Service部分面试精华汇总
1.Service是在主线程执行吗?service里能做耗时操作吗?
- 1.Service是在主线程UI运行
- 2.不能做耗时操作(网络请求,拷贝数据库,大文件).
- 3.通过配置清单文件让service**改变成其他进程,是进程**
<service
android:name="com.baidu.location.f"
android:enabled="true"
android:process=":remote" >
</service>注意:里面的:remote有冒号
是在一个新的线程里
- 1.android:process=”:remote“,代表在应用程序里,当需要该service时,会自动创建新的进程。
- 2.而如果是android:process=”remote”,没有“:”分号的,则创建全局进程,不同的应用程序共享该进程。
2.Activity怎么和Service”绑定”?怎么在Activiy中启动自己对应的Service?
1.通过bindService(Intent service,ServiceConnection conn,int flags)绑定
- 都会提示创建 conn
- flags: 提示,一般选:BIND_AUTO_CREATE
- 2.绑定后Servic会将代理对象通过回调形式返回给conn,我们就能拿到了Service提供的”服务代理对象.”
3.启动Service:通过startService和BindService.
- 1.如果想获得服务对象:通过绑定bindService
- 音乐播放器
- 第三方支付
- 2.如果仅仅是想启动一个后台任务可以startService()方法即可
- 1.如果想获得服务对象:通过绑定bindService
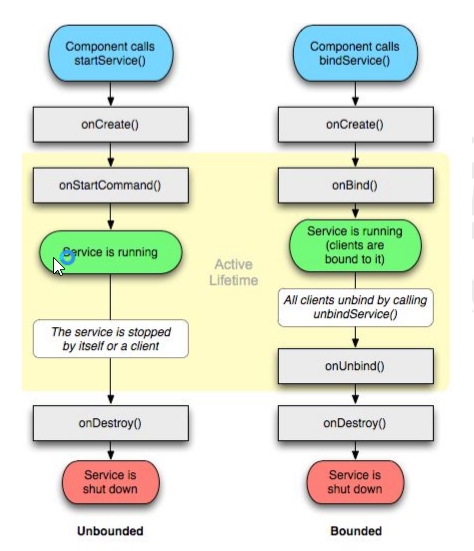
3.请描述一下Service的生命周期
非绑定模式
- 1.定义MyService继承Service
- 2.重写onCreate,onStartCommand,onStart,onDestroy方法,并打印
- 3.开始按钮方法
public void start(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
//普通启动
startService(intent);
}- 4.停止按钮方法
public void stop(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
//停止服务
stopService(intent);
}点击开始按钮打印的日志:
System.out: onCreate... System.out: onStartCommand... System.out: onStart点击停止按钮打印的日志:
System.out: onDestroy
绑定模式
- 1.同上有:“onCreate“,自动有onBind(),再重写onUnbind(),同上有onDestroy
- 2.绑定的方法
public void bind(View view) {
//绑定服务
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
//conn
mConn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//回调回来的conn内容,可以得到服务的IBinder
//连接
System.out.println("回调了conn-IBinder..........并连接");
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
//取消连接
System.out.println("回调了conn-取消连接...............");
}
};
//conn
bindService(intent, mConn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}3.解除绑定的方法
public void unbind(View view) { //解除绑定 unbindService(mConn); }点击绑定按钮日志
System.out: onCreate. System.out: onBind...点击取消绑定按钮日志
System.out: onUnbind... System.out: onDestroy如果已经绑定了,此时再点击绑定按钮,那么不会再次创建和绑定
- 如果一个Service被多个用户绑定,只有所有的都执行onBind()那么该Service**才会销毁**
- 如果一个客户执行了onStart()方法,那么所有的用户都执行了unBind()也不会销毁.
- 以下是两种方式的生命周期图:
开发情况:
- 按标准来,一般是先startService,再bindService,再unBindService,再StopServcie.
- 就符合标准的:启动->绑定->解绑->停止服务.
4.什么是IntentService?有何优点?
- 1.简介和Service的区别
- 1.是Service的子类,有额外的功能.
- 2.区别如下:
- Service 不会专门启动一条单独线程,和应用存在同一个线程的
- 因为不是一个新线程,因此不能在Service进行耗时操作
- 2.IntentService特征
- 会创建一个独立的worker线程处理所有的Intent请求,清单注册.
- 写一个类继承IntentService,就会自动要求写一个onHandleIntent(Intent intent)
- 可以从这个方法里面拿到Activity发过来带数据的intent
- 所有请求都请求完后,就会自动停止IntentService,不用我们退出.
代码演示:
- 添加一个按钮:
public void clic(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyIntentService.class);
intent.putExtra("info","information");
startService(intent);
}- MyIntentService.java
package goodjobtome.com.lrucechepic;
import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyIntentService extends IntentService {
