旅行商问题(Travelling Salesman Problem,即TSP问题)是数学领域中著名问题之一。假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路经的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。
TSP问题是一个组合优化问题,也是一个NP完全问题,使用通常的解法往往需要耗费大量的时间,不过我们也可以使用遗传算法,在较短的时间里找到一个可接受(不一定是最优)的解。
下面是我的代码,一共有三个文件。
1、TSP.py
2、GA.py
3、Life.py
运行TSP.py,即可开始程序。几个快捷键说明如下:
n: 开始新的计算(随机产生32个新的城市)
e: 开始进化
s: 停止
q: 退出
程序没有设置终止进化条件,进化一旦开始,如果不手动停止,会一直计算下去。
遗传算法主要是一种思想,并没有很具体的代码,在解决大多数问题时,最难解决的部分主要是编码(如何将问题转化为合适的方便操作的“基因”)、评价(如何评价各个“基因”的得分)部分。在本例中,我们将城市的顺序做为基因编码,路径总长度的倒数为基因的得分。这种做法不一定是最好的,不过是有效的。
下面是我运行时的一次截图:
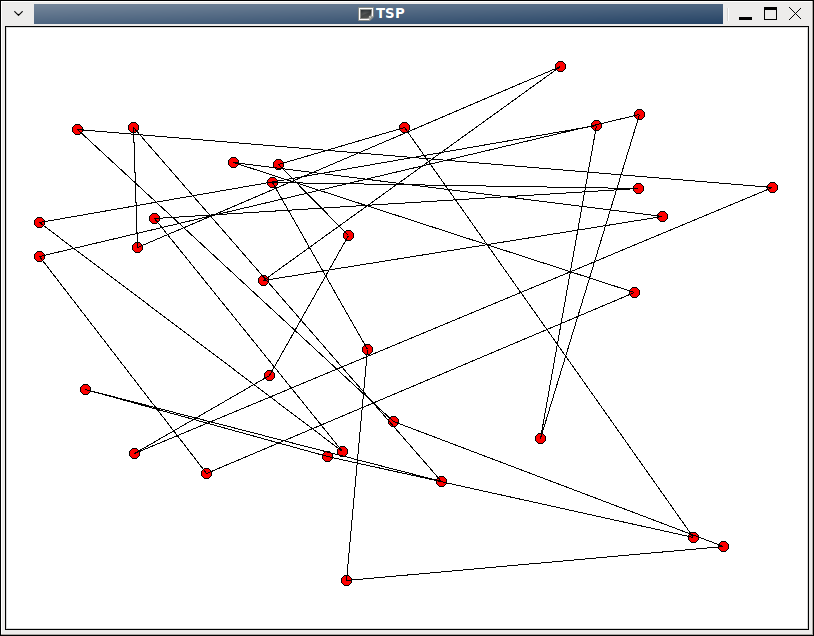
初始状态。
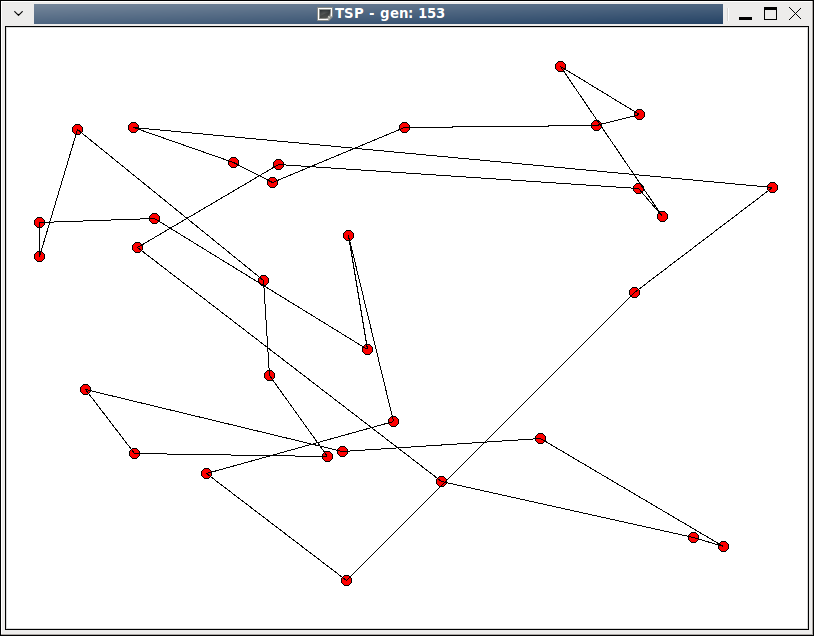
第153代。
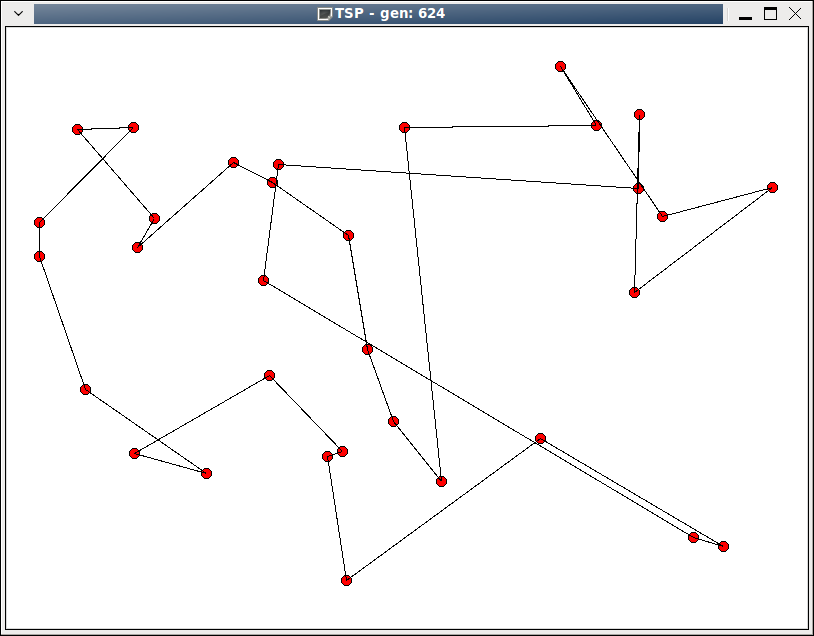
第624代,可以看到,已经比初始状态好多了。
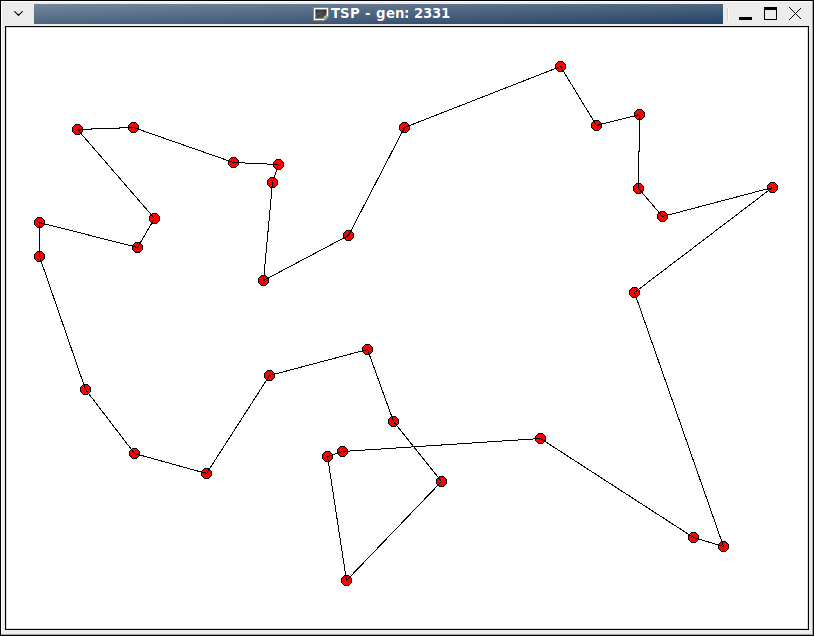
第2331代,除了下方有一些交叉外,已经基本差不多了。
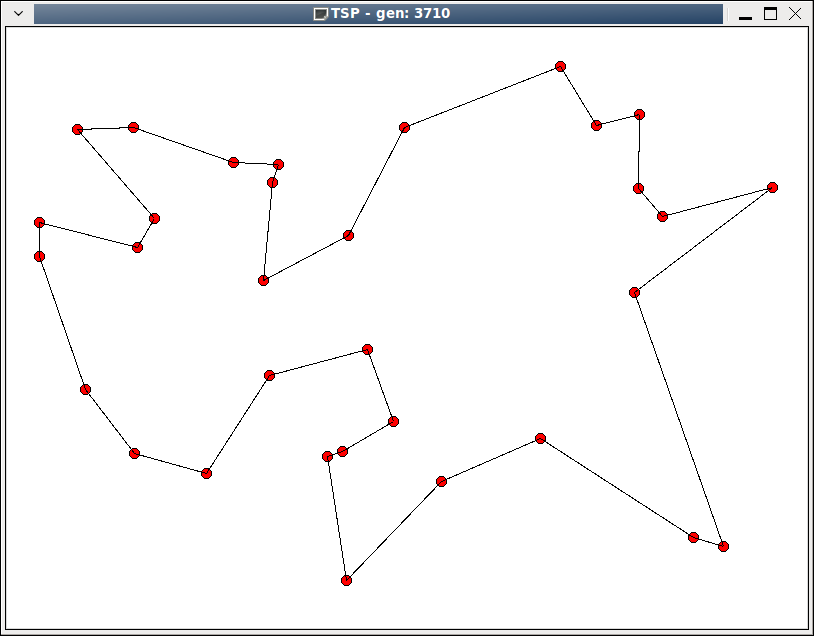
第3710代,完成。






















 347
347

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








