、快速分配
1.实例的创建首先需要知道该类型是否被加载和正确解析,根据字节码所指定的CONSTANT_Class_info常量池索引,获取对象的类型信息并调用is_unresovled_klass()验证该类是否被解析过,在创建类的实例之前,必须确保该类型已经被正确加载和解析。
|
1
2
3
4
|
CASE(_new): {
u2 index = Bytes::get_Java_u2(pc+
1
);
constantPoolOop constants = istate->method()->constants();
if
(!constants->tag_at(index).is_unresolved_klass()) {
|
2.接下来获取该类型在虚拟机中的表示instanceKlass(具体可以参考前文实例探索Java对象的组织结构)
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
oop entry = constants->slot_at(index).get_oop();
assert
(entry->is_klass(),
"Should be resolved klass"
);
klassOop k_entry = (klassOop) entry;
assert
(k_entry->klass_part()->oop_is_instance(),
"Should be instanceKlass"
);
instanceKlass* ik = (instanceKlass*) k_entry->klass_part();
|
3.当类型已经被初始化并且可以被快速分配时,那么将根据UseTLAB来决定是否使用TLAB技术(Thread-Local Allocation Buffers,线程局部分配缓存技术)来将分配工作交由线程自行完成。TLAB是每个线程在Java堆中预先分配了一小块内存,当有对象创建请求内存分配时,就会在该块内存上进行分配,而不需要在Eden区通过同步控制进行内存分配。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
if
( ik->is_initialized() && ik->can_be_fastpath_allocated() ) {
size_t obj_size = ik->size_helper();
oop result = NULL;
// If the TLAB isn't pre-zeroed then we'll have to do it
bool need_zero = !ZeroTLAB;
if
(UseTLAB) {
result = (oop) THREAD->tlab().allocate(obj_size);
}
if
(result == NULL) {
need_zero =
true
;
|
4.如果不使用TLAB或在TLAB上分配失败,则会尝试在堆的Eden区上进行分配。Universe::heap()返回虚拟机内存体系所使用的CollectedHeap,其top_addr()返回的是Eden区空闲块的起始地址变量_top的地址,end_addr()是Eden区空闲块的结束地址变量_end的地址。故这里compare_to是Eden区空闲块的起始地址,new_top为使用该块空闲块进行分配后新的空闲块起始地址。这里使用CAS操作进行空闲块的同步操作,即观察_top的预期值,若与compare_to相同,即没有其他线程操作该变量,则将new_top赋给_top真正成为新的空闲块起始地址值,这种分配技术叫做bump-the-pointer(指针碰撞技术)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
retry:
HeapWord* compare_to = *Universe::heap()->top_addr();
HeapWord* new_top = compare_to + obj_size;
if
(new_top <= *Universe::heap()->end_addr()) {
if
(Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(new_top, Universe::heap()->top_addr(), compare_to) != compare_to) {
goto
retry;
}
result = (oop) compare_to;
}
}
|
5.根据是否需要填0选项,对分配空间的对象数据区进行填0
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
if
(result != NULL) {
// Initialize object (if nonzero size and need) and then the header
if
(need_zero ) {
HeapWord* to_zero = (HeapWord*) result + sizeof(oopDesc) / oopSize;
obj_size -= sizeof(oopDesc) / oopSize;
if
(obj_size >
0
) {
memset(to_zero,
0
, obj_size * HeapWordSize);
}
}
|
6.根据是否使用偏向锁,设置对象头信息,然后设置对象的klassOop引用(这样对象本身就获取了获取类型数据的途径)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if
(UseBiasedLocking) {
result->set_mark(ik->prototype_header());
}
else
{
result->set_mark(markOopDesc::prototype());
}
result->set_klass_gap(
0
);
result->set_klass(k_entry);
|
7.把对象地址引入栈,并继续执行下一个字节码
|
1
2
|
SET_STACK_OBJECT(result,
0
);
UPDATE_PC_AND_TOS_AND_CONTINUE(
3
,
1
);
|
8.若该类型没有被解析,就会调用InterpreterRuntime的_new函数完成慢速分配
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
// Slow case allocation
CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::_new(THREAD, METHOD->constants(), index),
handle_exception);
SET_STACK_OBJECT(THREAD->vm_result(),
0
);
THREAD->set_vm_result(NULL);
UPDATE_PC_AND_TOS_AND_CONTINUE(
3
,
1
);
|
以上就是快速分配的过程,其流程图如下,关键在于快速分配在Eden区所使用的无锁指针碰撞技术
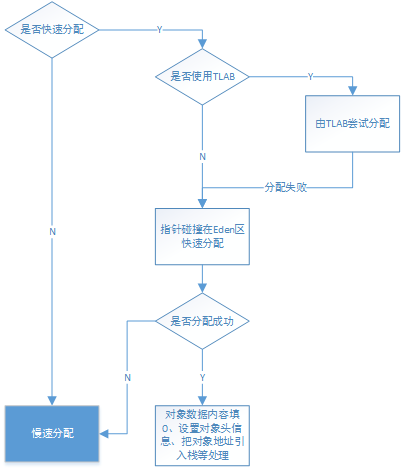
二、慢速分配
接下来看看慢速分配是如何进行的:
1.InterpreterRuntime的_new函数定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/interpreter/interpreterRuntime.cpp中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
