Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
For example, you may serialize the following tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
as
"[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
, just the same as
how LeetCode OJ serializes a binary tree
. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Note: Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your serialize and deserialize algorithms should be stateless.
要求我们将二叉树序列化和反序列化。
序列化:是对象的信息进行存储。
这里采用的方法是二叉树的层次遍历。用queue来存储节点
以上面的二叉树为例,第一层输出 1
第二层输出2,3
第三层输出null null 3
第四层输出null null null null
最终输出的String为:1,2,3,null,null,4,5,null,null,null,null
(因为null 变量不能放入queue中,如果碰到了null变量,伪造一个值为Inter.Max_Value的节点,用来替代null节点)
Serialize的代码:
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<TreeNode> store = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return "null";
}
store.add(root);
while (!store.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode temp = store.poll();
if (temp.val == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
sb.append("null,");
} else {
sb.append(temp.val + ",");
if (temp.left != null) {
store.add(temp.left);
} else {
store.add(new TreeNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
if (temp.right != null) {
store.add(temp.right);
} else {
store.add(new TreeNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
}
}
return sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1).toString();
}对于给定的String: 1,2,3,null,null,4,5,null,null,null,null
反序列的考虑是,给定一个节点,去找它对应的左节点和右节点。
如何找呢?
我们知道对于一棵满二叉树来说。
将节点的值层次遍历,放在数组中,下标为i 的节点,它的左节点的下标为2 * i + 1,它的右节点的下标为 2 * i + 2.
0
/ \
1 2
/ \ / \
3 4 5 6
如图,满二叉树,这里节点的index 和 值相当,易得出这个规律。
现在我们的树中,是会有null节点的。受满二叉树启发。
如果我们统计一个某个节点前面的null节点的个数。
那么不是可以通过 2 * ( i - num of null ) + 1, 2 * ( i - num of null ) + 1得到它的左右节点的下标了吗?
代码:
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] list = data.split(",");
if (list.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int[] missNum = new int[list.length];
int missCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
missNum[i] = missCount;
if (list[i].equals("null")) {
missCount++;
}
}
return buildTree(list, 0, missNum);
}
private TreeNode buildTree(String[] list, int index, int[] missNum) {
if (list[index].equals("null")) {
return null;
}
int val = Integer.parseInt(list[index]);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
root.left = buildTree(list, (index - missNum[index]) * 2 + 1, missNum);
root.right = buildTree(list, (index - missNum[index]) * 2 + 2, missNum);
return root;
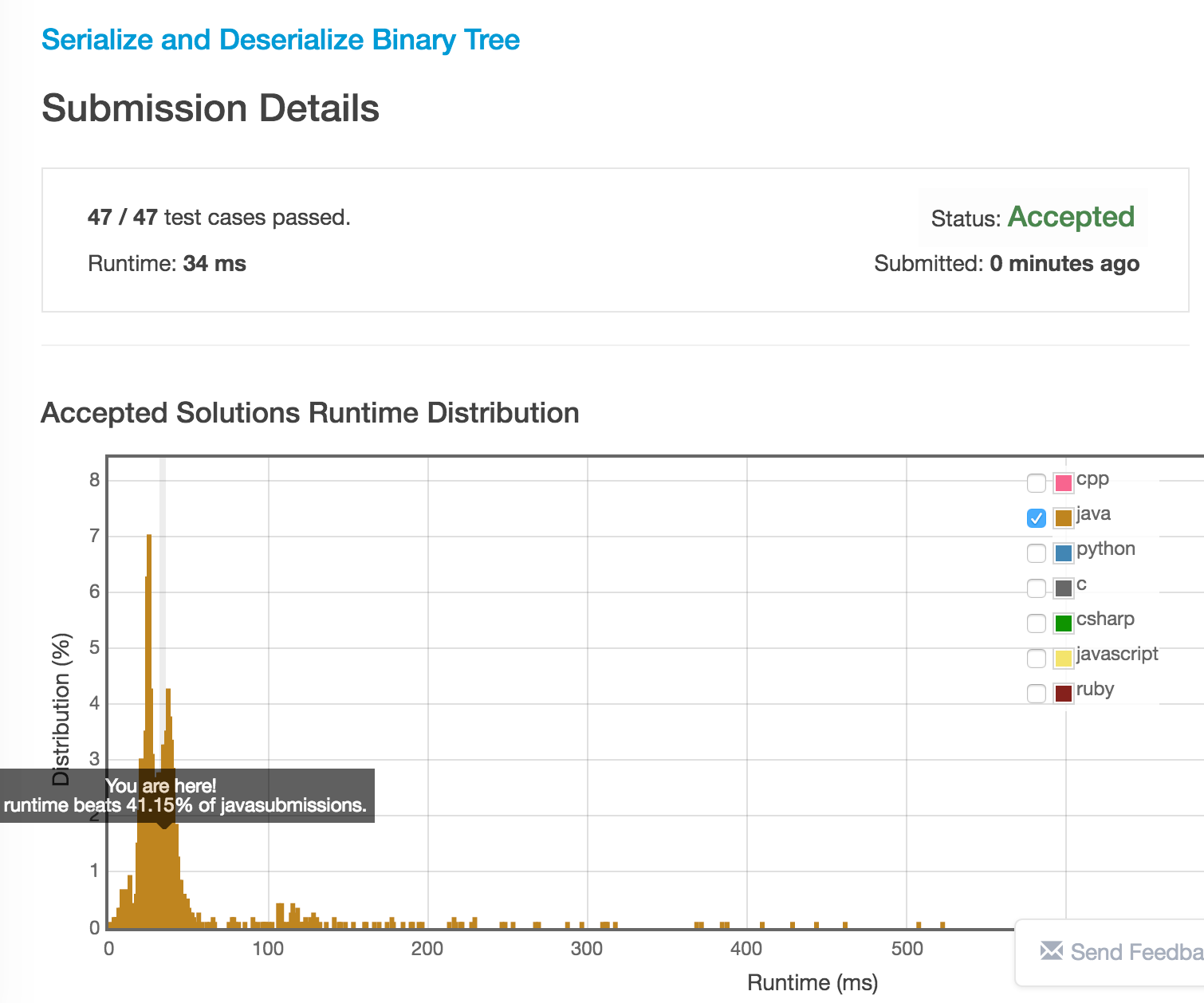
}最后,
运行时间:






















 190
190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








