Iahub likes trees very much. Recently he discovered an interesting tree named propagating tree. The tree consists of n nodes numbered from 1 to n, each node i having an initial value ai. The root of the tree is node 1.
This tree has a special property: when a value val is added to a value of node i, the value -val is added to values of all the children of node i. Note that when you add value -val to a child of node i, you also add -(-val) to all children of the child of node i and so on. Look an example explanation to understand better how it works.
This tree supports two types of queries:
- "1 x val" — val is added to the value of node x;
- "2 x" — print the current value of node x.
In order to help Iahub understand the tree better, you must answer m queries of the preceding type.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200000). The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1000). Each of the next n–1 lines contains two integers vi and ui (1 ≤ vi, ui ≤ n), meaning that there is an edge between nodes vi and ui.
Each of the next m lines contains a query in the format described above. It is guaranteed that the following constraints hold for all queries:1 ≤ x ≤ n, 1 ≤ val ≤ 1000.
For each query of type two (print the value of node x) you must print the answer to the query on a separate line. The queries must be answered in the order given in the input.
5 5 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 1 2 3 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 4
3 3 0
The values of the nodes are [1, 2, 1, 1, 2] at the beginning.
Then value 3 is added to node 2. It propagates and value -3 is added to it's sons, node 4 and node 5. Then it cannot propagate any more. So the values of the nodes are [1, 5, 1, - 2, - 1].
Then value 2 is added to node 1. It propagates and value -2 is added to it's sons, node 2 and node 3. From node 2 it propagates again, adding value 2 to it's sons, node 4 and node 5. Node 3 has no sons, so it cannot propagate from there. The values of the nodes are [3, 3, - 1, 0, 1].
You can see all the definitions about the tree at the following link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(graph_theory)
这题看了,想了下就会了.. 只不过拍出来太慢了,个人还需要大大提高代码能力
首先,题目给了一棵树,但这棵树的结点顺序不是我们希望的,
这是这个方法解决这道题最重要的地方,所以我特意做了两幅图来解释(做得不好勿喷0.0)
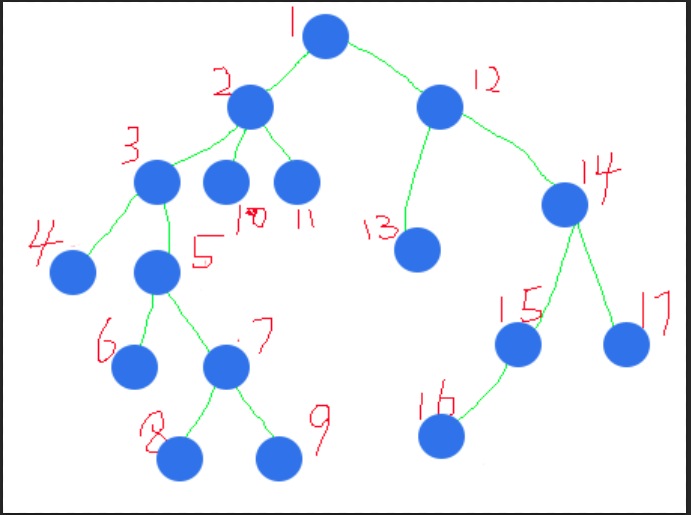
如上图这一棵树
我们会发现,1的儿子是2,3;2的儿子是4,6,7;16的儿子却是5
这样子,我们就不好进行操作了
我们希望对一个点加上一个val的时候,直接将下它和它的子树所有的点加上一个值,最后查询的时候,直接查询对应点的值,并用一些技巧取正负即可
那么,我们就希望待加上val值的结点和它的子树的所有结点,整体的编号是逐一递增的,例4 5 6 7 8...这样子
如果能构成一个这个样子的结构,我们在进行第一种操作时,只需从它到 它子树最远可到的点 之间的所有点加上一个val值即可
那么,这就可以用一棵线段树来做了,这样子就满足了线段树所需要的点紧密分布的条件,其更新和查询的时间复杂度是O(log)级别的
那么,我们将上面那一棵树映射成下面这一棵树:
(将结点乱而无序的一棵树 变成 结点有序有规律的一棵树)
发现,点的编号顺序改变了
根结点始终为1,这个不变
每个结点i,其子树的结点是 i,i+1,i+2,i+3,...... ,i+n,n为其子树的结点总数
例如,7的子树,就是7,8,9三个结点;14的子树是,14,15,16,17四个结点
而2的子树就是,2,3,.......,11 十个结点
我们会发现,这样子的一个结构,正好满足其子树的结点编号是类似于自然数那样紧密分布的,例4,5,6,7,8.......
那么,我们可以考虑用树上hash的办法,将原树(第一幅图)的结点映射到现在这棵树的结点,可以保证这个映射是双射(单射+满射)
同时,我们可以知道树(指的是现在这棵树,下同)每个结点其子树最远到达哪个结点
比如:7最远到达9;14最远到达17;1最远到达17,6最远达到6;
那么,当进行第一种操作的时候,就只需要在线段树上将from到to进行懒操作更新,其中from是当前结点,to是最远可达结点;这是相当快速的
接下来讲第二种操作,查询操作
有了上面的方法,查询操作就显而易见。先找到需要查询的结点x在树上对应的是哪个结点now,然后查询now的值
就可以了吗?
现在就遇到了一个问题,我们会发现,根据题意,将14加上val的时候,15和17是加上一个-val,16是加上一个val
如果子树都只是加上一个val,而没有什么正负,就好了,可题意偏偏有,怎么办呢?
