本文是看David Silver的强化学习视频的时候记的笔记,整理了视频的思路,补充了一些证明。
1,什么是动态规划?
跳过,不写。
2,迭代策略估计
任务:估计给定策略的状态值函数
方法1:迭代算法(iterative application of Bellman expectation backup,咋翻译?),
使用synchronous backups(区别于asynchronous backups)
可以证明,上述迭代算法下,当时,
。(PPT的后面有相关证明)
3,举例(grid world)
如下图,估计5x5 gridworld的状态值函数
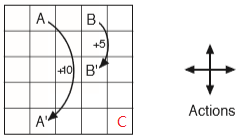
动作:north, south, west, east;
状态:25个格子对应了25个状态;
奖励:1)若处于A,不论执行什么动作,都将移动到A',并获得奖励+10;
2)若处于B,不论执行什么动作,都将移动到A',并获得奖励+10;
3)若在边界处,例如C,如果执行动作right,或者动作down,只会停留在原处,并获得奖励-1;
4)其他位置都将获得奖励0,并根据动作移动到相应的位置;
折扣:
策略:采用随机策略,任意一个状态(位置),采用4个动作的概率均为0.25
![]()
python 编程实现:
在Shangtong Zhang代码上做了些修改,上代码:
#######################################################################
# Copyright (C) #
# 2016-2018 Shangtong Zhang(zhangshangtong.cpp@gmail.com) #
# 2016 Kenta Shimada(hyperkentakun@gmail.com) #
# Permission given to modify the code as long as you keep this #
# declaration at the top #
#######################################################################
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.table import Table
WORLD_SIZE = 5
A_POS = [0, 1]
A_PRIME_POS = [4, 1]
B_POS = [0, 3]
B_PRIME_POS = [2, 3]
gamma = 0.9
ACTIONS = np.array([[0, -1], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0]]);
ACTION_PROB = 0.25
def move(state, action):
if state == A_POS:
return A_PRIME_POS, 10
if state == B_POS:
return B_PRIME_POS, 5
state = np.array(state)
next_state = (state + action).tolist()
x, y = next_state
if x < 0 or x >= WORLD_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= WORLD_SIZE:
reward = -1.0
next_state = state
else:
reward = 0
return next_state, reward
def policyEvaluation():
Vk = np.zeros((WORLD_SIZE, WORLD_SIZE));
iteration = 0;
while True:
# keep iteration until convergence
Vkk = np.zeros(Vk.shape);
iteration += 1;
for i in range(0, WORLD_SIZE):
for j in range(0, WORLD_SIZE):
for action in ACTIONS:
(next_i, next_j), reward = move([i, j], action);
# bellman equation
Vkk[i, j] += ACTION_PROB * (reward + gamma * Vk[next_i, next_j]);
if np.sum(np.abs(Vk - Vkk)) < 1e-4:
print("iteration:", iteration);
print(np.around(Vk, 1));
break;
Vk = Vkk;
if __name__ == '__main__':
policyEvaluation();运行结果为:
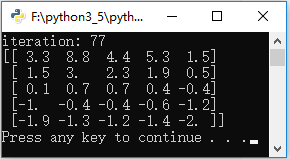
4,策略改进
问题提出:
已知一确定性策略和其对应的状态值函数
,怎样改进策略
,得到一个新的策略
使得,
。
一个思路:
先看的原始形式:
注意下标的含义,表示在t,t+1, t+2....时刻,均使用策略
,执行对应的动作
,
,
...,得到的累积奖赏的数学期望作为
。
再看的Bellman方程:
注意由于已有下标
,可以写成:
于是有改进思路,分两步,对t+1, t+2....时刻时的状态,
...仍然使用策略
,对t时刻
使用新的策略
,并且
有:
,此时,是否有
呢?即是否有
?
