倒排索引源于实际应用中需要根据属性的值来查找记录。这种索引表中的每一项都包括一个属性值和具有该属性值的各记录的地址。由于不是由记录来确定属性值,而是由属性值来确定记录的位置,因而称为倒排索引(inverted index)。带有倒排索引的文件我们称为倒排索引文件,简称倒排文件(inverted file)。
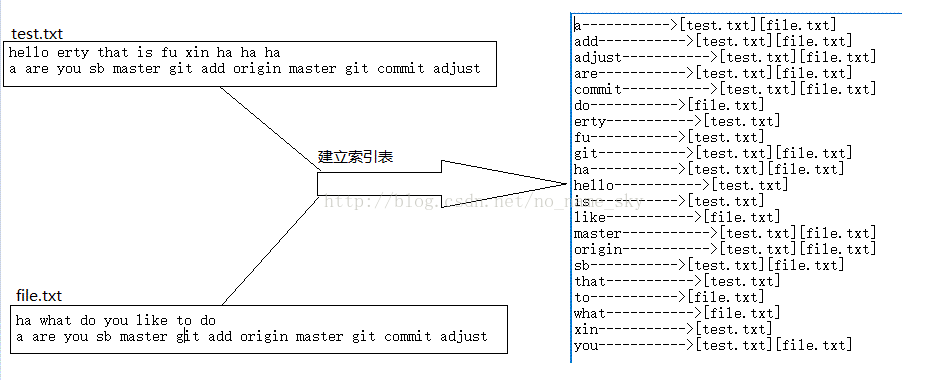
现在这里有三个英文文件:
file1(sort,hello....)
file2(hello,what....)
file3(peter,son....)
索引表用map和vector实现:map<string,vector<string> > //第一个参数是单词,第二个是包含该单词的所有文件名;
建立索引之后为:
sort(file1);
hello(flie1,file2);
what(file2);
peter(file3);
son(file3);
...
根据单词建立与文件之间的索引关系。
代码:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
/*倒排索引源于需要根据属性的值来查找记录,这种索引表中的每一项都包括一个属性值和具有该属性值的各记录地址。
由于不是有记录来确定属性值,二是有属性值来确定记录的位置,因而称为倒排索引。*/
#define MAXLINE 1024
class InvertedIndex
{
public:
bool StatWord(const char *fileName)
{
FILE *file = fopen(fileName,"r");
if (file == NULL)
{
cout << "打开文件" << (*fileName) << "失败" << endl;
}
char strLine[MAXLINE];
while (fgets(strLine, MAXLINE, file) != NULL) //读到错误,文件结尾返回NULL;
{
//读到一行数据或MAXLINE个数据,读完后会在strLine的最后插入字符串结束符'\0'
//若是一行结束会有"\n\0",此时就要弃掉\n
int len = strlen(strLine);
if (strLine[len - 1] == '\n') //去掉\n
{
strLine[len - 1] = '\0';
}
//这一行单词的信息写入;先写入一个文件的,在遍历其他文件进行写入map
WordByLine(strLine,fileName);
}
fclose(file);
return true;
}
bool WordByLine(char strLine[],const char *fileName)
{
//把这一行的单词分离出来,并插入map中;
if (strlen(strLine) == 0)
{
return false;
}
char *delin = " ";
char *word = strtok(strLine, delin); //首次调用时,s指向要分解的字符串,之后再次调用要把s设成NULL。
while (word != NULL)
{
InsertWord(word,fileName);
word = strtok(NULL,delin);
}
return true;
}
void InsertWord(char *word,const char *fileName) //将信息插入索引表;
{
vector<string> str;
str.push_back(fileName);
vector<string>::iterator it = _index[word].begin();
while (it != _index[word].end())
{
if ((*it) == fileName)
{
break;
}
it++;
}
//判断该文件名fileName是否已存在,看其是否需要插入;
if (it == _index[word].end() || _index[word].size() == 0)
{
_index[word].push_back(fileName);
}
else
{
return;
}
}
void WriteToFile(const char *fileName) //索引表写入指定文件
{
FILE *file = fopen(fileName,"w");
if (file == NULL)
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return;
}
map<string, vector<string>>::iterator it = _index.begin();
while (it != _index.end())
{
const char *word = (*it).first.c_str();
fputs(word,file);
fputs("----------->", file);
vector<string>::iterator itStr = _index[word].begin();
while (itStr != _index[word].end())
{
fputc('[', file);
fputs((*itStr).c_str(),file);
itStr++;
fputc(']', file);
}
fputc('\n', file);
it++;
}
fclose(file);
}
protected:
map<string, vector<string> > _index; //key为单词,value为存储有此单词的文件名;
};
void Test()
{
InvertedIndex in;
in.StatWord("test.txt");
in.StatWord("file.txt");
in.WriteToFile("result.txt");
}运行效果:
给上千个文件,每个文件大小为1K—100M。给n个词,设计算法对每个词找到所有包含它的文件,你只有100K内存;
解法一:对于每个词都去遍历上千个文件,只要文件中存在这个词直接保存该文件名;这个方法每判断一个词都要重复遍历这上千个文件,100M让计算机去遍历也是需要很长时间的,更何况还是成千的文件,这个解法太费时间;
解法二:直接对这成千个文件中的所有单词建立倒排索引,属性值为单词,包含该属性值的文件名为包含该单词的文件名;建好之后,根据这n个单词去遍历索引表,即可完成本题;
代码只要稍稍修改上述代码即可;





















 618
618











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








