下面的python代码是基于ipython2.7.10(没装也没关系,只是没那么方便),sudo apt-get install ipython
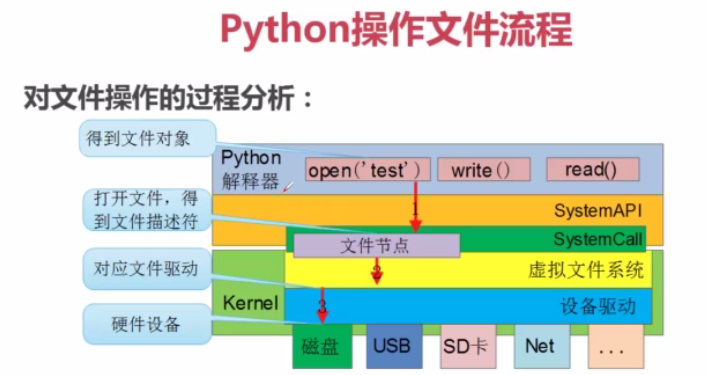
一、Python文件基础操作
1-1.文件打开方式
文件打开方法: open(name [, mode[buf]])name : 文件路径
mode : 打开方式
buf : 缓冲buffering大小
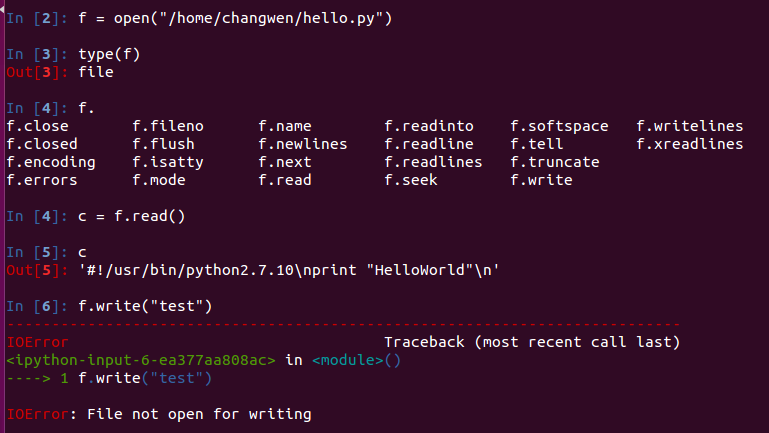
1.上面的f.然后按tab显示的内容要是ipython工具上才行
2.由于只是简单的创建一个文件,所以其权限只能读而不能写
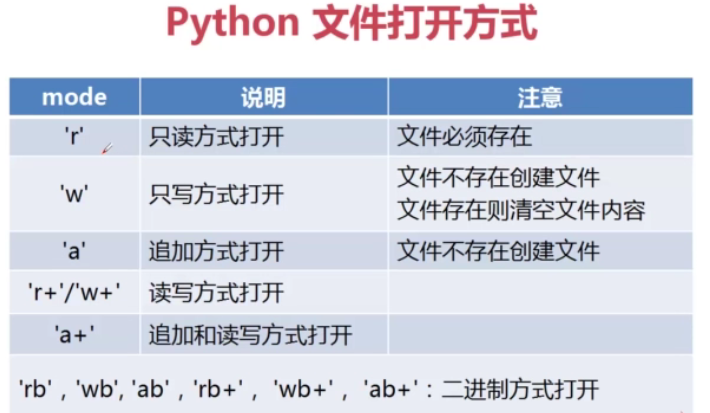
文件打开的方式权限如下 :
f = open("/home/changwen/hello2.py", 'w')1-2.文件读取文件
文件读取方式:
1.read([size]): 读取文件(读取size个字节,默认读取全部),如果文件很大,不建议用这个
2.readline([size]): 读取一行。(如果size<line,则返回size个数据,如果size>line,返回一行)
In [29]: f =open("/home/changwen/hello.py")
In [30]: f.readline(3)
Out[30]: '#!/'
In [31]: f.readline(100)
Out[31]: 'usr/bin/python2.7.10\n'
3.readlines([size]): 读取完文件,返回每一行所组成的列表
4.iter: 使用迭代器读取文件
In [1]: f =open("/home/changwen/hello.py")
In [2]: iter_f = iter(f)
In [3]: lines = 0
In [4]: for line in iter_f:
...: lines += 1
...:
In [6]: lines
Out[6]: 21-3.文件写入与写缓存
文件写入方式:1.write(str): 将字符串写入文件
2.writelines(sequence_of_strings): 写多行到文件,参数为可迭代对象
In [7]: f = open("/home/changwen/1.txt" ,'w')
In [8]: f.writelines((1,2,3))
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-8-0a3726375675> in <module>()
----> 1 f.writelines((1,2,3))
TypeError: writelines() argument must be a sequence of strings
In [9]: f.writelines(('1','2','3'))
In [10]: f.writelines(['1','2','3'])
In [11]: cat 1.txt
In [12]: f.close()
In [13]: cat 1.txt
123123
解决方法
1.主动调用close()或者flush()方法,写缓存同步到磁盘
2.写入数据量大于或者等于写缓存,写缓存自动同步到磁盘
1-4.文件关闭
1.将写缓存同步到磁盘2.linux系统中每个进程打开文件的个数是有限的;
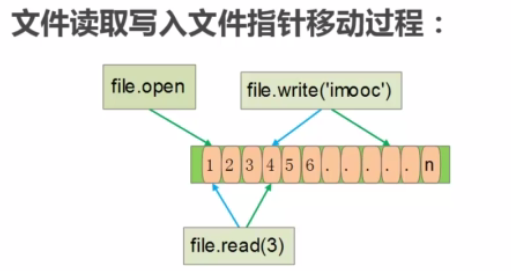
1-5.文件指针
Python 写入和读取问题1.写入文件后,必须打开才能读取写入内容
2.读取文件后,无法重新再次读取读取读过的内容
Python文件指针操作:
1.seek(offset[, whence]):移动文件指针
2.offset:偏移量,可以为负数
3.whence:偏移相对位置
Python文件指针定位方式:
1.os.SEEK_SET:相对文件起始位置
2.os.SEEK_CUR:相对文件当前位置
3.os.SEEK_END:相对文件结尾位置
In [1]: f = open("/home/changwen/1.txt", 'r+')
