LinkedList的模拟实现(双向链表)
// 2、无头双向链表实现
public class MyLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){ }
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){}
public void display(){}
public void clear(){}
}具体实现参考如下:
public class MyLinkedList {
public class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head ;
public ListNode last ;
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode a = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null){
head = a;
last = a;
return;
}
a.next = head;
head.prev = a;
head = a;
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode a = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null){
head = a;
last = a;
return;
}
last.next = a;
a.prev = last;
last = a;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()){
addLast(index);
return;
}
ListNode a = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = head;
while(index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
cur.prev.next = a;
a.prev = cur.prev;
a.next = cur;
cur.prev = a;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else{
last = null;
}
return;
}
if(cur.next == null){
cur.prev.next = null;
last = last.prev;
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
} else {
last = null;
}
}
if (cur.next == null) {
cur.prev.next = null;
last = last.prev;
} else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
ListNode cur = head;
int len = 0;
while(cur != null){
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
public void display(){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear(){
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curN;
}
head = null;
last = null;
}
}
LinkedList的使用
LinkedList介绍
LinkedList
的底层是双向链表结构
(
链表后面介绍
)
,由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的节点中,然后通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高。
具体可以去看官方文档:
LinkedList (Java Platform SE 8 )
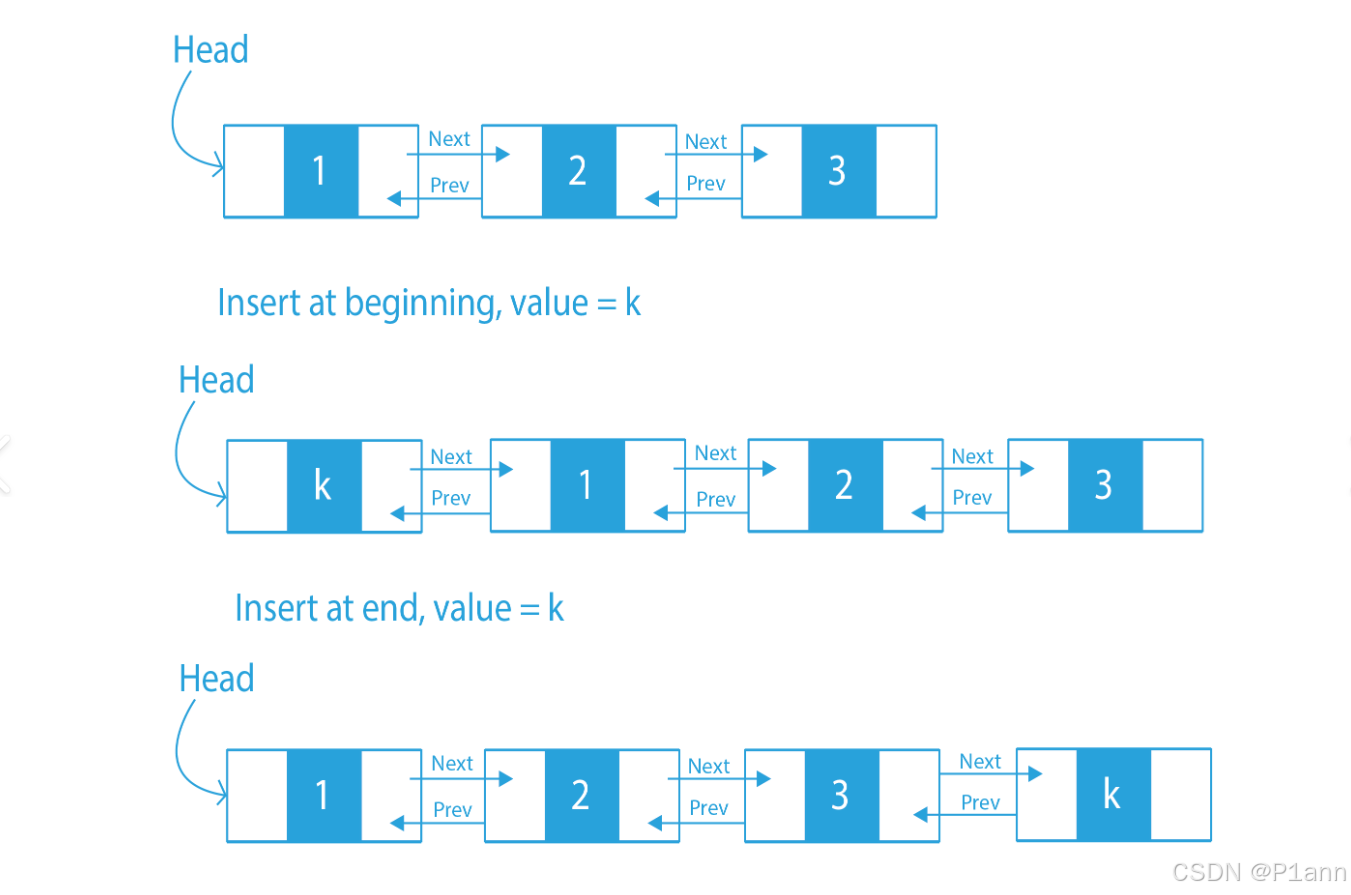
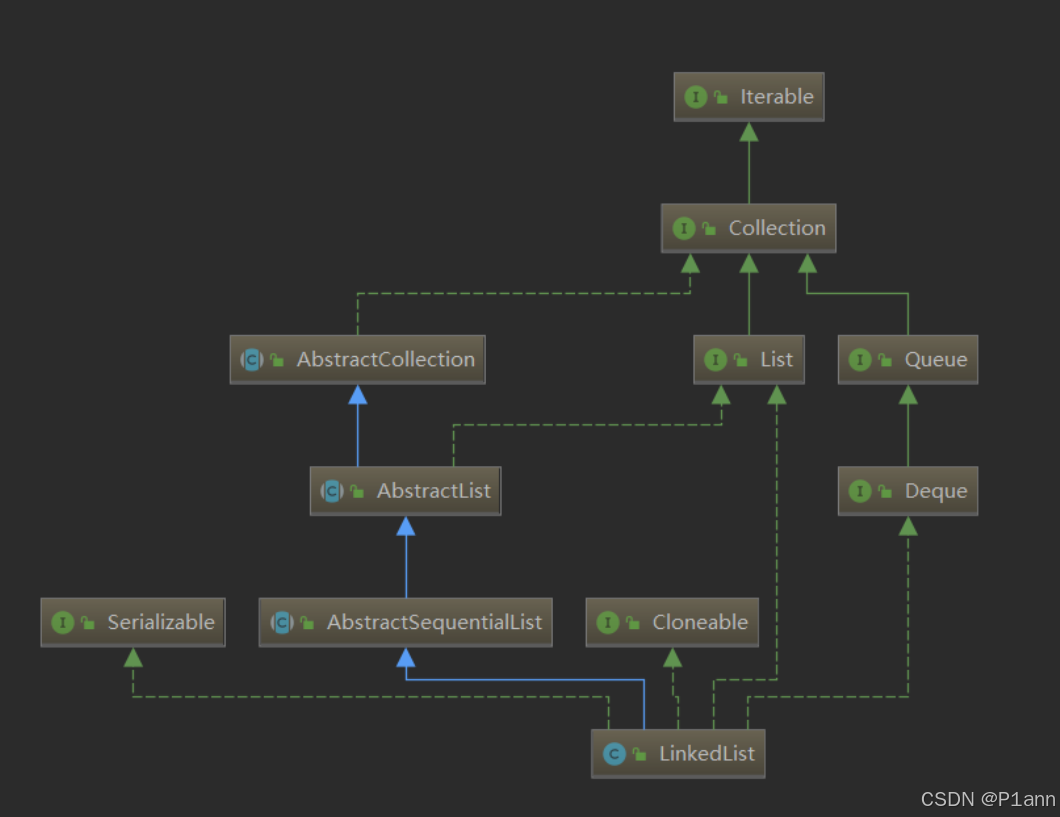
在集合框架中,
LinkedList
也实现了
List
接口,具体如下:
LinkedList的使用
LinkedList的构造
|
方法
|
解释
|
|
LinkedList
()
|
无参构造
|
|
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c)
|
使用其他集合容器中元素构造
List
|
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
// 使用ArrayList构造LinkedList
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList1 = new LinkedList<>(arrayList);LinkedList的常用方法介绍
