C语言函数指针与调用
平时我们使用函数传递的参数一般为数据变量,那么是否可以传递函数呢?
答案是不但可以,而且习惯以后,会用上瘾的。通过传递不同的函数指针,我们可以实现在函数中调用不同的子函数。
下面就举个栗子,说一下函数指针的用法。
有四个函数:
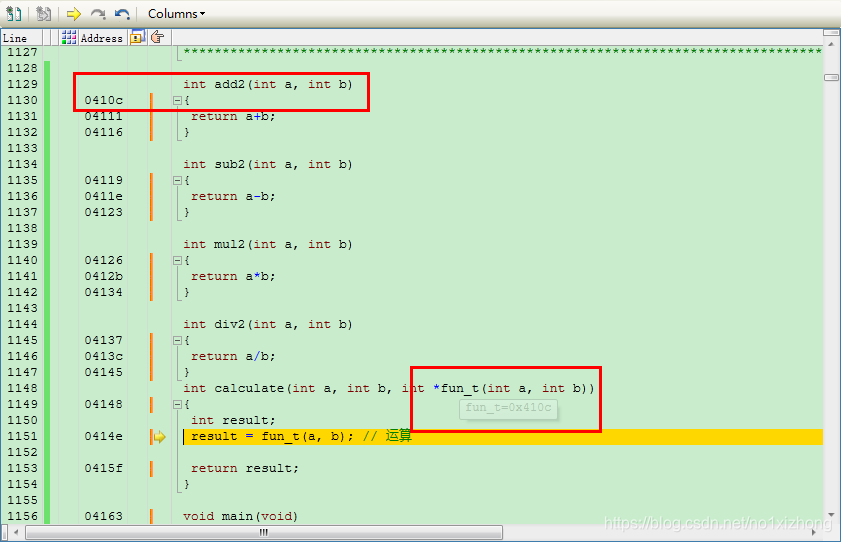
int add2(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int sub2(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int mul2(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;
}
int div2(int a, int b)
{
return a/b;
}
下面将演示如何天下一统,通过一个函数实现对两个输入形参的不同运算!
定义一个函数:
int calculate(int a, int b, int (*fun_t)(int a, int b))
{
int result;
result = fun_t(a, b); // 运算
result++;
return result;
}
形参 int (*fun_t)(int a, int b),int表示返回值类型,也可写成
int calculate(int a, int b, int *fun_t(int a, int b))。
在main中使用此函数:
void main(void)
{
int result1,result2;
int a = 192, b = 48;
/* 两个数相加的操作 */
result1 = calculate(a, b, add2);
result2 = calculate(a, b, mul2);
}
仿真跟踪,进入第一次调用,形参fun_t值为0x410C,即add2函数地址。
感觉形参int *fun_t(int a, int b)太繁琐?
我们可以这样定义函数:
int calculate(int a, int b, int *fun_t(int , int ))
{
int result;
result = fun_t(a, b); // 运算
return result;
}
还嫌麻烦?有办法,别忘了typedef!
typedef int *fun_t(int, int);
int calculate(int a, int b, fun_t operation)
{
int result;
result = operation(a, b); // 运算
return result;
}
编译仿真,运行结果相同。






















 7593
7593











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








