转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/22493621
题目:
Imagine a (literal) stack of plates. If the stack gets too high, it might topple. Therefore, in real life, we would likely start a new stack when the previous stack exceeds some threshold. Implement a data structure SetOfStacks that mimics this. SetOfStacks should be composed of several stacks, and should create a new stack once the previous one exceeds capacity. SetOfStacks.push() and SetOfStacks.pop() should behave identically to a single stack (that is, pop() should return the same values as it would if there were just a single stack).
FOLLOW UP
Implement a function popAt(int index) which performs a pop operation on a specific sub-stack.
翻译:
想象一个由盘子叠起的栈,当栈叠得太高时,就可能倒下。因此,在现实生活中,当一个栈超过了一定的高度时,我们就会另起一个栈。实现数据结构SetOfStacks 来模拟这种情况。SetOfStacks由几个栈组成,当前一栈超出容量时,需要创建一个新的栈 来存放数据。SetOfStacks.push()和SetOfStacks.pop()的行为应当和只有一个栈时 表现的一样。
进一步地,
实现函数popAt(int index)在指定的子栈上进行pop操作。
思路:
其实跟上一题有一定的相似性,只是上一题使用一个数组来实现三个栈,我们这里要用多个数组实现多个栈,而后将它们联系在一起,这样我们就需要一个变量cur指向进行出入栈操作的当前数组,而对于栈顶指针top,如果当前数组已满,执行push操作,这时候cur++,而top重新置为-1(根据程序设置,有些程序设置为0),而如果当前数组为空,执行pop操作,这时候cur--,而top重新置为MAX-1(数组的顶部)。这样我们可以用个哈希数组来保存指向每个数组的指针。同样,如果要进行popAt操作,直接使用哈希数组的下标索引即可。
实现代码:
这里与上一题策略不同,我们直接将cur和top两个变量设为了全局变量,上一题用的引用传递参数
#define M 5
#define MAX 3
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct HashNode
{
int *Arr;
}HashNode,*pHashTable;
int top = -1; //全局变量,记录栈顶
int cur = 0; //全局变量,记录当前所用的数组的序号
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
pHashTable create_HashTable()
{
//使用calloc直接将内部的每个Arr初始化为NULL
pHashTable hashtable = (pHashTable)calloc(M,sizeof(HashNode));
if(!hashtable)
{
printf("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
return hashtable;
}
void push(pHashTable hashtable,ElemType data)
{
if(cur==0 && top==-1)
{
//内部元素全部初始化为0
hashtable[cur].Arr = (int *)calloc(MAX,sizeof(int));
if(!hashtable[cur].Arr)
{
printf("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
}
if(cur>M-1)
return;
if(top<MAX-1)
hashtable[cur].Arr[++top] = data;
else if(top>MAX-1)
return;
else
{
//如果当前数组已经满了,则转到下一个数组进行push操作
cur++;
top = -1;
hashtable[cur].Arr = (int *)calloc(MAX,sizeof(int));
if(!hashtable[cur].Arr)
{
printf("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
push(hashtable,data);
}
}
void pop(pHashTable hashtable)
{
if(cur>M-1 || cur<0)
return;
if(top>-1)
hashtable[cur].Arr[top--] = 0; //将pop的元素置为0,即还原到默认初值值
else if(top<-1)
return;
else
{
//如果当前数组为空了,则释放掉给数组空间,转到上一个数组进行pop操作
free(hashtable[cur].Arr);
hashtable[cur].Arr = NULL;
cur--;
top = MAX-1;
pop(hashtable);
}
}
int main()
{
pHashTable hashtable = create_HashTable();
push(hashtable,1);
push(hashtable,2);
push(hashtable,3);
push(hashtable,4);
push(hashtable,5);
push(hashtable,6);
push(hashtable,7);
int i,j;
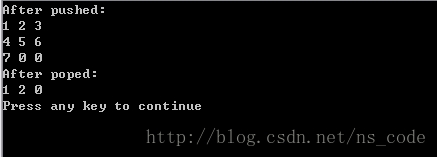
printf("After pushed:\n");
for(i=0;i<M;i++)
{
if(hashtable[i].Arr)
{
for(j=0;j<MAX;j++)
printf("%d ",hashtable[i].Arr[j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
pop(hashtable);
pop(hashtable);
pop(hashtable);
pop(hashtable);
pop(hashtable);
printf("After poped:\n");
for(i=0;i<M;i++)
{
if(hashtable[i].Arr)
{
for(j=0;j<MAX;j++)
printf("%d ",hashtable[i].Arr[j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
























 314
314

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