5,策略改进定理
和
是确定性策略,如果有
,
,则
,即
。
证明如下:
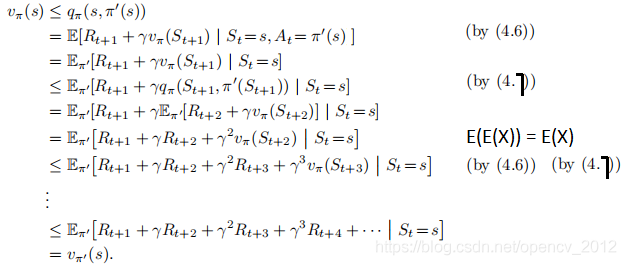
当改进终止时有:
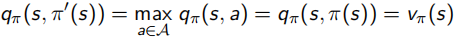 (1)
(1)
此时,满足了Bellman最优方程的形式:
![]()
有,因此
就是最优策略
(没想通)
6,策略迭代
由策略改进定理,于是有获取最优策略的算法:策略迭代;
算法描述如下:
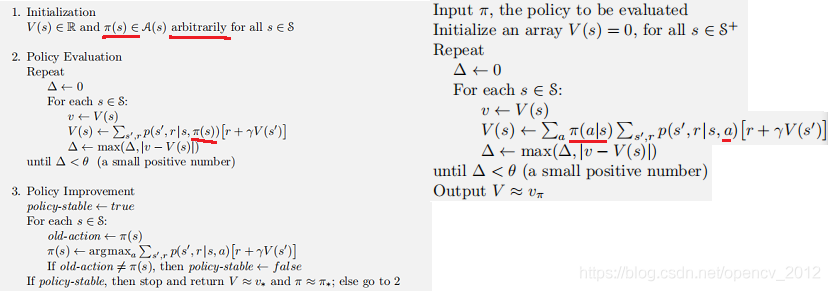
对照右边的值函数估计,这里没有了π(a|s),其实相当于将π(a|s)设置为1,因为现在的a = π(s)
7,策略迭代示例
仍以前面的grid world为例,找最优策略;
#######################################################################
# Copyright (C) #
# 2016-2018 Shangtong Zhang(zhangshangtong.cpp@gmail.com) #
# 2016 Kenta Shimada(hyperkentakun@gmail.com) #
# Permission given to modify the code as long as you keep this #
# declaration at the top #
#######################################################################
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
#matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.table import Table
WORLD_SIZE = 5
A_POS = [0, 1]
A_PRIME_POS = [4, 1]
B_POS = [0, 3]
B_PRIME_POS = [2, 3]
gamma = 0.9
ACTIONS = np.array([[0, -1], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0]]);
ACTION_PROB = 0.25
def move(state, action):
if state == A_POS:
return A_PRIME_POS, 10
if state == B_POS:
return B_PRIME_POS, 5
state = np.array(state)
next_state = (state + action).tolist()
x, y = next_state
if x < 0 or x >= WORLD_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= WORLD_SIZE:
reward = -1.0
next_state = state
else:
reward = 0
return next_state, reward
def Evaluation(value, policy):
Q = np.zeros(value.shape);
while True:
Q = value.copy();
for i in np.arange(0, WORLD_SIZE):
for j in np.arange(0, WORLD_SIZE):
action = ACTIONS[policy[i, j]];
(next_i, next_j), reward = move([i, j], action);
value[i, j] = reward + gamma * value[next_i, next_j];
delta = np.abs(value - Q);
if delta.max() < 0.000001:
break;
return;
def Improvement(value, policy):
isOptimal = True;
new_policy = np.zeros(policy.shape);
new_policy = policy.copy();
for i in np.arange(0, WORLD_SIZE):
for j in np.arange(0, WORLD_SIZE):
Q = [];
maxQ = -99999999.0;
index = policy[i, j];
for action in ACTIONS:
(next_i, next_j), reward = move([i, j], action);
Q.append(reward + gamma * value[next_i, next_j]);
for k in np.arange(0, ACTIONS.itemsize):
if(maxQ <= Q[k]):
maxQ = Q[k];
new_policy[i, j] = k;
if new_policy[i, j] != policy[i, j]:
isOptimal = False;
policy[i, j] = new_policy[i, j];
return isOptimal;
def policyIteration():
value = np.zeros((WORLD_SIZE, WORLD_SIZE));
policy = np.zeros((WORLD_SIZE, WORLD_SIZE), dtype = int);
while True:
Evaluation(value, policy);
isOptimal = Improvement(value, policy);
if(isOptimal == True):
print(policy);
print(np.around(value, 2));
break;
if __name__ == '__main__':
policyIteration();8,值迭代
利用了Bellman最优方程
上代码:
#######################################################################
# Copyright (C) #
# 2016-2018 Shangtong Zhang(zhangshangtong.cpp@gmail.com) #
# 2016 Kenta Shimada(hyperkentakun@gmail.com) #
# Permission given to modify the code as long as you keep this #
# declaration at the top #
#######################################################################
import numpy as np
#import matplotlib
#matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.table import Table
WORLD_SIZE = 5
A_POS = [0, 1]
A_PRIME_POS = [4, 1]
B_POS = [0, 3]
B_PRIME_POS = [2, 3]
gamma = 0.9
ACTIONS = np.array([[0, -1], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0]]);
ACTION_PROB = 0.25
def move(state, action):
if state == A_POS:
return A_PRIME_POS, 10
if state == B_POS:
return B_PRIME_POS, 5
state = np.array(state)
next_state = (state + action).tolist()
x, y = next_state
if x < 0 or x >= WORLD_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= WORLD_SIZE:
reward = -1.0
next_state = state
else:
reward = 0
return next_state, reward
def valueIteration():
Vk = np.zeros((WORLD_SIZE, WORLD_SIZE));
policy = np.zeros((WORLD_SIZE, WORLD_SIZE), dtype = int);
iteration = 0;
while True:
# keep iteration until convergence
iteration += 1;
Vkk = np.zeros(Vk.shape)
for i in range(0, WORLD_SIZE):
for j in range(0, WORLD_SIZE):
Q = []
for action in ACTIONS:
(next_i, next_j), reward = move([i, j], action)
# value iteration
Q.append(reward + gamma * Vk[next_i, next_j])
Vkk[i, j] = np.max(Q)
maxQ = -99999999.0;
for k in np.arange(0, ACTIONS.itemsize):
if(maxQ <= Q[k]):
maxQ = Q[k];
policy[i, j] = k;
if np.sum(np.abs(Vkk - Vk)) < 1e-4:
print("value iteration:", iteration);
print(policy)
print(np.around(Vk, 2));
break
Vk = Vkk
if __name__ == '__main__':
valueIteration();






















 880
880











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