我的方法是用两棵树,一棵称为奇树,一棵为偶树
举个栗子来说明:
我需要将2结点加上一个val,我们发现,2这个结点在第2层,“”第2层“中的2是偶数,那么就在偶树上进行操作
将偶树中,2到11加上一个val
同样,如果这个结点在奇数层(比如14,在第3层),就在奇树上进行操作
然后,查询的时候
如果now在偶数层,ans=初始值+偶树上now的值-奇树上now的值
如果now在奇数层,ans=初始值+奇树上now的值-偶树上now的值
具体为什么这样子可以成功,相信大家都能够看出来吧。我希望花力气再去说明了
上面方法所需要的 记录每个原树结点对应现树的哪个结点,现树每个结点的子树最远到哪个结点,现树每个结点在哪一层
这些方法,都可以用dfs搜索来实现,注意标记染色即可,具体怎么写 我就不提了
该方法的时间复杂度是:O(n*logn),n为原树结点的个数
代码如下:
//Hello. I'm Peter.
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<cctype>
#include<ctime>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
#define peter cout<<"i am peter"<<endl
#define input freopen("data.txt","r",stdin)
#define randin srand((unsigned int)time(NULL))
#define INT (0x3f3f3f3f)*2
#define LL (0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f)*2
#define gsize(a) (int)a.size()
#define len(a) (int)strlen(a)
#define slen(s) (int)s.length()
#define pb(a) push_back(a)
#define clr(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define clr_minus1(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define clr_INT(a) memset(a,INT,sizeof(a))
#define clr_true(a) memset(a,true,sizeof(a))
#define clr_false(a) memset(a,false,sizeof(a))
#define clr_queue(q) while(!q.empty()) q.pop()
#define clr_stack(s) while(!s.empty()) s.pop()
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i < b; i++)
#define dep(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i > b; i--)
#define repin(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define depin(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--)
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define eps 1e-6
#define MOD 1000000007
#define MAXN 200100
#define N
#define M
struct Segment_Tree
{
int left,right;
ll sum,lazy;
}eventree[4*MAXN],oddtree[4*MAXN];
void plant_tree(int id,int l,int r,Segment_Tree *tree){
tree[id].left=l,tree[id].right=r;
tree[id].lazy=0;
if(l==r){
tree[id].sum=0;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
plant_tree(2*id,l,mid,tree);
plant_tree(2*id+1,mid+1,r,tree);
tree[id].sum=tree[2*id].sum+tree[2*id+1].sum;
}
void push_down(int id,Segment_Tree *tree){//lazy operation;
if(!tree[id].lazy) return;
tree[id].sum+=(tree[id].right-tree[id].left+1)*tree[id].lazy;
if(tree[id].left==tree[id].right){
tree[id].lazy=0;
return;
}
tree[2*id].lazy+=tree[id].lazy;
tree[2*id+1].lazy+=tree[id].lazy;
tree[id].lazy=0;
}
void update_leaf(int id,int l,int r,ll val,Segment_Tree *tree){
if(tree[id].left==l && tree[id].right==r){
tree[id].lazy+=val;
push_down(id,tree);
return;
}
push_down(id,tree);
int mid=(tree[id].left+tree[id].right)>>1;
if(r<=mid) update_leaf(2*id,l,r,val,tree);
else if(mid<l) update_leaf(2*id+1,l,r,val,tree);
else{
update_leaf(2*id,l,mid,val,tree);
update_leaf(2*id+1,mid+1,r,val,tree);
}
tree[id].sum=tree[2*id].sum+tree[2*id+1].sum;
}
ll query(int id,int l,int r,Segment_Tree *tree){
if(tree[id].left==l && tree[id].right==r){
push_down(id,tree);
return tree[id].sum;
}
push_down(id,tree);
int mid=(tree[id].left+tree[id].right)>>1;
if(r<=mid) return query(2*id,l,r,tree);
else if(mid<l) return query(2*id+1,l,r,tree);
else return query(2*id,l,mid,tree)+query(2*id+1,mid+1,r,tree);
}
int n,m,a[MAXN];
struct Edge{//It's a tree by description
int from,to,next;
}edge[2*MAXN];
int head[MAXN],w,u,v;
void add_edge(int from,int to){
w+=1;
edge[w].from=from;
edge[w].to=to;
edge[w].next=head[from];
head[from]=w;
}
bool vis[MAXN];
int num_node,nodemap[MAXN],nodeupto[MAXN],nodefloor[MAXN];
void dfs(int now,int floor){
vis[now]=true;
nodemap[now]=++num_node;
int i,to;
for(i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next){
to=edge[i].to;
if(vis[to]) continue;
dfs(to,floor+1);
}
nodefloor[nodemap[now]]=floor;
nodeupto[nodemap[now]]=num_node;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
repin(i,1,n){
scanf("%d",a+i);
}
w=0;
repin(i,1,n){
head[i]=-1;
vis[i]=false;
}
repin(i,1,n-1){
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
add_edge(u,v);
add_edge(v,u);
}
num_node=0;
dfs(1,1);
plant_tree(1,1,n,eventree),plant_tree(1,1,n,oddtree);
repin(ii,1,m){
int type,x,val,from,to,now;
ll ans;
scanf("%d",&type);
switch(type){
case 1:{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&val);
from=nodemap[x];
to=nodeupto[from];
if(nodefloor[from]%2==0) update_leaf(1,from,to,val,eventree);
else update_leaf(1,from,to,val,oddtree);
break;
}
case 2:{
scanf("%d",&x);
now=nodemap[x];
ans=a[x];
if(nodefloor[now]%2==0) ans+=query(1,now,now,eventree)-query(1,now,now,oddtree);
else ans+=query(1,now,now,oddtree)-query(1,now,now,eventree);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
}
}























 825
825











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








