上一篇文章当中介绍了Fleury算法是什么以及算法流程,本篇文章将介绍如何用代码来实现求解欧拉回路。废话不多说先来三个例子,这三个例子分别是两个欧拉图和一个非欧拉图。
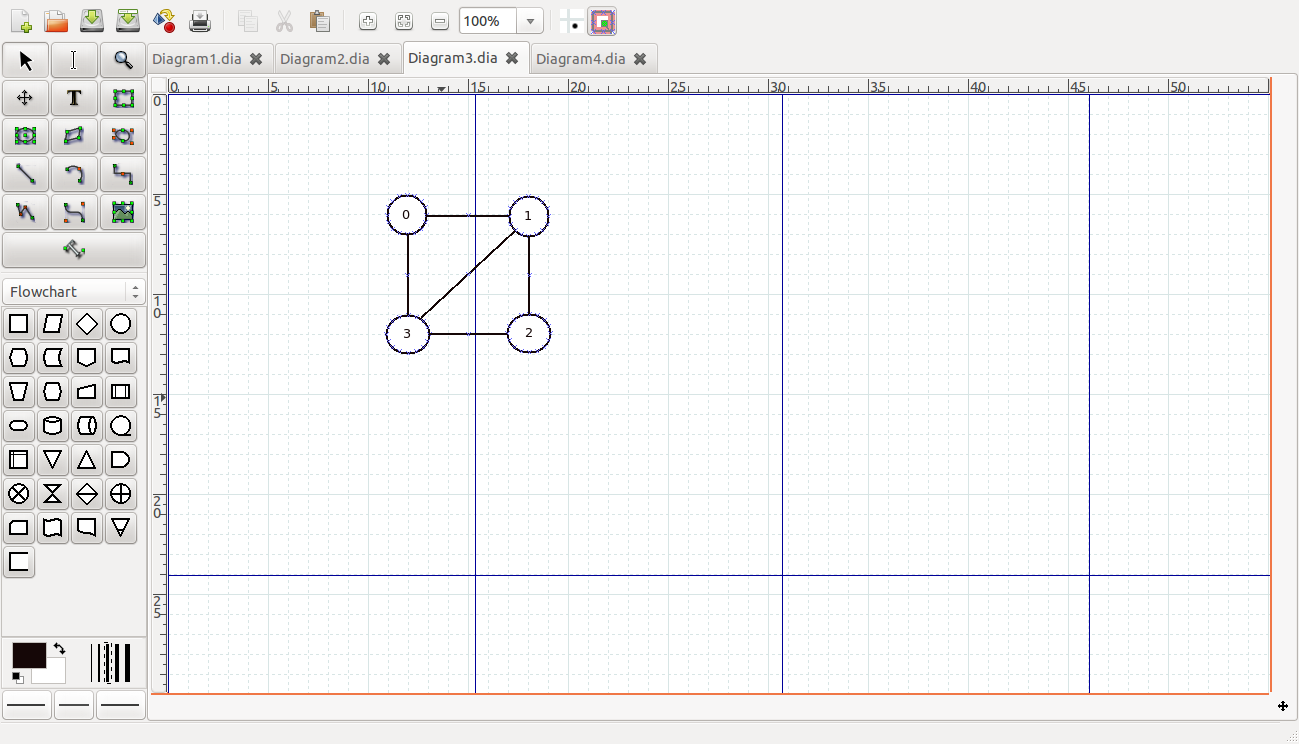
非欧拉图:
图 1
欧拉图一:
图 2 (此图来自《离散数学教程》p135)
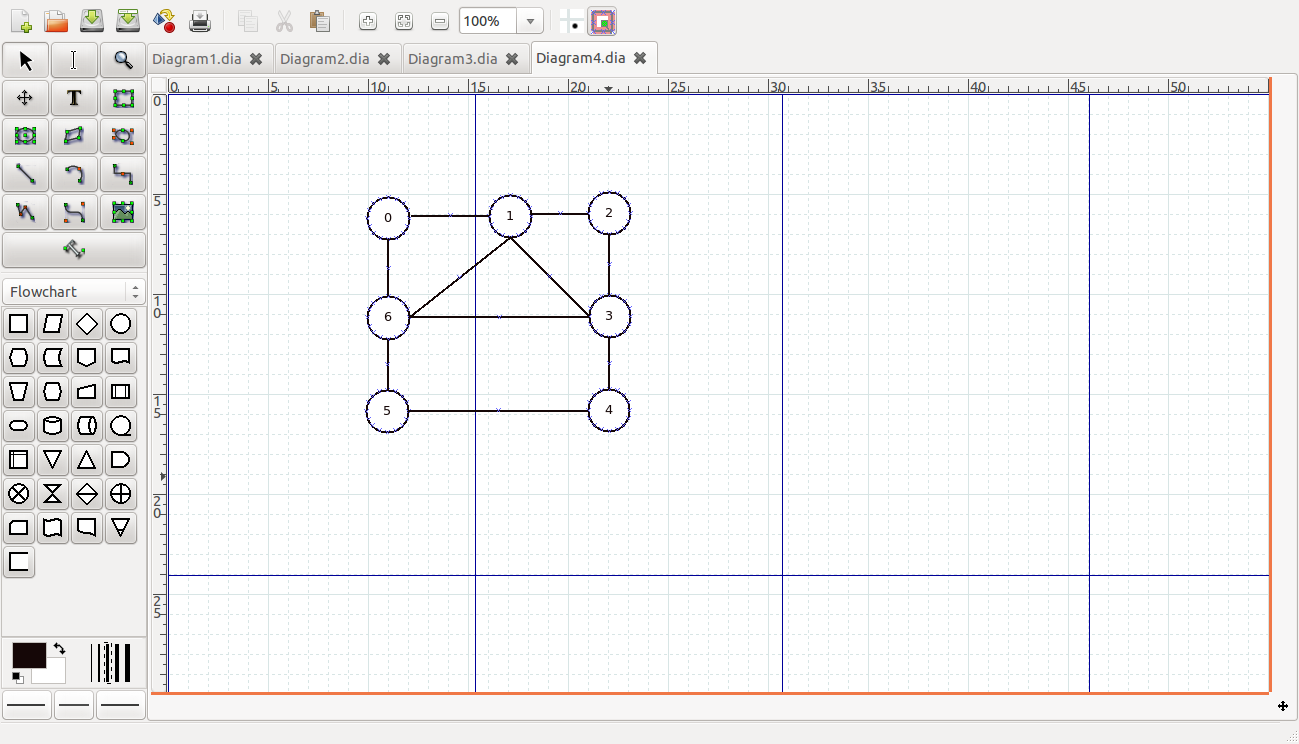
欧拉图二:(这是一个七个点的图,每一个点都是6条边)
图 3
现在我们来开始编码,首先,创建一个二维数组来存储图,然后是输入点的个数和边的个数,以及哪两个点有边。以下是代码片段:
#include<stdio.h>
int eulerGraph[1000][1000] = {{0}};//用来存储图,全局的二维数组
int V,E;//边以及点的个数
printf("please input the number of V (no more than 1000): \n");
scanf("%d",&V);
printf("please input the number of E : \n");
scanf("%d",&E);
printf("please input E : \n");
int i,j;
//Init eulerGraph
for(i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < V; j++) {
eulerGraph[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int m,n;
//create graph
for (i = 0; i < E; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
if ((m >= V) || (n >= V)) {
printf("cannot more than V\n");
return 1;
}
eulerGraph[m][n] = eulerGraph[n][m] = 1;
}打印你的点,看看是否输入正确:
for(i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < V; j++) {
printf("%d ",eulerGraph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}if (!isEulerGraph()) {
printf("the graph is not euler graph!\n");
return 1;
}
int isEulerGraph() {
int i,j;
int count = 0;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (1 == eulerGraph[i][j])
count++;
