1.缓存使用前提:
服务器必须支持,缓存,配置Cache-Control等头信息,因为Volley需要从这些头信息判断缓存是否已经过期。以及一些其他Header的参数
https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec14.html#sec14.32 http协议文档
预设问题:
1.缓存机制
2.是如何实现的-技术方案。
3.缓存位置(读/写方式)。
4.缓存更新方式!缓存多长时间
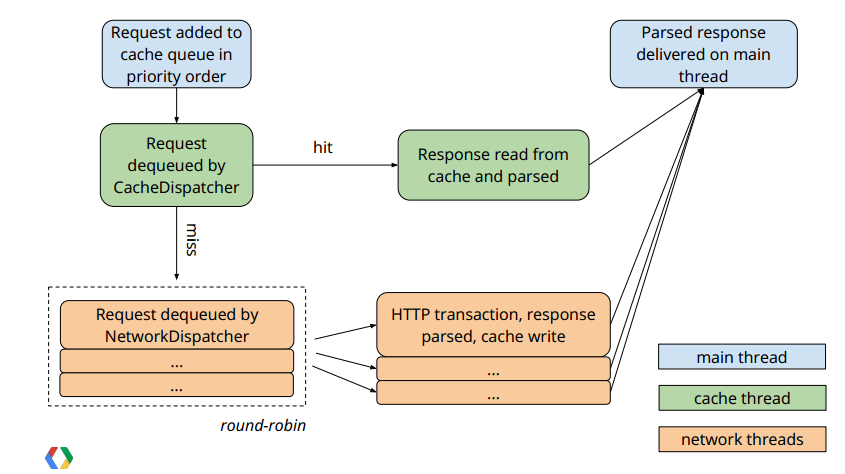
2 .Volley官方提供的流程图
(图1) volley缓存机制
Volley缓存实现,需要服务端进行配合,根据request—-response 中交互的 http中具体Header 字段。例如下图
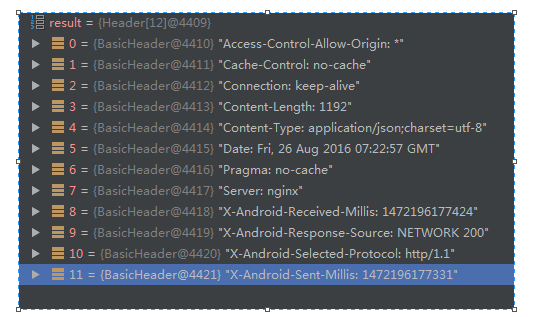
(图2) Http请求的头
当然不止这一种:blog
request时用到:
| "no-cache"
| "no-store"
| "max-age" "=" delta-seconds
| "max-stale" [ "=" delta-seconds ]
| "min-fresh" "=" delta-seconds
| "no-transform"
| "only-if-cached"
| "cache-extension"
response时用到:
| "public"
| "private" [ "=" <"> field-name <"> ]
| "no-cache" [ "=" <"> field-name <"> ]
| "no-store"
| "no-transform"
| "must-revalidate"
| "proxy-revalidate"
| "max-age" "=" delta-seconds
| "s-maxage" "=" delta-seconds
| "cache-extension"具体细节下面进行分析
3.具体缓存存放的位置,是在首次初始化传入进去的。context.getCacheDir()。当然可以随意修改存储位置,做好相应的容错即可。
缓存字段主要在HttpHeaderParser 中进行定义,并进行包装内部类Entity结构
long serverDate = 0;
long lastModified = 0;
long serverExpires = 0;
long softExpire = 0;
long finalExpire = 0;
long maxAge = 0;
long staleWhileRevalidate = 0;
boolean hasCacheControl = false;
boolean mustRevalidate = false;当然这些字段都是可以在Http 协议中Header 找到对应的字段。缓存内容也是这些字段
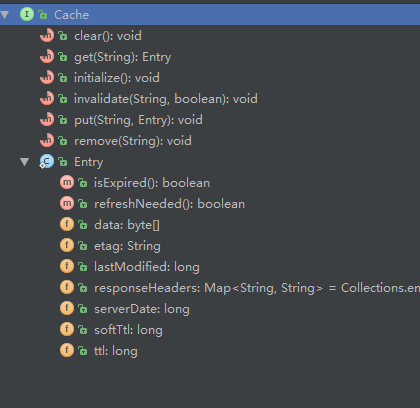
Cache 接口的实现类有两个 NoCache 和 DiskBasedCache,前一个是空实现。DiskBasedCache进行具体的缓存逻辑
(图3) Cache接口结构
在网络请求成功地方进行缓存,key= request url ,entry为具体response相应封装后的实体
/**
* Puts the entry with the specified key into the cache.
