一、参数乱码现象
当我去请求第三方接口时,接口接收格式为Form表单的时候,使用HttpClient工具类。这时,对于封装进HttpPost对象里的请求参数,如果有中文参数,会出现乱码的现象。
二、代码现象复现
controller层
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/http")
public class HttpClientController {
@GetMapping(value = "/get")
public PrePayResultVO getHttpClientDemo() {
String url = "https://xxxx.xxxx.com/xxxx/Xxxxx";
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("cardId", "1234567890");
map.put("carNumber", "粤LX255Q");
map.put("parkCode", "1234567890");
map.put("startTime", "2018-09-18");
map.put("endTime", "2018-10-18");
map.put("defferMoney", "0.01");
JSONObject jsonObject = HttpClientUtils.postForForm(url, map);
PrePayResultVO prePayResultVO =JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toString(), PrePayResultVO.class);
return prePayResultVO;
}
}
httpClientUtils
public static JSONObject postForForm(String url, Map<String, String> parms) {
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
ArrayList<BasicNameValuePair> list = new ArrayList<>();
parms.forEach((key, value) -> list.add(new BasicNameValuePair(key, value)));
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
try {
if (Objects.nonNull(parms) && parms.size() >0) {
httpPost.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(list, "UTF-8"));
}
InputStream content = httpPost.getEntity().getContent();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(content, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String readLine = bufferedReader.readLine();
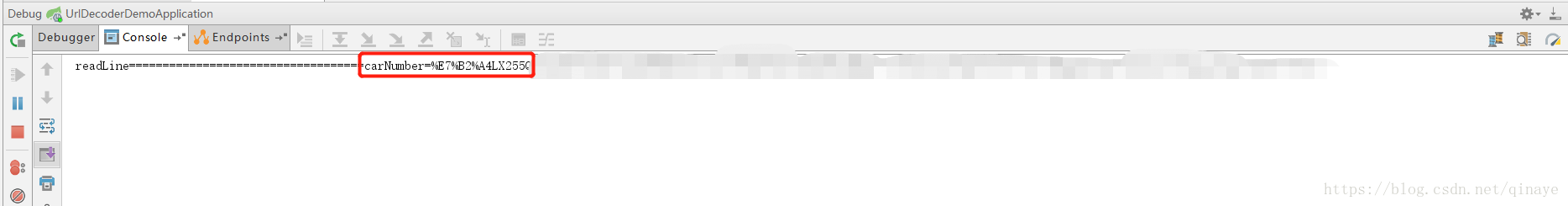
System.out.println("readLine===================================" + readLine);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8"));
return jsonObject;
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (Objects.nonNull(httpClient)){
try {
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
打印结果
由此可见,本应打印中的请求参数 “粤LX255Q”,却变成了 “%E7%B2%A4LX255Q” 这种格式的字符串。
三、产生原因
在我们发起请求时,浏览器首先会将这些中文字符进行编码然后再发送给服务器。实际上,浏览器会将它们转换为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME 字符串。
四、解决方法
public static JSONObject postForForm(String url, Map<String, String> parms) {
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
ArrayList<BasicNameValuePair> list = new ArrayList<>();
parms.forEach((key, value) -> list.add(new BasicNameValuePair(key, value)));
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
try {
if (Objects.nonNull(parms) && parms.size() >0) {
httpPost.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(list, "UTF-8"));
}
InputStream content = httpPost.getEntity().getContent();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(content, "UTF-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String readLine = bufferedReader.readLine();
String s = URLDecoder.decode(readLine, "UTF-8");
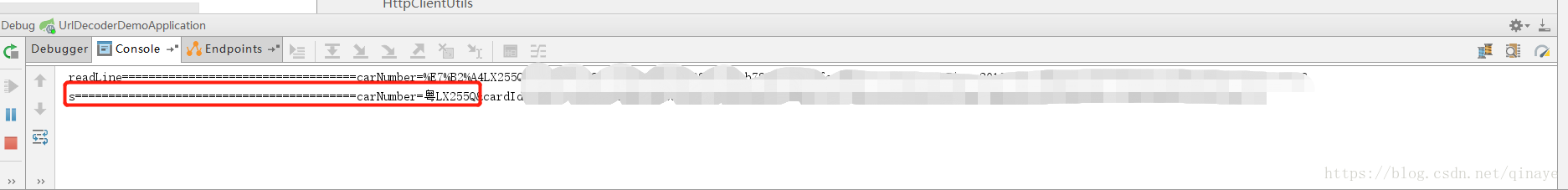
System.out.println("readLine===================================" + readLine);
System.out.println("s==========================================" + s);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8"));
return jsonObject;
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (Objects.nonNull(httpClient)){
try {
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
在获取请求参数时,再对其使用URLDecoder将application/x-www-form-rulencoded MIME字符串转换为对应编码的普通字符串。
打印结果
五、URLDecoder和URLEncoder的使用总结
-
URLDecoder类包含一个decode(String s,String enc)静态方法,它可以将application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串转成普通字符串;
-
URLEncoder类包含一个encode(String s,String enc)静态方法,它可以将普通字符串转换成application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串。
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String name = "千夜";
String decode = URLDecoder.decode("%E5%8D%83%E5%A4%9C", "UTF-8");
System.out.println("application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串转成普通字符串===============" + decode);
String encode = URLEncoder.encode(name, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("普通字符串转换成application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串=============" +encode);
}





















 1000
1000











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








