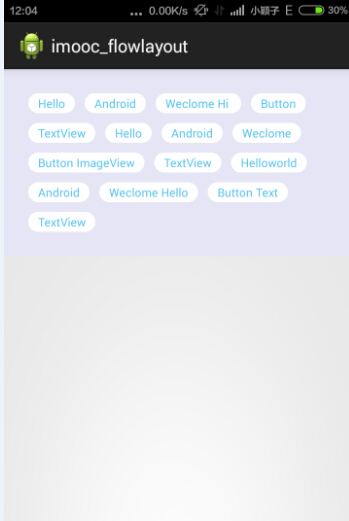
首先声明一下,此博文实际上是一个笔记形式的文章,思路和代码都是由慕课网提供。敝人只是更加详细化地加以说明。首先上一张图
如图所示的布局就是流式布局。即它会自动识别每一行是否能完全填充下一个View,如果能容下,就放在上一个View的后面,如果容不下,就另起一行。这种布局让人感觉到很清新随和。在android中可以把诸如标签,选项,之类的空间做成这个样子,肯定会为你的APP增色不少。下面我们来看一下这是如何实现的。
正如标题所说,需要自定义ViewGroup来实现此效果。
自定义ViewGroup的两个步骤:
1.重载onMeasure()方法:测量子控件和自己的大小。
2.重载onLayout()方法:确定子View的位置。
下面先重载onMeasure()方法,测量子控件和自己的大小。
首先定义两个变量:
/**
* 存储所有的View
*/
private List<List<View>> mAllViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>();
/**
* 每一行的高度
*/
private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<Integer>();重载onLayout()方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// wrap_content
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// 记录每一行的宽度与高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 得到内部元素的个数
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量子View的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
// 子View占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
// 子View占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin;
//几率每一行的View
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
// 换行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft()
- getPaddingRight()) {
// 对比得到最大的宽度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
// 重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
// 记录行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
mLineHeight.add(childHeight);
} else
// 未换行
{
// 叠加行宽
lineWidth += childWidth;
// 得到当前行最大的高度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 最后一个控件
if (i == cCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, width);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(
//
modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width
+ getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(),
modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height
+ getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom()//
);
}
再来重载onLayout()方法,确定子View的位置。
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
// 当前ViewGroup的宽度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果需要换行
if (childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width
- getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
// 记录LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 记录当前行的Views
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 重置我们的行宽和行高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
// 重置我们的View集合
lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
}
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}// for end
// 处理最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 设置子View的位置
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 行数
int lineNum = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNum; i++) {
// 当前行的所有的View
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
// 判断child的状态
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 为子View进行布局
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
}
left = getPaddingLeft();
top += lineHeight;
}
还有一个方法需要重载一下;
/**
* 与当前ViewGroup对应的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}(这里有一点需要说一下,调用一个View的getLayoutParams()得到的是其父控件的LayoutParams类型,调用一个View的setLayoutParams()方法时也是得设置成父控件的LayoutParams类型。比如说在一个AbsListView中有一个Button,那么Button的LayoutParams都是android.view.abslistview.layoutparams,而不是其他的。)
























 313
313

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








