CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner
背景:
项目启动之前,预先加载数据。比如,权限容器、特殊用户数据等。通常我们可以使用监听器、事件来操作。但是,springboot提供了一个简单的方式来实现此类需求,即,CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner。
话不多说,先看源码:
CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 都是两个接口,继承了 Runner 接口。
CommandLineRunner
帮大家翻译一下:接口的实现必须包含在bean中,多个实现了CommandLineRunner的bean可以用@Order注解标识执行顺序。这里还说了,如果需要访问原始 ApplicationArguments 而不是字符串数组,可以使用ApplicationRunner。因为CommandLineRunner中run()方法的参数是字符串数组。
package org.springframework.boot;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link CommandLineRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
* <p>
* If you need access to {@link ApplicationArguments} instead of the raw String array
* consider using {@link ApplicationRunner}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.0.0
* @see ApplicationRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner extends Runner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}
ApplicationRunner
这里的注释与上面CommandLineRunner的注释差不多,就不介绍了。
package org.springframework.boot;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link ApplicationRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.3.0
* @see CommandLineRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner extends Runner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming application arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}
两者的使用:
CommandLineRunner
/**
* @Author: wangrongyi
* @Date: 2024/9/30 10:46
* @Description:
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CommandInitConfig implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("CommandInitConfig执行了");
for (String arg : args) {
log.info("arg = {}", arg);
}
}
}
项目启动之后,接着就会执行所有实现了CommandLineRunner接口的run方法,如果有多个,执行顺序跟bean的注入顺序相同。
如果有携带的参数,直接跟在启动命令后面
java -jar xxx.jar args1 args2 args3