In [2]: f.read(3)
Out[2]: '123'
In [3]: f.tell()
Out[3]: 3
In [4]: import os
In [6]: f.seek(0, os.SEEK_SET)
In [7]: f.tell()
Out[7]: 0
In [8]: f.read(3)
Out[8]: '123'
<pre name="code" class="python">In [9]: f.seek(0, os.SEEK_END)
In [10]: f.tell()
Out[10]: 10
In [11]: f.seek(-12, os.SEEK_CUR)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IOError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-11-f98aded80004> in <module>()
----> 1 f.seek(-12, os.SEEK_CUR)
IOError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument二、文件属性及OS模块使用
2-1.文件属性编码格式
Python文件属性 1.file.fileno():文件描述符 2.file.mode:文件打开权限 3.file.encoding:文件编码格式 4.file.closed:文件是否关闭In [13]: f = open("/home/changwen/1.txt")
In [15]: f.fileno()
Out[15]: 6 # 说明文件描述符为6
In [16]: f.mode
Out[16]: 'r' # 这里输出为'r',说明为可读的
In [17]: f.closed
Out[17]: False # 说明没有关闭
In [18]: f.encoding
# 返回为空,说明是ASCII码1.文件标准输入:sys.stdin;
2.文件标准输出:sys.stdout;
3.文件标准错误:sys.stderr;
In [4]: sys.stdin.mode
Out[4]: 'r'
In [5]: sys.stdout.mode
Out[5]: 'w'
In [6]: sys.stderr.mode
Out[6]: 'w'
sys模块提供sys.argv属性,通过该属性可以得到命令行参数;
sys.argv:字符串组成的列表;
#!/usr/bin/python2.7.10
import sys
if __name__ == '__main__':
print len(sys.argv)
for arg in sys.argv:
print arg
changwen@ubuntu:~$ python arg.py 1 2 3
4
arg.py
1
2
3
使用普通方式打开文件:写入u'编程',则会有UnicodeEncodeError
解决方案:将unicode转码为’utf-8'
In [1]: a = unicode.encode(u'编程', 'utf-8')
In [2]: a
Out[2]: '\xe7\xbc\x96\xe7\xa8\x8b'
open(fname,mode, encoding, errors, buffering):使用指定编码格式打开文件
In [3]: import codecs
In [5]: f = codecs.open("/home/changwen/1.txt", 'w', 'utf-8')
In [6]: f.encoding
Out[6]: 'utf-8'
In [7]: f.write(u'编程')
In [9]: f.close()
In [10]: cat 1.txt
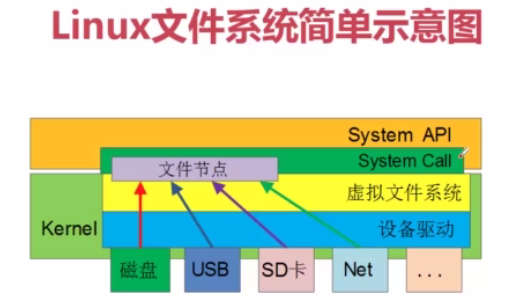
编程 2-2.Linux文件系统简介
linux文件包括:磁盘(ext2, ext4)文件,NFS文件系统,各种外设(sd卡, USB设备)等;
Linux如何来管理外设,为应用层提供统一接口?