IRT_ENTRY(
void
, InterpreterRuntime::_new(JavaThread* thread, constantPoolOopDesc* pool,
int
index))
klassOop k_oop = pool->klass_at(index, CHECK);
instanceKlassHandle klass (THREAD, k_oop);
// Make sure we are not instantiating an abstract klass
klass->check_valid_for_instantiation(
true
, CHECK);
// Make sure klass is initialized
klass->initialize(CHECK);
oop obj = klass->allocate_instance(CHECK);
thread->set_vm_result(obj);
IRT_END
|
该函数在进行了对象类的检查(确保不是抽象类)和对该类型进行初始化后,调用instanceKlassHandle的allocate_instance进行内存分配。
其中instanceKlassHandle类由DEF_KLASS_HANDLE宏进行声明,注意该类重载了成员访问运算符”->”,这里的一系列成员方法的访问实际上是instanceKlass对象的访问。
type* operator -> () const { return (type*)obj()->klass_part(); }
2.所以实际上是调用了instanceKlass的allocate_instance()成员函数:
allocate_instance()定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/oops/instanceKlass.cpp
(1).检查是否设置了Finalizer函数,获取对象所需空间的大小
|
1
2
3
|
instanceOop instanceKlass::allocate_instance(TRAPS) {
bool has_finalizer_flag = has_finalizer();
// Query before possible GC
int
size = size_helper();
// Query before forming handle.
|
(2).调用CollectedHeap的obj_allocate()创建一个instanceOop(堆上的对象实例),并根据情况注册Finalizer函数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
KlassHandle h_k(THREAD, as_klassOop());
instanceOop i;
i = (instanceOop)CollectedHeap::obj_allocate(h_k, size, CHECK_NULL);
if
(has_finalizer_flag && !RegisterFinalizersAtInit) {
i = register_finalizer(i, CHECK_NULL);
}
return
i;
|
3.CollectedHeap::ojb_allocate()定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/gc_interface/CollectedHeap.hpp中,它将转而调用内联函数obj_allocate()
4.obj_allocate()定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/gc_interface/CollectedHeap.inline.h中,若当正处于gc状态时,不允许进行内存分配申请,否则将调用common_mem_allocate_init()进行内存分配并返回获得内存的起始地址,随后将调用post_allocation_setup_obj()进行一些初始化工作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
oop CollectedHeap::obj_allocate(KlassHandle klass,
int
size, TRAPS) {
//...assert
HeapWord* obj = common_mem_allocate_init(size,
false
, CHECK_NULL);
post_allocation_setup_obj(klass, obj, size);
NOT_PRODUCT(Universe::heap()->check_for_bad_heap_word_value(obj, size));
return
(oop)obj;
}
|
5.common_mem_allocate_init()分为两部分,将分别调用common_mem_allocate_noinit()进行内存空间的分配和调用init_obj()进行对象空间的初始化
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
HeapWord* CollectedHeap::common_mem_allocate_init(size_t size, bool is_noref, TRAPS) {
HeapWord* obj = common_mem_allocate_noinit(size, is_noref, CHECK_NULL);
init_obj(obj, size);
return
obj;
}
|
6.common_mem_allocate_noinit()如下:
(1).若使用了本地线程分配缓冲TLAB,则会调用allocate_from_tlab()尝试从TLAB中分配内存
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
HeapWord* result = NULL;
if
(UseTLAB) {
result = CollectedHeap::allocate_from_tlab(THREAD, size);
if
(result != NULL) {
assert
(!HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION,
"Unexpected exception, will result in uninitialized storage"
);
return
result;
}
}
|
(2).否则会调用堆的mem_allocate()尝试分配
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
bool gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded =
false
;
result = Universe::heap()->mem_allocate(size,
is_noref,
false
,
&gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded);
|
(3).统计分配的字节数
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
if
(result != NULL) {
//...
