常见的内存框架:
Guava Cache、EHcache、Caffeine
什么时候用:
1.愿意消耗一些内存空间来提升速度
2.预料到某些键会被多次查询
3.缓存中存放的数据总量不会超出内存容量
性能:
Caffeine不论读还是写的效率都远高于其他缓存。

详细请看官方官方 https://github.com/ben-manes/caffeine/wiki/Benchmarks
Caffeine简介
Caffeine基于java8的高性能,接近最优的缓存库。Caffeine提供的内存缓存使用参考Google guava的API。Caffeine是基于Google guava和 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap的设计经验上改进的成果。
Caffeine可以通过建造者模式灵活的组合以下特性:
1.通过异步自动加载实体到缓存中
2.基于大小的回收策略
3.基于时间的回收策略
4.自动刷新
5.key自动封装虚引用
6.value自动封装弱引用或软引用
7.实体过期或被删除的通知
8.写入外部资源
9.统计累计访问缓存
依赖
caffeine 依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.ben-manes.caffeine/caffeine -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
新建对象
// 1、最简单
Cache<String, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.build();
// 2、真实使用过程中我们需要自己配置参数。这里只列举部分,具体请看下面列表
Cache<String, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(2)//初始大小
.maximumSize(2)//最大数量
.expireAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//过期时间
.build();
//3.异步加载
AsyncCache<Object, Object> asyncCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.buildAsync();
参数含义:
initialCapacity: 初始的缓存空间大小
maximumSize: 缓存的最大数量
maximumWeight: 缓存的最大权重
expireAfterAccess: 最后一次读或写操作后经过指定时间过期
expireAfterWrite: 最后一次写操作后经过指定时间过期
refreshAfterWrite: 创建缓存或者最近一次更新缓存后经过指定时间间隔,刷新缓存
weakKeys: 打开key的弱引用
weakValues:打开value的弱引用
softValues:打开value的软引用
recordStats:开发统计功能
注意:
expireAfterWrite和expireAfterAccess同时存在时,以expireAfterWrite为准。
maximumSize和maximumWeight不可以同时使用
加载策略
Caffeine提供了3种加载策略:手动加载,同步加载,异步加载
手动加载:
Cache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.maximumSize(10_000)
.build();
// 检索一个entry,如果没有则为null
Graph graph = cache.getIfPresent(key);
// 检索一个entry,如果entry为null,则通过key创建一个entry并加入缓存
graph = cache.get(key, k -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
// 插入或更新一个实体
cache.put(key, graph);
// 移除一个实体
cache.invalidate(key);
同步加载
构造Cache时候,build方法传入一个CacheLoader实现类。实现load方法,通过key加载value。
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
//如果缓存种没有对应的value,通过createExpensiveGraph方法加载
Graph graph = cache.get(key);
Map<Key, Graph> graphs = cache.getAll(keys);
异步加载
AsyncLoadingCache<Key, Graph> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.buildAsync((key, executor) -> createExpensiveGraphAsync(key, executor));
CompletableFuture<Graph> graph = cache.get(key);
CompletableFuture<Map<Key, Graph>> graphs = cache.getAll(keys);
AsyncLoadingCache 是 LoadingCache 的变体, 可以异步计算实体在一个线程池(Executor)上并且返回 CompletableFuture.
过期策略
Caffeine提供三类驱逐策略:
1.基于大小回收(size-based)
// 1.基于实体数量淘汰实体
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
// 2.通过权重来计算,每个实体都有不同的权重,总权重到达最高时淘汰实体。
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(10_000)
.weigher((Key key, Graph graph) -> graph.vertices().size())
.build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
//测试代码
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
cache.put("key2", "value2");
cache.put("key3", "value3");
cache.put("key4", "value4");
cache.put("key5", "value5");
cache.cleanUp();
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key4"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key5"));
到达最大大小时淘汰最近最少使用的实体
2.基于时间回收(time-based)
- expireAfterAccess(long, TimeUnit):在最后一次访问或者写入后开始计时,在指定的时间后过期。假如一直有请求访问该key,那么这个缓存将一直不会过期。
- expireAfterWrite(long, TimeUnit): 在最后一次写入缓存后开始计时,在指定的时间后过期。
- expireAfter(Expiry): 自定义策略,过期时间由Expiry实现独自计算。
缓存的删除策略使用的是惰性删除和定时删除。这两个删除策略的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
expireAfterWrite
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
cache.put("key2", "value2");
cache.put("key3", "value3");
cache.put("key4", "value4");
cache.put("key5", "value5");
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
Thread.sleep(3*1000);
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key3"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key4"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key5"));
expireAfterAccess : Access就是读和写
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterAccess(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
