Java多线程编程-Thread API
当我们想让主线程等待相应的子线程全部运行完在运行完怎么解决这个问题呢? 我们可以使用Thread.join()方法
Thread.join()方法
等待当前线程死亡
源码:
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
还有一个带参数join方法,等会试试
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
我们先不使用join方法试试,对比一下:
线程:
public class ThreadNoJoinT1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int count = (int) (Math.random() * 100000);
System.out.println(count);
Thread.sleep(count);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这里使用sleep故意让线程时间变长一点,等主线程运行。
运行代码:
public class ThreadNoJoinMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadNoJoinT1 threadNoJoinT1 = new ThreadNoJoinT1();
threadNoJoinT1.start();
System.out.println("if sub thread had do it after is show?");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
运行结果:
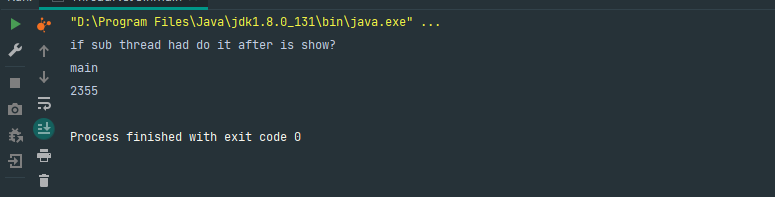
从运行结果来看,主线程没有等子线程运行完在打印,我们现在使用join方法试试,修改运行代码:
public class ThreadNoJoinMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ThreadNoJoinT1 threadNoJoinT1 = new ThreadNoJoinT1();
threadNoJoinT1.start();
threadNoJoinT1.join();
System.out.println("if sub thread had do it after is show?");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
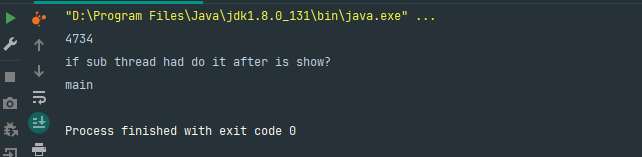
有运行结果可以看出,主线程等子线程运行完成之后再运行。
我们再来看看带参数的join方法,会有不一样的结果,修改代码:
public class ThreadNoJoinMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ThreadNoJoinT1 threadNoJoinT1 = new ThreadNoJoinT1();
threadNoJoinT1.start();
threadNoJoinT1.join(1000);
System.out.println("if sub thread had do it after is show?");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
join 1秒,我们在看看线程类:
public class ThreadNoJoinT1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int count = (int) (Math.random() * 10000);
System.out.println(count);
Thread.sleep(count);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
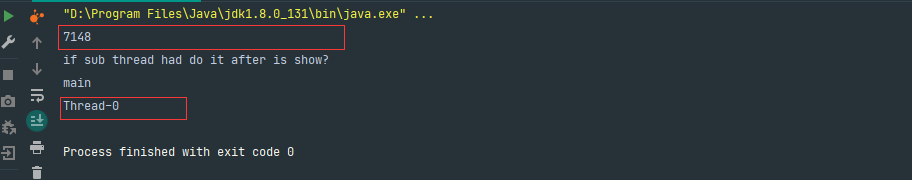
添加join的时候,说明子线程在1秒钟没有结束,所以thread-0线程名会打出来,我们看看join原理,从源码可以看出,其实是通过Object.wait()方法处理的。
由此可以得出,join的作用使所属的线程对象正常执行run方法中的任务,而使当前线程进行无限期等待,等待子线程销毁后再继续执行线程后的代码。
在当前线程中如果发生异常导致线程对象中断,当前线程出现异常。
public class ThreadJoinExceptionMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
System.out.println("thread2 is run end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("thread2 is happend exception end");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
thread2.interrupt();
});
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
運行結果:
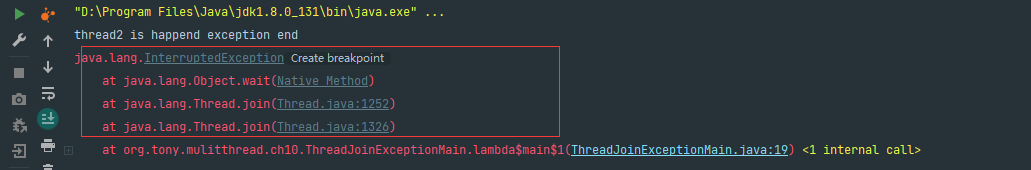
我通过源码可以看看,Thread.sleep()和Thread.join()的区别:
sleep方法不释放锁,join方法释放锁,join是通过wait方法使用的。我们创建三个线程试试:
public class ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 extends Thread {
public synchronized void testFun() {
System.out.println("print timer:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("current time :" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("current end time:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1 extends Thread {
private ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
public ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1(ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2, String threadName) {
this.setName(threadName);
this.threadSleepDontGetupLockT2 = threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (threadSleepDontGetupLockT2) {
threadSleepDontGetupLockT2.start();
Thread.sleep(6000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT3 extends Thread {
private ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
public ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT3(ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2, String threadName) {
this.setName(threadName);
this.threadSleepDontGetupLockT2 = threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
threadSleepDontGetupLockT2.testFun();
}
}
运行代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2 = new ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2();
ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1 threadSleepDontGetupLockT1 = new ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1(threadSleepDontGetupLockT2, "thread01");
threadSleepDontGetupLockT1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT3 threadSleepDontGetupLockT3 = new ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT3(threadSleepDontGetupLockT2, "thread02");
threadSleepDontGetupLockT3.start();
}
运行结果:
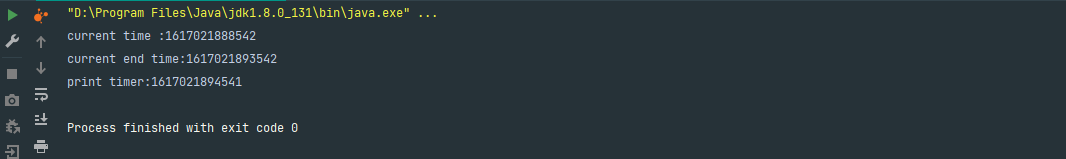
由此可以得出,sleep方法不释放锁。我们可以将sleep改为join试试:
public class ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1 extends Thread {
private ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
public ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT1(ThreadSleepDontGetupLockT2 threadSleepDontGetupLockT2, String threadName) {
this.setName(threadName);
this.threadSleepDontGetupLockT2 = threadSleepDontGetupLockT2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (threadSleepDontGetupLockT2) {
threadSleepDontGetupLockT2.start();
// Thread.sleep(6000);
threadSleepDontGetupLockT2.join();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
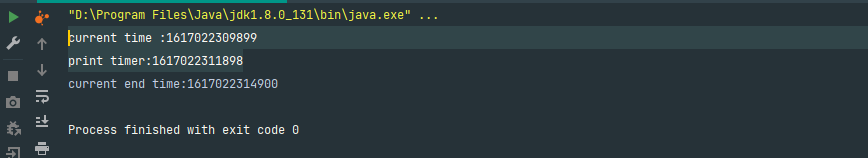
线程3不需要等待线程1释放锁就可以运行,由此可得join方法是释放锁的。






















 843
843











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