THREAD->incr_allocated_bytes(size * HeapWordSize);
return
result;
}
|
(4).否则说明申请失败,若在申请过程中gc没有超时,则抛出OOM异常
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
if
(!gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded) {
// -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError and -XX:OnOutOfMemoryError support
report_java_out_of_memory(
"Java heap space"
);
if
(JvmtiExport::should_post_resource_exhausted()) {
JvmtiExport::post_resource_exhausted(
JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_OOM_ERROR | JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_JAVA_HEAP,
"Java heap space"
);
}
THROW_OOP_0(Universe::out_of_memory_error_java_heap());
|
7.对象内存分配后的初始化过程包括两部分,一个是init_obj()完成对对象内存空间的对齐和填充,一个是post_allocation_setup_obj()对堆上的oop对象进行初始化。
(1).init_obj():
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void
CollectedHeap::init_obj(HeapWord* obj, size_t size) {
assert
(obj != NULL,
"cannot initialize NULL object"
);
const
size_t hs = oopDesc::header_size();
assert
(size >= hs,
"unexpected object size"
);
((oop)obj)->set_klass_gap(
0
);
Copy::fill_to_aligned_words(obj + hs, size - hs);
}
|
hs就是对象头的大小,fill_to_aligned_words将对象空间除去对象头的部分做填0处理,该函数定义在/hotspot/src/share/vm/utilities/copy.h中,并转而调用pd_fill_to_aligned_words()。
pd_fill_to_aligned_words根据不同平台实现,以x86平台为例,该函数定义在/hotspot/src/cpu/x86/vm/copy_x86.h中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
static
void
pd_fill_to_words(HeapWord* tohw, size_t count, juint value) {
#ifdef AMD64
julong* to = (julong*) tohw;
julong v = ((julong) value <<
32
) | value;
while
(count-- >
0
) {
*to++ = v;
}
#
else
juint* to = (juint*)tohw;
count *= HeapWordSize / BytesPerInt;
while
(count-- >
0
) {
*to++ = value;
}
#endif
// AMD64
}
|
该函数的作用就是先将地址类型转换,然后把堆的字数转化为字节数,再对该段内存进行填值(value = 0)处理
(2).post_allocation_setup_obj()调用了post_allocation_setup_common()进行初始化工作,然后调用post_allocation_notify()通知JVMTI和dtrace
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
void
CollectedHeap::post_allocation_setup_obj(KlassHandle klass,
HeapWord* obj,
size_t size) {
post_allocation_setup_common(klass, obj, size);
assert
(Universe::is_bootstrapping() ||
!((oop)obj)->blueprint()->oop_is_array(),
"must not be an array"
);
// notify jvmti and dtrace
post_allocation_notify(klass, (oop)obj);
}
|
post_allocation_setup_common()如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void
CollectedHeap::post_allocation_setup_common(KlassHandle klass,
