接口
定义:由关键字interface引导,分为接口的声明和接口体。 在接口中只进行方法的声明,不能进行方法的实现。
一个接口定义一个协定。接口本身不提供它所定义的成员的实现,只指定实现该接口的类必须提供的成员,继承接口的任何非抽象类型都必须实现接口的所有成员。
虽然java类不支持基类的多重继承,只是单继承,但类和结构可从多个接口继承,接口自身可从多个接口继承。
- 接口的声明:
interface A{
public static final int age = 10;//属性
public abstract void fun();//方法 抽象方法不能有任何实现
}
interface B{
int AGE =100;
void fun1();
}
Tips
- 接口不能实例化。
- 接口中声明的所有成员方法隐式地为public和abstract。接口可以包含抽象方法和静态常量字段。
- 接口的成员变量默认静态常量字段(public static final)。
- 接口的成员方法默认为公共抽象方法(public abstract)。
- 接口的实现:
使用关键字implements 实现接口,必须实现方法。
一个类可以实现多个接口,用逗号分隔接口列表。
interface A{
public static final int age = 10;//属性
public abstract void fun();//方法 抽象方法不能有任何实现
}
interface B{
int AGE =100;
void fun1();
}
class C implements A,B{ //implements 实现接口 A,B 可实现多个接口,用逗号隔开
public void fun(){
System.out.println("A.fun()");
}
public void fun1(){
System.out.println("B.fun1()");
}
}
public class InterFace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C c = new C();
c.fun();
c.fun1();
}
}
//输出:
A.fun()
B.fun1()
- 接口的继承:
使用关键字extends 实现继承的接口。
interface A{
public static final int age = 10;//属性
public abstract void fun();//方法
}
interface B{
int AGE =100;
void fun1();
}
interface D extends A,B{ //接口的继承:接口继承接口 内部可不实现方法
void fun3();
}
abstract class Person {
}
class C extends Person implements D { //必须实现方法
public void fun() {
System.out.println("A.FUN");
}
public void fun2() {
System.out.println("B.FUN");
}
@Override
public void fun3() {
}
}
- 练习问题:报警门。
思路:单独将报警设计为一个接口,包含alarm()行为,Door设计为单独的一个抽象类,包含open和close两种行为。再设计一个报警门继承Door类和实现Alarm接口。
实现:
abstract class Door{
public abstract void open();
public abstract void close();
}
interface Alarm{
public abstract void alarm();
}
class AlarmDoor extends Door implements Alarm{
public void alarm(){
System.out.println("Door.alarm()");
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
@Override
public void open() {
}
}
Tips
@注意:(接口与抽象类的区别)
- 接口内的方法,必须不能被实现,而抽象类可以有部分非抽象方法。
- 抽象类只能继承一次,但是接口可以被实现或者继承多个。
- 一个抽象类可以继承一个抽象父类,但是接口可以使用关键字extends 继承多个接口。
- 抽象类中的成员变量可以是各种类型的,但是抽象类当中的方法不能是private,而接口中的成员变量只能是public static final类型的。
- 抽象类是对类整体的抽象 而接口是对行为进行抽象 。
- 在接口中的成员变量和成员方法默认为public static final和public abstract。
四个常用接口
1.Cloneable
实现Clonable接口,并且需要重写Object的clone方法。
Tips
- 空接口,标记接口。请问这个空接口的设计有什么作用?
public interface Cloneable{ }
它是标记这个类可以进行clone,如果不实现这个接口JVM不能够识别。
浅拷贝:
class Money{
double money = 10.0 ;
}
class Person2 implements Cloneable{
private String name;
Money m;
public Person2(String name){
this.name = name;
this.m = new Money();
}
//注意: 重写基类Object的克隆方法 idea快捷键 Ctrl + o
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class FourInterFace {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person2 person2 = new Person2("caocao");
Person2 person21 = (Person2)person2.clone(); //强制转换 基类引用派生类对象 浅拷贝
System.out.println(person2.m.money);
System.out.println(person21.m.money);
person2.m.money = 1000.0;
System.out.println(person2.m.money);
System.out.println(person21.m.money);
}
}
//输出:
10.0
10.0
1000.0
1000.0
深拷贝:
class Money implements Cloneable{
double money = 10.0;
@Override //重写基类Object的克隆方法
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class Person2 implements Cloneable{
private String name;
Money m;
public Person2(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.m = new Money();
}
//重写Object的克隆方法 注意点
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person2 person2 = (Person2)super.clone();
person2.m = (Money)this.m.clone();
return person2;
}
}
public class TestInterfaceAble {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person2 person2 = new Person2("caocao");
Person2 person21 = (Person2)person2.clone();
System.out.println(person2.m.money);
System.out.println(person21.m.money);
person2.m.money = 1000.0;
System.out.println(person2.m.money);
System.out.println(person21.m.money);
}
}
//输出:
10.0
10.0
1000.0
10.0
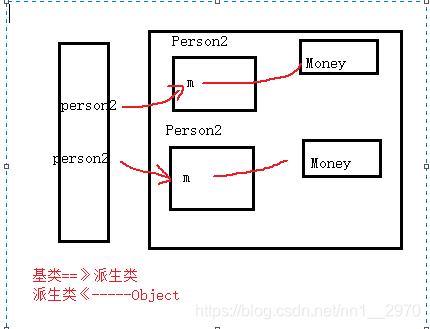
部分内存分析:
Person2 person2 = (Person2)super.clone();
person2.m = (Money)this.m.clone();
2. Comparable:
源代码:
public interface Comparable<T> { //泛型<T>数组
public int compareTo(T o); //方法
}
举例:
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ //接口
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public Student (String name,int age,double score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) { //compareTo方法
return age-o.age;
}
}
public class FourInterFace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = new Student("Lili",10,100);
students[1] = new Student("Amy",3,85);
students[2] = new Student("Tom",18,60);
Arrays.sort(students);//使用Arrays。sort()方法排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));//以字符串形式输出
}
}
[Student{name='Amy', age=3, score=85.0}, Student{name='Lili', age=10, score=100.0}, Student{name='Tom', age=18, score=60.0}]
- Comparator:
源代码:
int compare(T o1, T o2);
public interface Comparator<T> {
int compare(T o1, T o2);
}
举例:
class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public Student (String name,int age,double score){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
public class FourInterFace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = new Student("Lili",10,100);
students[1] = new Student("Amy",3,85);
students[2] = new Student("Tom",18,60);
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {//类内部使用接口
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {//compare方法
return (int)(o1.getScore()-o2.getScore());
//return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
//return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
}
}
[Student{name='Tom', age=18, score=60.0}, Student{name='Amy', age=3, score=85.0}, Student{name='Lili', age=10, score=100.0}]
Tips
面试问题:Comparable 和Comparator的区别??
(1)Comparable :类内部; Comparator : 类外部;
(2)源码 ===> * Interable/Iterator
关于Interable/Iterable:
- 迭代器生成接口Interable,用于生成一个具体迭代器
public interface Iterable<T>{
Interator<T> iterator();
}
- 迭代器接口Iterator,用于遍历集合和移除元素,只能向前移动
public interface Iterator<T>{
boolean hasNext(); //判断下一个元素是否存在
T next(); //返回下一个元素
void remove(); //移除元素
}
Over…关于Cloneable接口的使用要注意,对于Comparable和Compartor 接口注意使用的不同点。加油yayaya

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