* 在网络请求成功中进行缓存
*/
@Override
public synchronized void put(String key, Entry entry) {
pruneIfNeeded(entry.data.length);
File file = getFileForKey(key);
try {
BufferedOutputStream fos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
CacheHeader e = new CacheHeader(key, entry);
boolean success = e.writeHeader(fos);
if (!success) {
fos.close();
VolleyLog.d("Failed to write header for %s", file.getAbsolutePath());
throw new IOException();
}
fos.write(entry.data);
fos.close();
putEntry(key, e);
return;
} catch (IOException e) {
}
boolean deleted = file.delete();
if (!deleted) {
VolleyLog.d("Could not clean up file %s", file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}1.首先进行判断缓存内容是否超过限制的最大容量,超过了就需要清除排在队列最前面的缓存数据
2.根据一些规则生成文件名,并以文件的形式进行返回
3.将key,entity 包装成DiskBasedCache 内部类 CacheHeader结构
4.通过OutputStream 序列化到本地文件中
下面是写入的方式
/**
* Writes the contents of this CacheHeader to the specified OutputStream.
*/
public boolean writeHeader(OutputStream os) {
try {
writeInt(os, CACHE_MAGIC);
writeString(os, key);
writeString(os, etag == null ? "" : etag);
writeLong(os, serverDate);
writeLong(os, lastModified);
writeLong(os, ttl);
writeLong(os, softTtl);
writeStringStringMap(responseHeaders, os);
os.flush();
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
VolleyLog.d("%s", e.toString());
return false;
}
}缓存的读取同样根据 key去拿对应的Entity内容。下面是读取缓存的源码
/**
* Returns the cache entry with the specified key if it exists, null otherwise.
*/
@Override
public synchronized Entry get(String key) {
CacheHeader entry = mEntries.get(key);
// if the entry does not exist, return.
if (entry == null) {
return null;
}
File file = getFileForKey(key);
CountingInputStream cis = null;
try {
cis = new CountingInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)));
CacheHeader.readHeader(cis); // eat header
byte[] data = streamToBytes(cis, (int) (file.length() - cis.bytesRead));
return entry.toCacheEntry(data);
} catch (IOException e) {
VolleyLog.d("%s: %s", file.getAbsolutePath(), e.toString());
remove(key);
return null;
} finally {
if (cis != null) {
try {
cis.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
return null;
}
}
}
}1.根据生成文件名的方式,拿到存入文件对应的路径,
2.BufferedInputStream 进行读流,然后逆序转换为Cache.Entity
下面是对缓存文件的源码
/**
* Reads the header off of an InputStream and returns a CacheHeader object.
*
* @param is The InputStream to read from.
* @throws IOException
*/
public static CacheHeader readHeader(InputStream is) throws IOException {
CacheHeader entry = new CacheHeader();
int magic = readInt(is);
if (magic != CACHE_MAGIC) {
// don't bother deleting, it'll get pruned eventually
throw new IOException();
}
entry.key = readString(is);
entry.etag = readString(is);
if (entry.etag.equals("")) {
entry.etag = null;
}
entry.serverDate = readLong(is);
entry.lastModified = readLong(is);
entry.ttl = readLong(is);
entry.softTtl = readLong(is);
entry.responseHeaders = readStringStringMap(is);
return entry;
}何时需要更新缓存,以及如何进行缓存清理。
/* True if a refresh is needed from the original data source. /
public boolean refreshNeeded() {
return this.softTtl < System.currentTimeMillis();
}
根据服务端返回值,进行判断,是否需要刷新缓存。设置参数为true
/ Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;Request时可以动态设置是否进行响应缓存
public final Request<?> setShouldCache(boolean shouldCache) {
mShouldCache = shouldCache;
return this;
}引用1: https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000004711321 Volley源码中ImageLoader类的batchResponse方法的实现问题
引用2:http://blog.csdn.net/soft_po/article/details/51511546 Volley缓存机制























 235
235

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