Thread.sleep(1*1000);
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
Thread.sleep(1*1000);
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
Thread.sleep(1*1000);
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
Thread.sleep(3*1000);
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
自定义策略Expiry,可以自定义在实体被读,被更新,被创建后的时间过期
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfter(new Expiry<Key, Graph>() {
public long expireAfterCreate(Key key, Graph graph, long currentTime) {
// Use wall clock time, rather than nanotime, if from an external resource
long seconds = graph.creationDate().plusHours(5)
.minus(System.currentTimeMillis(), MILLIS)
.toEpochSecond();
return TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(seconds);
}
public long expireAfterUpdate(Key key, Graph graph,
long currentTime, long currentDuration) {
return currentDuration;
}
public long expireAfterRead(Key key, Graph graph,
long currentTime, long currentDuration) {
return currentDuration;
}
})
.build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
自动刷新
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.refreshAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(key -> createExpensiveGraph(key));
expireAfter 和 refreshAfter 之间的区别
- expireAfter 条件触发后,新的值更新完成前,所有请求都会被阻塞,更新完成后其他请求才能访问这个值。这样能确保获取到的都是最新的值,但是有性能损失。
- refreshAfter 条件触发后,新的值更新完成前也可以访问,不会被阻塞,只是获取的是旧的数据。更新结束后,获取的才是新的数据。有可能获取到脏数据。
3.基于引用回收(reference-based)
- Caffeine.weakKeys() 使用弱引用存储key。如果没有其他地方对该key有强引用,那么该缓存就会被垃圾回收器回收。
- Caffeine.weakValues()使用弱引用存储value。如果没有其他地方对该value有强引用,那么该缓存就会被垃圾回收器回收。
- Caffeine.softValues() 使用软引用存储value。
Cache<String, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.weakValues()
.build();
Object value1 = new Object();
Object value2 = new Object();
cache.put("key1", value1);
cache.put("key2", value2);
value2 = new Object(); // 原对象不再有强引用
System.gc();
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key1"));
System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("key2"));
结果
java.lang.Object@7a4f0f29
null
解释:当给value2引用赋值一个新的对象之后,就不再有任何一个强引用指向原对象。System.gc()触发垃圾回收后,原对象就被清除了。
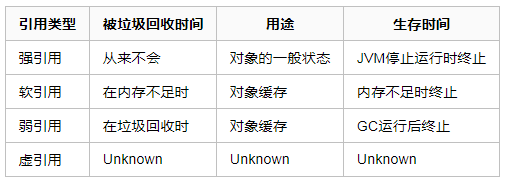
java种有四种引用:强引用,软引用,弱引用和虚引用
caffeine可以将值封装成弱引用或软引用。
软引用:如果一个对象只具有软引用,则内存空间足够,垃圾回收器就不会回收它;如果内存空间不足了,就会回收这些对象的内存。
弱引用:弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存
Java4种引用的级别由高到低依次为:强引用 > 软引用 > 弱引用 > 虚引用
显式删除缓存
除了通过上面的缓存淘汰策略删除缓存,我们还可以手动的删除
// 1、指定key删除
cache.invalidate("key1");
// 2、批量指定key删除
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("key1");
list.add("key2");
cache.invalidateAll(list);//批量清除list中全部key对应的记录
// 3、删除全部
cache.invalidateAll();
淘汰、移除监听器
可以为缓存对象添加一个移除监听器,这样当有记录被删除时可以感知到这个事件。
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterAccess(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Object, Object>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(@Nullable Object key, @Nullable Object value, @NonNull RemovalCause cause) {
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value + ",删除原因:" + cause);
}
})
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
cache.put("key2", "value2");
cache.invalidate("key1");
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);
cache.cleanUp();
统计
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(3)
.recordStats()
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
cache.put("key2", "value2");
cache.put("key3", "value3");
cache.put("key4", "value4");
cache.getIfPresent("key1");
cache.getIfPresent("key2");
cache.getIfPresent("key3");
cache.getIfPresent("key4");
cache.getIfPresent("key5");
cache.getIfPresent("key6");
System.out.println(cache.stats());
CacheStats{hitCount=4, missCount=2, loadSuccessCount=0, loadFailureCount=0, totalLoadTime=0, evictionCount=0, evictionWeight=0}
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/CrankZ/p/10889859.html
https://wujiazhen2.github.io/2018/09/30/Caffeine/






















 1471
1471











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








