工厂类,提供了一些工具方法。支持以下各种方法:
- 创建并返回设置有常用配置字符串的 ExecutorService 的方法。
- 创建并返回设置有常用配置字符串的 ScheduledExecutorService 的方法。
- 创建并返回“包装的”ExecutorService 方法,它通过使特定于实现的方法不可访问来禁用重新配置。
- 创建并返回 ThreadFactory 的方法,它可将新创建的线程设置为已知的状态。
- 创建并返回非闭包形式的 Callable 的方法,这样可将其用于需要 Callable 的执行方法中。
Executors类位于java.util.concurrent包下,提供了一些方便构建ThreadPoolExecutor和线程管理的方法。
主要方法有以下几个:
1.创建一个固定大小的线程池
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
} 参数nThreads为线程池的大小,线程keepAliveTime为0,ThreadPoolExecutor中启动的corePoolSize线程启动后会一直运行,并不会超时退出,线程池的缓冲队列为LinkedBlockingQueue,大小为Integer.MAX_VALUE,当使用此线程池时,在同时执行的任务数量超过corePoolSize时,将会放入LinkedBlockingQueue,在LinkedBlockingQueue中的任务需要等待其他线程空闲后来执行。
2.创建一个corePoolSize为0,最大线程数为整形最大值得线程池,
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
} 线程keepAliveTime为60,单位为秒,缓存队列为SynchronousQueue的线程池。在使用时,放入线程池的任务都会复用或启动新的线程来执行,直到线程数达到整形最大数后抛出异常RejectedExecutionException。与直接实例化Thread来处理的好处就是在60秒内可重用池内已创建的线程。
3.创建一个大小为1的固定线程池
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}当使用此线程池时,同时执行的任务只有1个,其他任务在LinkedBlockingQueue中,等待轮询执行。
4.创建一个corePoolSize为传入参数,最大线程数为整形的最大数的线程池,此线程池支持定时以及周期性执行任务
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
} ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类的构造:
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
} 此线程池keepAliveTime参数为0,缓存对列为DelayedWorkQueue。
jdk1.5之前的版本中更多的是借助Timer类来实现,Timer和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的区别:
a.Timer单线程运行,一旦任务执行缓慢,下一个任务就会推迟,而如果使用了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor线程数可以自行控制
b.当Timer中的一个任务抛出异常时,会导致其他所有任务不在执行
c.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor可执行异步的任务,从而得到执行结果
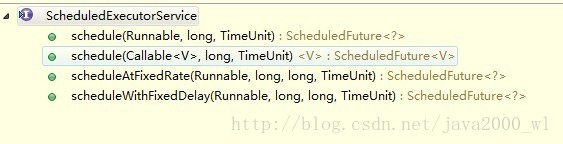
ScheduledExecutorService接口继承了ExecutorService,在ExecutorService的基础上新增了以下几个方法:
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit); command:执行的任务 Callable或Runnable接口实现类
delay:延时执行任务的时间
unit:延迟时间单位
示例:
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
ScheduledFuture<String> scheduledFuture = executorService.schedule(new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
return "call";
}
}, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(scheduledFuture.get());
executorService.shutdown(); 延迟10秒后,返回call字符串并输出。
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit); command:执行的任务 Callable或Runnable接口实现类
initialDelay:第一次执行任务延迟时间
period:连续执行任务之间的周期,从上一个任务开始执行时计算延迟多少开始执行下一个任务,但是还会等上一个任务结束之后。
unit:initialDelay和period时间单位
示例: 注意看输出结果
final SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("时间:" + sf.format(new Date()) );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 输出结果:
时间:2014-04-01 23:44:48
时间:2014-04-01 23:44:53
时间:2014-04-01 23:44:58
时间:2014-04-01 23:45:03
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit); command:执行的任务 Callable或Runnable接口实现类
initialDelay:第一次执行任务延迟时间
period:连续执行任务之间的周期,从上一个任务全部执行完成时计算延迟多少开始执行下一个任务
unit:initialDelay和period时间单位
final SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("时间:" + sf.format(new Date()) );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 输出结果:
时间:2014-04-01 23:47:38
时间:2014-04-01 23:47:46
时间:2014-04-01 23:47:54
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/java2000_wl/article/details/22333257
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rommel1/article/details/7296695
http://www.xuehuile.com/blog/7458d46dca9e45b0a002e2a40155d8e7.html





















 701
701











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








