我在开发一款能源监测上位机时,使用一款国产串口服务器连接20多台RS485智能电表,串口服务器通过轮询方式每10秒把数据打包,传输至设置好的网络通道上(串口服务器为TCP_server模式),c#上位机程序收到数据后,再把数据截取、变换出来即可实现电能数据的传输和处理了。
C#上位机使用套接字的方式与串口服务器通信,如下图:
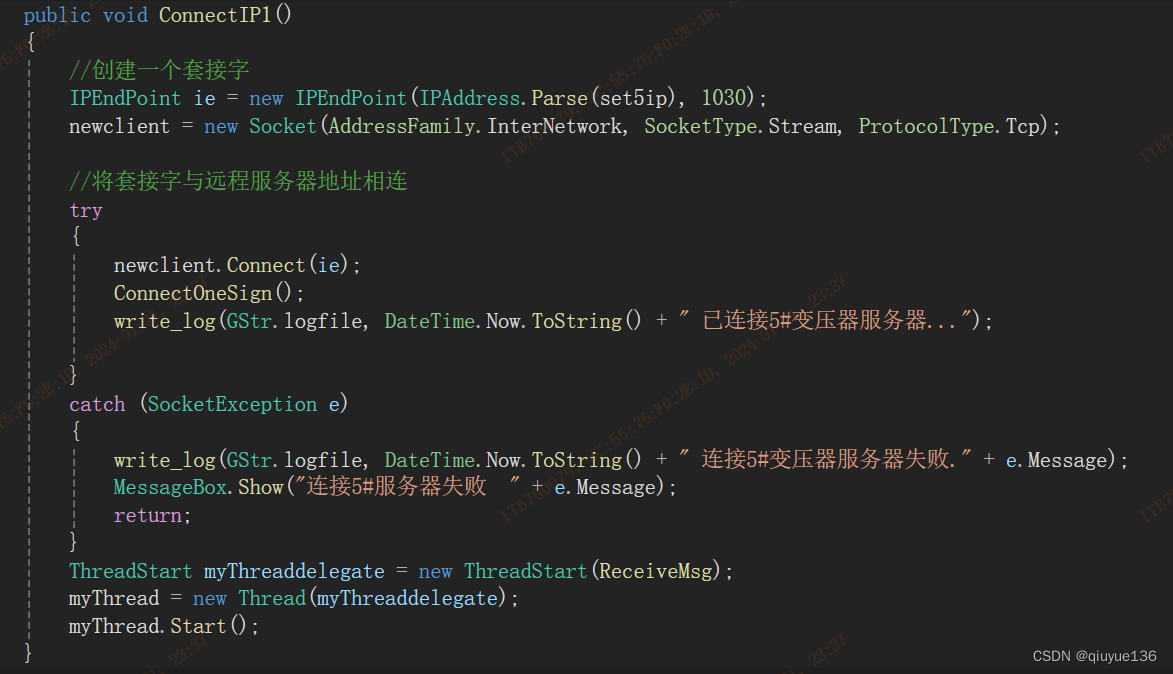
监控端口,数据过来读入DataFromTCP1数组中。
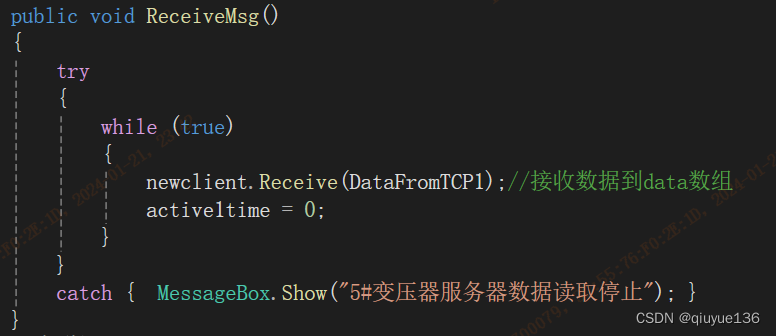 简单编写以上程序就可接收到串口服务器打包过来的数据了,然后显示到UI上及记录入数据库。
简单编写以上程序就可接收到串口服务器打包过来的数据了,然后显示到UI上及记录入数据库。
在实际使用以上TcpClient连接过程中,发现网络时有各种原因掉线,因此就增加自动重连功能,想当然使用client.Connected属性判断是否断网,断线后重连。
经过实际使用后发现断网后并不能实现重连功能,在CSDN上查找资料:
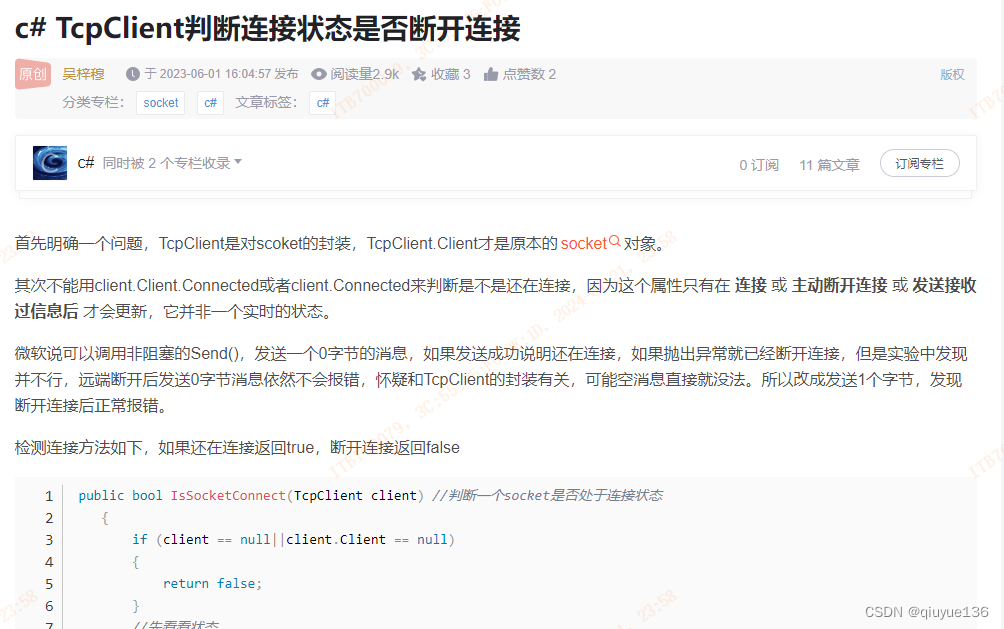
“ 不能用client.Client.Connected或者client.Connected来判断是不是还在连接,因为这个属性只有在 连接 或 主动断开连接 或 发送接收过信息后 才会更新,它并非一个实时的状态。”