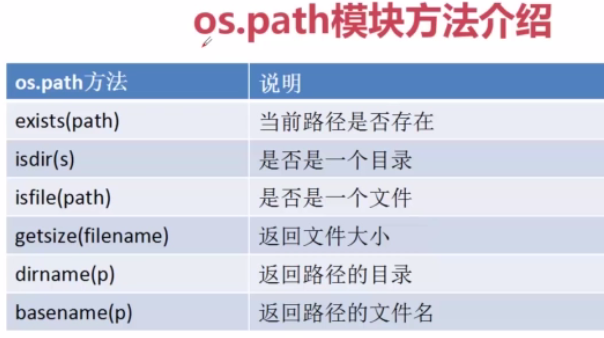
2-3.OS模块对文件和目录操作
使用os模块打开文件(偏于底层调用)
os.open(filename, flag[, mode]): 打开文件
flag: 打开文件方式
os.O_CREAT:创建文件
os.O_RDONLY:只读方式打开
os.O_WRONLY:只写方式打开
os.O_RDWR:读写方式打开
os.read(fd, buffersize):读取文件
os.write(fd, string):写入文件
fd:文件描述符
string:写入的数据
os.lseek(fd,pos, how):文件指针操作
os.close(fd):关闭文件
三、文件练习
练习内容: 使用Python管理ini文件:实现查询,添加,删除,保存
ini配置文件格式:
节: [session]
参数(键=值) name=value
准备数据1.txt
| [user info] name = changwen pwd = adc [study] python_base = 15 python_junior = 20 linux_base_ = 15 |
In [1]: import ConfigParser
In [2]: cfg=ConfigParser.ConfigParser()
In [4]: cfg.read("/home/changwen/1.txt")
Out[4]: ['/home/changwen/1.txt']
In [6]: cfg.sections()
Out[6]: ['user info', 'study']
<pre name="code" class="python">------------------------遍历-------------------------------
----------------------------修改------------
In [9]: cfg.set('user info', 'pwd', '123456')
In [10]: for se in cfg.sections():
print se
print cfg.items(se)
....:
user info
[('name', 'changwen'), ('pwd', '123456')]
study
[('python_base', '15'), ('python_junior', '20'), ('linux_base_', '15')]--------------------------插入-------------------------
In [11]: cfg.set('user info', 'email', '123@qq.com')
In [12]: for se in cfg.sections():
print se
print cfg.items(se)
....:
user info
[('name', 'changwen'), ('pwd', '123456'), ('email', '123@qq.com')]
study
[('python_base', '15'), ('python_junior', '20'), ('linux_base_', '15')]
---------------------------删除-----------------------------
#remove_option是删除一个键值对,_section是删除一个节
In [13]: cfg.rem
cfg.remove_option cfg.remove_section
In [13]: cfg.remove_option('user info', 'email')
Out[13]: True
In [14]: for se in cfg.sections():
print se
print cfg.items(se)
....:
user info
[('name', 'changwen'), ('pwd', '123456')]
study
[('python_base', '15'), ('python_junior', '20'), ('linux_base_', '15')]
实例 :
# coding:utf8
#!/usr/bin/python2.7.10
import os
import os.path
import ConfigParser
class student_info(object):
def __init__(self, recordfile):
self.logfile = recordfile
self.cfg = ConfigParser.ConfigParser()
#
def cfg_load(self):
self.cfg.read(self.logfile)
# 显示文件信息
def cfg_dump(self):
se_list = self.cfg.sections()
print "------------------->"
for se in se_list:
print se
print self.cfg.items(se)
print "<-------------------"
def delete_item(self, section, key):
self.cfg.remove_option(section, key)
def delete_section(self, section):
self.cfg.remove_section(section)
def add_section(self, section):
self.cfg.add_section(section)
def set_item(self, section, key, value):
self.cfg.set(section, key, value)
def save(self):
fp = open(self.logfile, 'w')
self.cfg.write(fp)
fp.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
info = student_info('/home/changwen/1.txt')
info.cfg_load()
info.cfg_dump()
info.set_item('user info', 'pwd', 'abc')
info.cfg_dump()
info.add_section('login')
info.set_item('login', '2016_07_22', '18')
info.save()| -------------------> user info [('name', 'changwen'), ('pwd', 'adc')] study [('python_base', '15'), ('python_junior', '20'), ('linux_base_', '15')] <------------------- -------------------> user info [('name', 'changwen'), ('pwd', 'abc')] study [('python_base', '15'), ('python_junior', '20'), ('linux_base_', '15')] <------------------- |
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