}
if (0 != count % 2 )
return 0;
count = 0;
}
return 1;
}接下来就是Fleury算法:
fleury();void fleury () {
//set a start ,v0
int temp[1000] ={0};
printf("%d -> ",temp[0]);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int top = 0;
int bridge = 1;
int tmp;
for (i = 0; i < E; i++) {//Traversal all E
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(1 == eulerGraph[temp[top]][j]) {
eulerGraph[temp[top]][j] = eulerGraph[j][temp[top]] = 0;
//if the E is bridge,take a signal in this E,else delete this E
if(isBridge(temp[top],j)) {
tmp = j;
eulerGraph[temp[top]][j] = eulerGraph[j][temp[top]] = 1;
}
else {
top++;
temp[top] = j;
bridge = 0;
printf("%d -> ",j);
break;
}
}
}
//if bridge == 1, no another E in this V that the E is not bridge
if (bridge) {
eulerGraph[temp[top]][tmp] = eulerGraph[tmp][temp[top]] = 0;
top++;
temp[top] = tmp;
printf("%d -> ",tmp);
}
bridge = 1;
}
// for (i = 0; i < (E - 1); i++) {
// printf("%d -> ",temp[i]);
// }
// printf ("%d",temp[E-1]);
}
调用的isBridge函数:
首先,建立一个数组用来存储要判断的Vi能够到达的点,只要数组里面的点未遍历完那么就把这些点能够到达的点,并且在数组中还未遍历过加进来。以下是源代码:
int isBridge (int m, int k) {
int temp[1000] = {-1};
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
temp[i] = -1;
}
int tmp = 0;
temp[tmp] = m;
int n = 0;
//判断从m->k是否还有其他路径
for (tmp = 0; temp[tmp] != -1; tmp++ ) {