那好吧,可以使用定时发送字节的程序根据返回值来判断,也就是常说的心跳信号。
在编写增加心跳程序后,还需要编写PC端的Client.Send( );语句并发送至串口服务器,有点麻烦,回头再看看我们程序实际的工作流程:每10秒接受串口服务器数据,那么我们上位机60秒没收到数据不是就可判断网络故障了吗?
1、timer2(1000ms)里增加 active1time++;,每秒自加一。
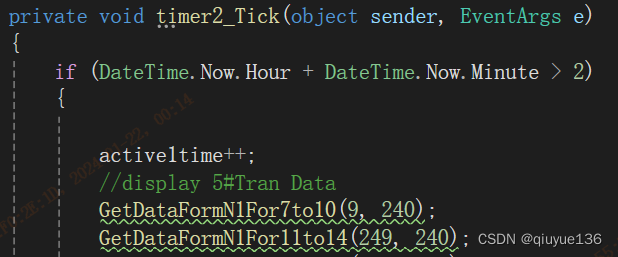
2、ReceiveMsg()方法里增加 active1time=0;,收到数据后active1time置0,重新计时。

3、如60秒后未收到数据,IP1Active()为false,同时开始延时3分钟后重连_ReconnetIP1()。

以上方法实际测试有效,我们在数采时一般使用定时发送数据或数据变化时发送两种方式,前者使用这个方法比较简单了,笔者长期与PLC 打交道,这也算是用PLC的思路解决上位机的问题,简单粗暴了。





















 1270
1270











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