ApplicationRunner
/**
* @Author: wangrongyi
* @Date: 2024/9/30 11:13
* @Description:
*/
@Component
public class ApplicationInitConfig implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
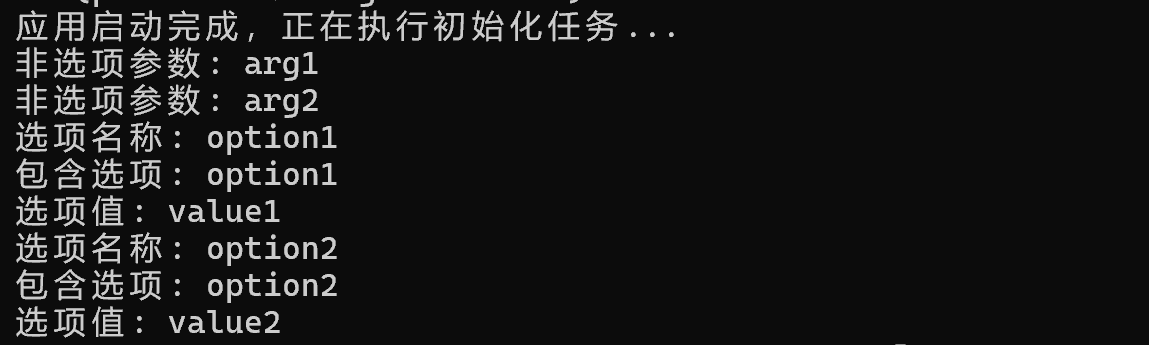
System.out.println("应用启动完成,正在执行初始化任务...");
// 获取非选项参数
String[] nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs().toArray(new String[0]);
for (String arg : nonOptionArgs) {
System.out.println("非选项参数: " + arg);
}
// 获取选项参数
String[] optionNames = args.getOptionNames().toArray(new String[0]);
for (String optionName : optionNames) {
System.out.println("选项名称: " + optionName);
if (args.containsOption(optionName)) {
System.out.println("包含选项: " + optionName);
String[] optionValues = args.getOptionValues(optionName).toArray(new String[0]);
for (String value : optionValues) {
System.out.println("选项值: " + value);
}
}
}
}
}
其中 ApplicationArguments 是 run()函数的参数,简单介绍一下这个接口:
ApplicationArguments 是 Spring Boot 提供的一个接口,用于处理命令行参数。它提供了一种更加结构化的方式来处理命令行参数,包括非选项参数(non-option arguments)和选项参数(option arguments)。该接口提供了几个获取参数的方法:
-
getNonOptionArgs():获取非选项参数列表。
获取所有非选项参数,即不带 - 或 – 的参数
-
getOptionNames():获取所有选项名称。
获取所有选项名称,即带 - 或 – 的参数。
-
containsOption(String name):判断是否包含指定选项。
判断是否包含指定选项。
-
getOptionValues(String name):获取指定选项的所有值。
获取指定选项的所有值。
ApplicationRunner 适合参数复杂的情况,打包后通过命令启动:
java -jar xxx.jar --option1=value1 --option2=value2 arg1 arg2
总结:
两者都可以在程序启动后执行操作,且都支持获取启动参数并进行处理。
使用 ApplicationArguments:通过 ApplicationRunner 和 ApplicationArguments 来处理参数。
使用 CommandLineRunner:通过 run(String… args) 方法来处理参数。
那么实现了ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner接口的run方法是如何调用的呢?
下面我们跟随源码解读:
- 进入主程序的run方法。
-
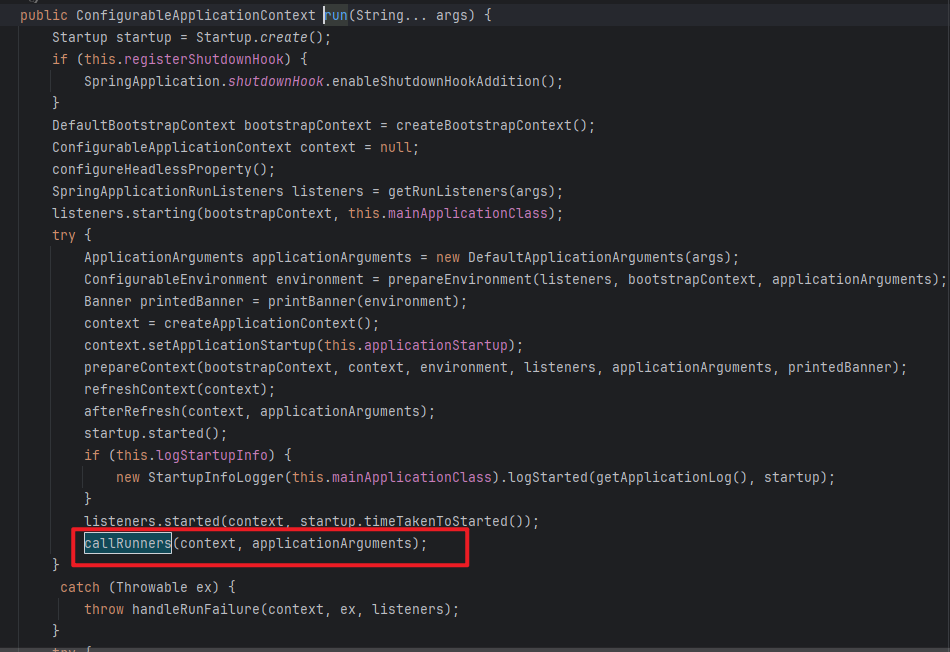
找到callRunners()方法
-
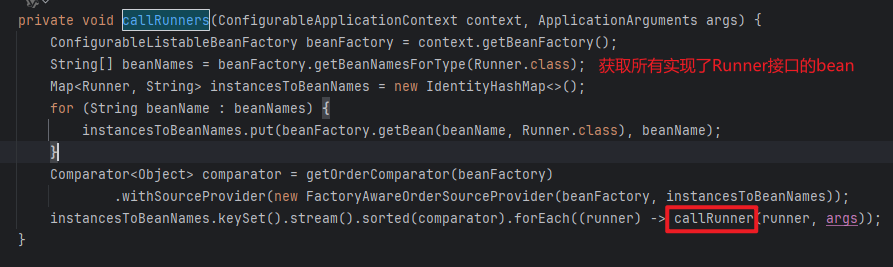
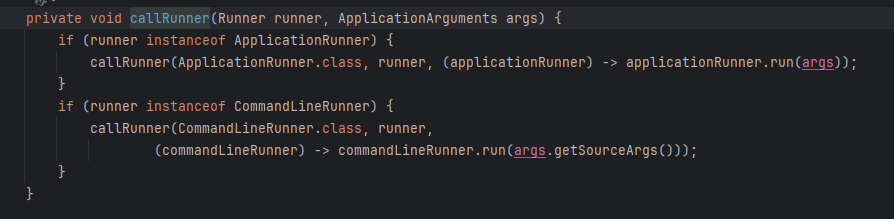
点进去之后会发现首选获取所有实现了Runner接口的bean,Runner接口只有两个子接口,所有也就是找到了所有实现了ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner接口的bean,然后遍历每个bean,调用callRunner方法执行。
-
callRunner方法中区分了bean的类型,执行不同的代码。
























 760
760

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