HeapWord* obj,
size_t size) {
post_allocation_setup_no_klass_install(klass, obj, size);
post_allocation_install_obj_klass(klass, oop(obj), (
int
) size);
}
|
post_allocation_setup_no_klass_install()根据是否使用偏向锁,设置对象头信息等,即初始化oop的_mark字段。post_allocation_install_obj_klass()设置对象实例的klassOop引用,即初始化oop的_metadata(_klass/_compressed_klass)字段 。
以上内容就是堆实现无关的慢速分配过程,其流程图如下:
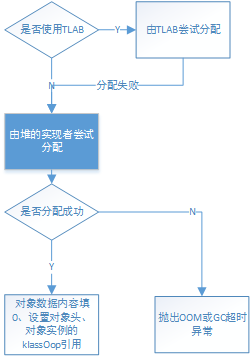
三、堆的分配实现
1.mem_allocate将由堆的实现类型定义,以GenCollectedHeap为例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
HeapWord* GenCollectedHeap::mem_allocate(size_t size,
bool is_large_noref,
bool is_tlab,
bool* gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded) {
return
collector_policy()->mem_allocate_work(size,
is_tlab,
gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded);
}
|
2.由之前分析,GenCollectedHeap根据用户配置有着不同的GC策略(默认的和配置UseSerialGC的MarkSweepPolicy、配置UseComcMarkSweepGC和UseAdaptiveSizePolicy的ASConcurrentMarkSweepPolicy、只配置UseComcMarkSweepGC的ConcurrentMarkSweepPolicy),但这里,对象内存空间的基本结构和分配的思想是一致的,所以统一由GenCollectorPolicy实现进行分代层级的对象分配操作,但具体的工作将交由各代的实现者来完成。
GenCollectedPolicy的mem_allocate_work()函数如下:
(1).gch指向GenCollectedHeap堆,内存分配请求将循环不断地进行尝试,直到分配成功或GC后分配失败
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
HeapWord* GenCollectorPolicy::mem_allocate_work(size_t size,
bool is_tlab,
bool* gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded) {
GenCollectedHeap *gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap();
//...
// Loop until the allocation is satisified,
// or unsatisfied after GC.
for
(
int
try_count =
1
;
/* return or throw */
; try_count +=
1
) {
|
对于占用空间比较大的对象,如果经常放在新生代,那么剩余的内存空间就会非常紧张,将可能会导致新生代内存垃圾回收的频繁触发。故若对象的大小超过一定值,那么就不应该分配在新生代。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
//...紧接上面部分
HandleMark hm;
// discard any handles allocated in each iteration
// First allocation attempt is lock-free.
Generation *gen0 = gch->get_gen(
0
);
if
(gen0->should_allocate(size, is_tlab)) {
result = gen0->par_allocate(size, is_tlab);
if
(result != NULL) {
assert
(gch->is_in_reserved(result),
"result not in heap"
);
return
result;
}
}
|
若对象应该在新生代上分配,就会调用新生代的par_allocate()进行分配,注意在新生代普遍是采用复制收集器的,而内存的分配对应采用了无锁式的指针碰撞技术。
(2).在新生代上尝试无锁式的分配失败,那么就获取堆的互斥锁,并尝试在各代空间内进行内存分配
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
unsigned
int
gc_count_before;
// read inside the Heap_lock locked region
{
MutexLocker ml(Heap_lock);
//...