private String mInfo;
Handler mHandler = new Handler();
//发现是需要"空"构造函数,否则不生效.
public MyIntentService() {
super("MyIntentService");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
//在这里获取意图信息,Service也可以
mInfo = intent.getStringExtra("info");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
//此方法是在"子线程"处理的,可以再这里处理耗时操作.
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
//其实这里也可以获得意图信息
//耗时两秒
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
//再谈吐司.
//子->UI
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MyIntentService.this, mInfo, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
当点击过了两秒后就弹吐司了.
- 总结,虽然平时的Service已经够我们用了,再开启一个子线程就能达到效果了,但是我们还是要懂这个.
5.说说Activity,Intent,Service是什么关系?
- 1.三者都是Android开发中最常用的三个类
- 2.Activity和Service是四大组件之一,他们都是在Contenxt子类的ContextWrapper(上下文包装类)的子类.可以说他两是兄弟(Context是他们的爷爷)
- 3.Activity负责窗口活动用户界面显示和交互的工作,Service负责的是后台任务处理的工作.
- 4.可以说Intent是他们的通信桥梁.
6.Service和Activity在同一个线程吗?
- 都在主线程中:main Thread(UI Thread)
7.Service里面可以弹吐司吗?
- 弹吐司的条件是:1.上下文,2.主线程,因为Service本身就是Context的子类(孙子),所以可弹(如下载完任务谈一个通知).
8.如何让一个Service成为前置线程?
- 一句话即可:
- startForeground()方法就可以让MyService变成一个前台Service
- 如墨迹天气,要用到前台进程,他的Service再后台更新数据的时候,状态栏显示天气信息.
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
System.out.println("onStartCommand...");
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(this);
builder.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
builder.setContentTitle("内容标题");
builder.setContentInfo("内容信息");
builder.setContentText("内容文本");
builder.setAutoCancel(true);//可清除
Intent myIntent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, myIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
Notification notification = builder.getNotification();
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
manager.notify(0,notification);
//设置成为前台进程
startForeground(1,notification);
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}9.Service的onStartCommand方法有几种返回值?各代码什么意思?
知道这以下4种即可
- 1.START_STICKY:
- 1.”粘贴性的”,如果服务被kill,保留Service为服务状态,不保留intent对象
- 2.系统会**尝试重新创建**Service
- 3.服务创建后继续调用onStartCommand()方法,如果这个期间没有传过来的intent,那么intent就为null;
- 2.START_NOT _STICKY:
- ”非粘贴性”,Service**被kill**掉,不会自动创建了.
3.START_REDELIVER _INTENT:
- ”重传Intent”,Service被kill,会自动创建,并且将intent传入
4.START_STICKY _COMPATIBILITY:
- START_STICKY的兼容版,不保证被kill一定能重启
10.Service的onRebind(intent)方法在什么情况下会执行?
- onUnbind()方法返回值为true的情况下(默认为false)执行
11.Activity调用Service都有哪些方法?
1.通过继承Binder类(常用)
2.通过Messenger(信使,信差)
3.通过AIDL(跨程序访问)
对于这三种方法,因为涉及的内容比较重要和细致,所以我给大家分开来写了三篇的小专题,大家只要点击就能访问啦.








 本文深入讲解Android中的Service组件,包括Service的基本概念、生命周期、启动方式、与Activity的交互方法及IntentService的特点等。同时探讨了Service如何进行后台任务处理、与前台进程的交互以及与Activity之间的关系。
本文深入讲解Android中的Service组件,包括Service的基本概念、生命周期、启动方式、与Activity的交互方法及IntentService的特点等。同时探讨了Service如何进行后台任务处理、与前台进程的交互以及与Activity之间的关系。














 2058
2058

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