|
方法
|
解释
|
|
boolean
add
(E e)
|
尾插
e
|
|
void
add
(int index, E element)
|
将
e
插入到
index
位置
|
|
boolean
addAll
(Collection<? extends E> c)
|
尾插
c
中的元素
|
|
E
remove
(int index)
|
删除
index
位置元素
|
|
boolean
remove
(Object o)
|
删除遇到的第一个
o
|
|
E
get
(int index)
|
获取下标
index
位置元素
|
|
E
set
(int index, E element)
|
将下标
index
位置元素设置为
element
|
|
void
clear
()
|
清空
|
|
boolean
contains
(Object o)
|
判断
o
是否在线性表中
|
|
int
indexOf
(Object o)
|
返回第一个
o
所在下标
|
|
int
lastIndexOf
(Object o)
|
返回最后一个
o
的下标
|
|
List<E>
subList
(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
|
截取部分
list
|
代码使用示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList1 = new LinkedList<>(arrayList);
linkedList1.add(1,4);
linkedList1.addAll(arrayList);
linkedList1.remove(2);
Integer c = linkedList1.get(2);
System.out.println(c);
List<Integer> link = linkedList1.subList(1,4);
for(Integer x : linkedList1){
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
System.out.println("==========");
for(Integer x : link){
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}LinkedList的遍历
遍历有三种方法,分别是for,foreach和Iterator。
代码如下:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList1 = new LinkedList<>(arrayList);
linkedList1.add(1, 4);
linkedList1.addAll(arrayList);
linkedList1.remove(2);
Integer c = linkedList1.get(2);
System.out.println(c);
List<Integer> link = linkedList1.subList(1, 4);
// foreach遍历
for (Integer x : linkedList1) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
System.out.println("==========");
for (Integer x : link) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> a = linkedList1.listIterator();
while (a.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(a.next() + " ");
}
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> b = linkedList1.listIterator(linkedList1.size());
while (b.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(b.previous() + " ");
}
}
}ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
|
不同点
|
ArrayList
|
LinkedList
|
|
存储空间上
|
物理上一定连续
|
逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续
|
|
随机访问
|
支持
O(1)
|
不支持:
O(N)
|
|
头插
|
需要搬移元素,效率低
O(N)
|
只需修改引用的指向,时间复杂度为
O(1)
|
|
插入
|
空间不够时需要扩容
|
没有容量的概念
|
|
应用场景
|
元素高效存储
+
频繁访问
|
任意位置插入和删除频繁
|





















 1217
1217

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








