Given a string s and a dictionary of words dict, add spaces in s to construct a sentence where each word is a valid dictionary word.
Return all such possible sentences.
For example, given
s = "catsanddog",
dict = ["cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"].
A solution is ["cats and dog", "cat sand dog"].
跟前面的单词分割系列1 的区别在于,这次需要给出所有的组合结果。
做这道题的思想跟前面的还是差不多,对于词典中的每一个词,如果跟当前的string的前面是相同的。那么看看剩下的string能不能被分割。
并且在递归的过程中,存储word。同时设置isReach数组,用来标记下标以 begin开始的能不能被分割。
如果isRead显示不能分割,那就没必要继续递归了。
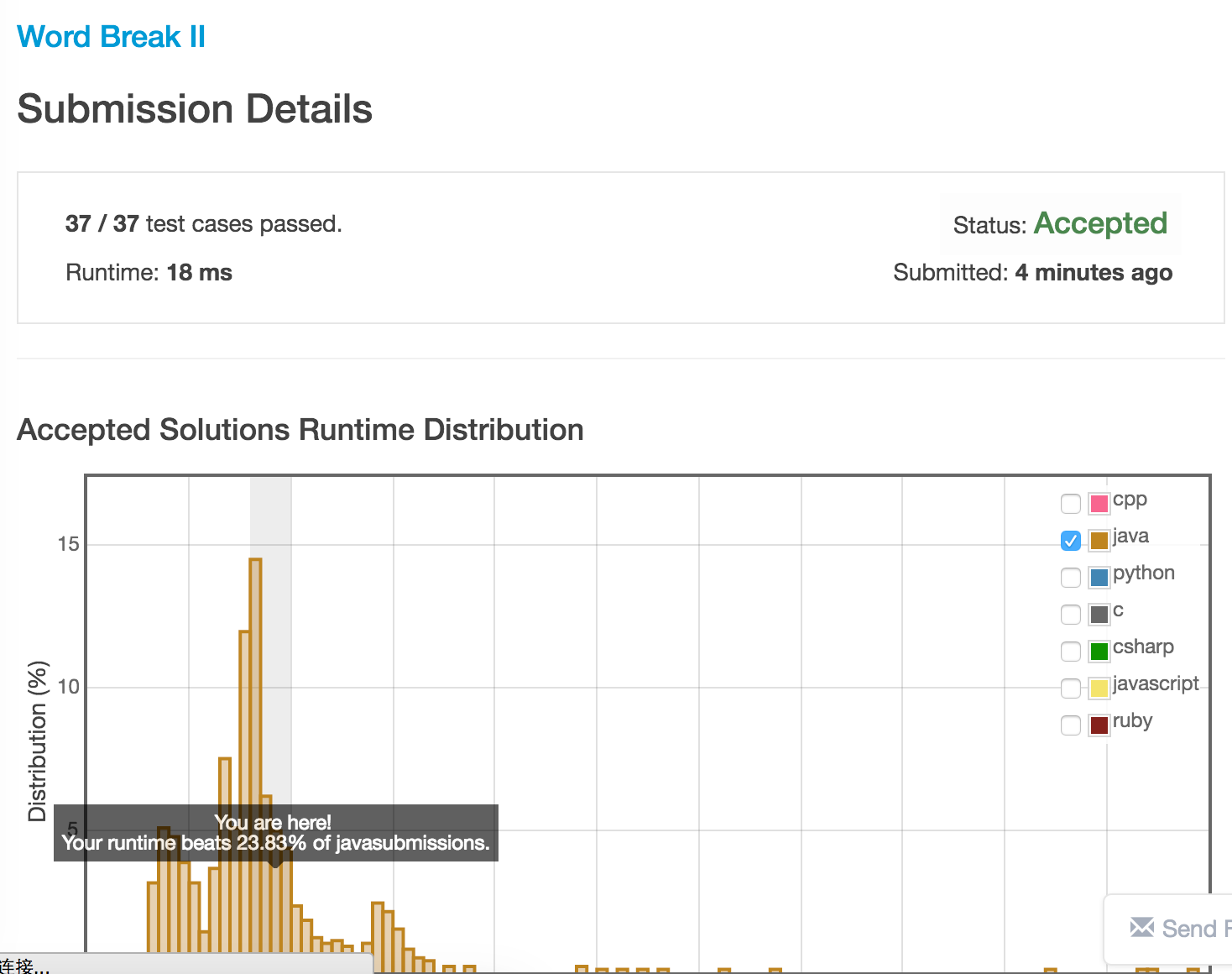
运行时间:
代码:
public class WordBreakII {
public List<String> wordBreak(String s, Set<String> wordDict) {
int[] canReach = new int[s.length()];
Arrays.fill(canReach, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
doWordBreak(result, new StringBuilder(), canReach, s, 0, wordDict);
Collections.sort(result);
return result;
}
private boolean doWordBreak(List<String> result, StringBuilder sb, int[] canReach, String s, int begin, Set<String> wordDict) {
if (begin > s.length()) {
return false;
}
if (begin == s.length()) {
String temp = sb.toString();
result.add(temp.substring(0, temp.length() - 1));
return true;
}
if (canReach[begin] == -1) {
return false;
}
boolean isRead = false;
for (String word : wordDict) {
if (begin + word.length() <= s.length()) {
if (s.substring(begin, begin + word.length()).compareTo(word) == 0) {
sb.append(word + " ");
boolean curResult = doWordBreak(result, sb, canReach, s, begin + word.length(), wordDict);
if (curResult) {
isRead = true;
}
sb.delete(sb.length() - word.length() - 1, sb.length());
}
}
}
canReach[begin] = isRead ? 1 : -1;
return isRead;
}
}





















 1185
1185

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