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (eulerGraph[temp[tmp]][i] == 1 && i == k) {
return 0;//because is exist another way to k,so m->k is not bridge
}
if (eulerGraph[temp[tmp]][i] == 1 && isExist(temp,i) == 0) {//将当前的点有边的点,前面没有到过的点加入到数组当中
n++;
temp[n] = i;//take new V into temp array
}
}
}
//not found k,so m->k is bridge
return 1;
}下面是判断之前是否已经遍历过这个点了,数组中是否存在
int isExist (int *temp,int m) {
int i = 0;
while (temp[i] != -1) {
if (temp[i] == m)
return 1;
i++;
}
return 0;
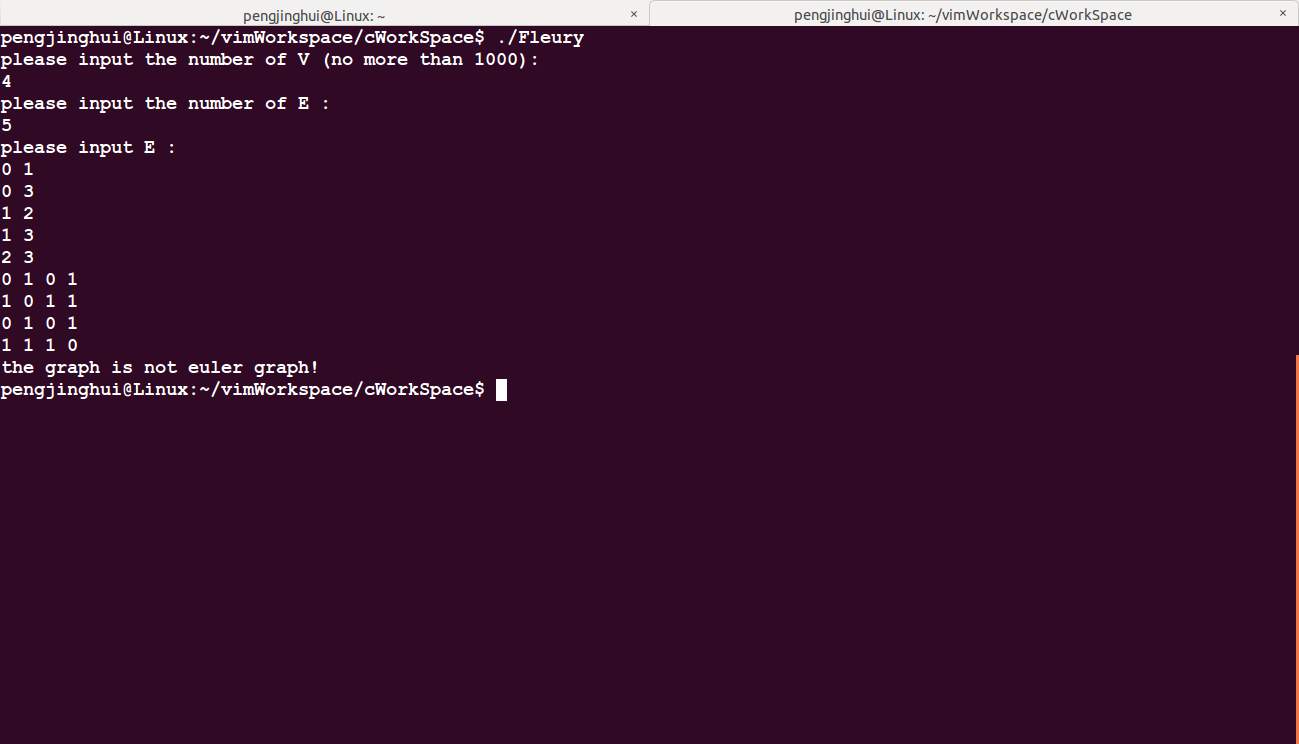
}测试非欧拉图:
测试欧拉图一:
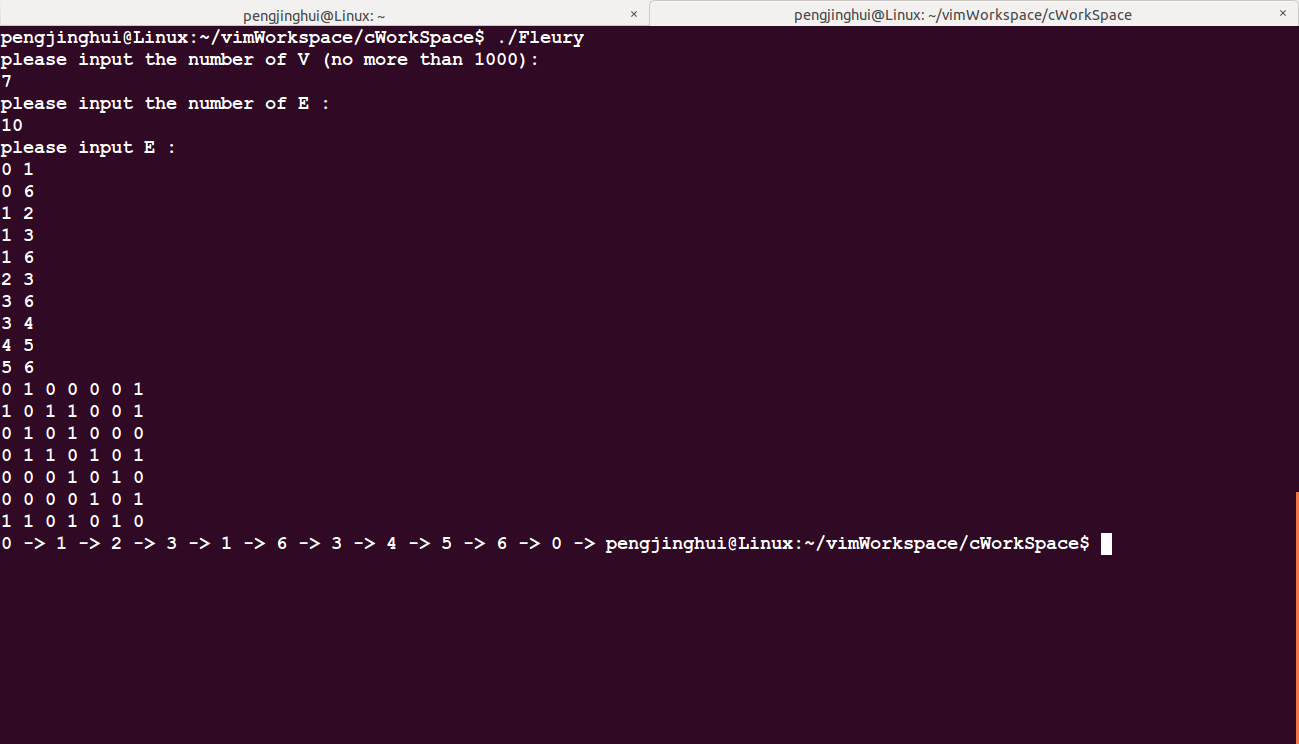
测试欧拉图二:(本人有点懒,所以就不打算使用手动输入的方式喽,采用输入重定向的方式来进行输入,大家平时测试的时候也可以这样做,毕竟比较方便一点)
输入:
7
21
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 4
0 5
0 6
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 4
3 5
3 6
4 5
4 6
5 6
输出:
以上就是我对于Fleury算法的理解,如果觉得还可以,请点个赞或者在下方评论,以下是我的源代码:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: Fleury.c
> Author: pengjinghui
> Mail: pengjinghui@126.com
> Created Time: 2015年09月24日 星期四 21时56分27秒
************************************************************************/
#include<stdio.h>
int eulerGraph[1000][1000] = {{0}};//用来存储图,全局的二维数组
int V,E;//边以及点的个数
int isEulerGraph() {
int i,j;
int count = 0;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (1 == eulerGraph[i][j])
