maven打包时,默认不会将当前pom文件所在module下的file文件打包进target,但似乎有时业务是需要存放一些资源文件
你可能会出现:
资源找不到,mybatis mapper报错:Invalid bound statement (not found)等错误
所以现在讲一下关于<resources>配置
directory:配置生效的文件夹目录
includes:指定文件夹目录下的指定资源文件都会被打包 可用通配符
excludes:指定文件夹目录下的指定资源文件都不会被打包 可用通配符
filtering:是否对指定文件夹目录下的指定资源文件进行占位符填充处理
** 表示多级目录匹配。* 表示一级目录匹配
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<!-- 把src/main/java下xml结尾的文件打包到target-->
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<excludes>
<!-- 把src/main/java下A.xml文件过滤掉-->
<exclude>**/A.xml</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.png</include>
<include>**/*.jpg</include>
<include>**/*.pdf</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.yml</include>
</includes>
<!--用pom文件中定义的属性替换指定目录下properties文件里的占位符(${XXX} / @XXX@)-->
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
不配置resources的默认情况:
src/main/resources:Maven 会将文件夹中的内容全部复制打包到 target 中
src/main/java: Maven 只会将文件夹中的 Java 文件编译,然后将编译后的 .class 文件打包到 target 中
filtering
false:
不开启配置文件变量替换 true:开启配置文件变量替换
在配置文件中使用${xx.xx}@xx.xx@占位符进行替换
默认是false
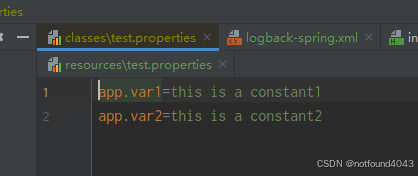
在 src/main/resources 下创建一个配置文件 test.properties
app.var1=${app.var1}
app.var2=@app.var2@
我们在 pom.xml 文件中设置
<properties>
<app.var1>this is a constant1</app.var1>
<app.var2>this is a constant2</app.var2>
</properties>
设置filtering = true
进行mvn编译,在target中可以看到变量被替换了:





















 2086
2086

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