bool first_only = ! should_try_older_generation_allocation(size);
result = gch->attempt_allocation(size, is_tlab, first_only);
if
(result != NULL) {
assert
(gch->is_in_reserved(result),
"result not in heap"
);
return
result;
}
|
其中should_try_older_generation_allocation()如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
bool GenCollectorPolicy::should_try_older_generation_allocation(
size_t word_size)
const
{
GenCollectedHeap* gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap();
size_t gen0_capacity = gch->get_gen(
0
)->capacity_before_gc();
return
(word_size > heap_word_size(gen0_capacity))
|| GC_locker::is_active_and_needs_gc()
|| gch->incremental_collection_failed();
}
|
当进行gc前,新生代的空闲空间大小不足以分配对象,或者有线程触发了gc,或前一次的FullGC是由MinorGC触发的情况,都应该不再尝试再更高的内存代上进行分配,以保证新分配的对象尽可能在新生代空间上。
attempt_allocation()实现如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
HeapWord* GenCollectedHeap::attempt_allocation(size_t size,
bool is_tlab,
bool first_only) {
HeapWord* res;
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < _n_gens; i++) {
if
(_gens[i]->should_allocate(size, is_tlab)) {
res = _gens[i]->allocate(size, is_tlab);
if
(res != NULL)
return
res;
else
if
(first_only)
break
;
}
}
// Otherwise...
return
NULL;
}
|
即由低内存代向高内存代尝试分配内存
(3).从各个代空间都找不到可用的空闲内存(或不应该在更高的内存代上分配时),如果已经有线程触发了gc,那么当各代空间还有virtual space可扩展空间可用时,将会尝试扩展代空间并再次尝试进行内存分配,有点在gc前想尽一切办法获得内存的意思。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
if
(GC_locker::is_active_and_needs_gc()) {
if
(is_tlab) {
return
NULL;
// Caller will retry allocating individual object
}
if
(!gch->is_maximal_no_gc()) {
// Try and expand heap to satisfy request
result = expand_heap_and_allocate(size, is_tlab);
// result could be null if we are out of space
if
(result != NULL) {
return
result;
}
}
|
(4).否则各代已经没有可用的可扩展空间时,当当前线程没有位于jni的临界区时,将释放堆的互斥锁,以使得请求gc的线程可以进行gc操作,等待所有本地线程退出临界区和gc完成后,将继续循环尝试进行对象的内存分配
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
JavaThread* jthr = JavaThread::current();
if
(!jthr->in_critical()) {
MutexUnlocker mul(Heap_lock);
// Wait for JNI critical section to be exited
GC_locker::stall_until_clear();
continue
;
}
|
(5).若各代无法分配对象的内存,并且没有gc被触发,那么当前请求内存分配的线程将发起一次gc,这里将提交给VM一个GenCollectForAllocation操作以触发gc,当操作执行成功并返回时,若gc锁已被获得,那么说明已经由其他线程触发了gc,将继续循环以等待gc完成
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
VM_GenCollectForAllocation op(size,
is_tlab,
gc_count_before);
VMThread::execute(&op);
if
(op.prologue_succeeded()) {
result = op.result();
if
(op.gc_locked()) {
assert
(result == NULL,
"must be NULL if gc_locked() is true"
);
continue
;
// retry and/or stall as necessary
}
|
否则将等待gc完成,若gc超时则会将gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded设置为true返回给调用者,并重置超时状态,并对分配的对象进行填充处理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
const
bool limit_exceeded = size_policy()->gc_overhead_limit_exceeded();
const
bool softrefs_clear = all_soft_refs_clear();
assert
(!limit_exceeded || softrefs_clear,
"Should have been cleared"
);
if
(limit_exceeded && softrefs_clear) {
*gc_overhead_limit_was_exceeded =
true
;
size_policy()->set_gc_overhead_limit_exceeded(
false
);
if
(op.result() != NULL) {
CollectedHeap::fill_with_object(op.result(), size);
}
return
NULL;
}
|
以上内容就是堆的实现相关、但代/GC实现无关的分配过程,其流程图归纳如下:
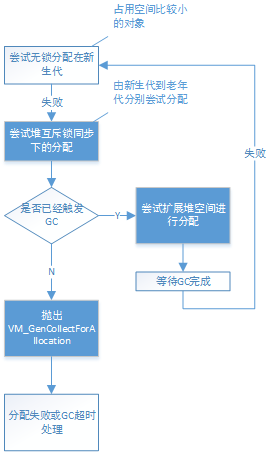





















 1969
1969











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