count++;
}
if (0 != count % 2 )
return 0;
count = 0;
}
return 1;
}
int isExist (int *temp,int m) {
int i = 0;
while (temp[i] != -1) {
if (temp[i] == m)
return 1;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
int isBridge (int m, int k) {
int temp[1000] = {-1};
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
temp[i] = -1;
}
int tmp = 0;
temp[tmp] = m;
int n = 0;
//判断从m->k是否还有其他路径
for (tmp = 0; temp[tmp] != -1; tmp++ ) {
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (eulerGraph[temp[tmp]][i] == 1 && i == k) {
return 0;//because is exist another way to k,so m->k is not bridge
}
if (eulerGraph[temp[tmp]][i] == 1 && isExist(temp,i) == 0) {//将当前的点有边的点,前面没有到过的点加入到数组当中
n++;
temp[n] = i;//take new V into temp array
}
}
}
//not found k,so m->k is bridge
return 1;
}
void fleury () {
//set a start ,v0
int temp[1000] ={0};
printf("%d -> ",temp[0]);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int top = 0;
int bridge = 1;
int tmp;
for (i = 0; i < E; i++) {//Traversal all E
for (j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(1 == eulerGraph[temp[top]][j]) {
eulerGraph[temp[top]][j] = eulerGraph[j][temp[top]] = 0;
//if the E is bridge,take a signal in this E,else delete this E
if(isBridge(temp[top],j)) {
tmp = j;
eulerGraph[temp[top]][j] = eulerGraph[j][temp[top]] = 1;
}
else {
top++;
temp[top] = j;
bridge = 0;
printf("%d -> ",j);
break;
}
}
}
//if bridge == 1, no another E in this V that the E is not bridge
if (bridge) {
eulerGraph[temp[top]][tmp] = eulerGraph[tmp][temp[top]] = 0;
top++;
temp[top] = tmp;
printf("%d -> ",tmp);
}
bridge = 1;
}
// for (i = 0; i < (E - 1); i++) {
// printf("%d -> ",temp[i]);
// }
// printf ("%d",temp[E-1]);
}
int main () {
printf("please input the number of V (no more than 1000): \n");
scanf("%d",&V);
printf("please input the number of E : \n");
scanf("%d",&E);
printf("please input E : \n");
int i,j;
//Init eulerGraph
for(i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < V; j++) {
eulerGraph[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int m,n;
//create graph
for (i = 0; i < E; i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
if ((m >= V) || (n >= V)) {
printf("cannot more than V\n");
return 1;
}
eulerGraph[m][n] = eulerGraph[n][m] = 1;
}
for(i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < V; j++) {
printf("%d ",eulerGraph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
if (!isEulerGraph()) {
printf("the graph is not euler graph!\n");
return 1;
}
fleury();
}























 2768
2768

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








