jdk1.8ConcurrentHashMap解析
本文部分内容来源于互联网和jdk1.8源码,如有不对请谅解并指正
1、前言
ConcurrentHashMap是一种同步的map,因为HashMap在多线程情况下不安全,而HashTable锁粒度又太大,所以出来了ConcurrentHashMap。
正式开始之前,先说明一个参数,这是HashMap里面没有的。
sizeCtl
/**
* Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
* table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
* else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
* when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
* creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
* next element count value upon which to resize the table.
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
用来控制table的初始化和扩容的操作,不同的值有不同的含义。
- sizeCtl=0 未初始化,并且没有指定初始容量。
- sizeCtl>0 可能未初始化,由指定的初始容量计算而来,这和HashMap初始化时指定大小是一个意思。也可能已经初始化完成,值为table.length * 0.75,是阈值大小。
- sizeCtl=-1 正在初始化。
- sizeCtl=-N 正在初始化。高15位是指定容量标记,低16位表示有m+1个线程在并行扩容。
2、put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());//hash操作
int binCount = 0;
//bitCount表示i处的节点数量,用来判断是否转换成红黑树
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {//CAS插入
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//除非构造时指定初始化集合,否则默认构造不初始化table
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
//当前table位置没有节点,创建一个新的
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
//当前节点正在扩容,让当前线程帮助扩容,扩容完指向新的table
else {
//正常插入到链表或者红黑树当中
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {//表明是链表结点类型
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
//onlyIfAbsent表示是新元素才加入,旧值不替换,默认为fase。
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
//加入链表尾部
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {//是红黑树
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
//默认table的一个链表结点数超过8个数据结构会转为红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);//更新size,检测扩容
return null;
}
下面具体说一下put里面用到的方法。
2.1 initTable()
初始化table,通过volatile的sizeCtl,置为-1,保证可见性,这样同时只有一个在初始化了。如果别的线程检测到sizeCtl为-1,就会 Thread.yield() 让出CPU一会。
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);//扩容阈值为新容量的0.75倍
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
2.2 tabAt()/casTabAt()/setTabAt()
ABASE表示table中首个元素的内存偏移地址,所以(long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE得到table[i]的内存偏移地址。这里像C语言一样,直接操作内存了。
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
// getObjectVolatile:通过给定的Java变量获取引用值。
//这里实际上是获取一个Java对象o中,获取偏移地址为offset的属性的值。
//此方法可以突破修饰符的抑制,也就是无视private、protected和default修饰符。
//会强制从主存中获取属性值。
}
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
//设置值的时候强制(JMM会保证获得锁到释放锁之间所有对象的状态更新都会在锁被释放之后)更新到主存,
//从而保证这些变更对其他线程是可见的。
}
casTabAt才能保证原子性,setTabAt并不能,只有在有锁的时候,才能用setTabAt。
3、 扩容
首先要了解扩容的时机。
- put的末尾会调用addCount,这里面检查扩容。
- 链表转红黑树(链表长度大于8)时如果table长度小于64(MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY),则会触发扩容。
- putAll一次加入很多元素。
后两种情况都会调用tryPresize()。
3.1 addCount()
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
// x为1,表示add的数量。check是节点数量。
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
// CounterCell数组来记录元素个数的,即每个table[i]元素的个数
//下面判断是否是新元素,如果不是直接返回
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();//算出加入元素之后的大小
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
//新容量大于当前扩容阈值并且小于最大扩容值才扩容,如果tab=null说明正在初始化,死循环等待初始化完成。
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
// rs的高16位置0,第16位为1,低15位存放当前容量n扩容标识,用于表示是对n的扩容
if (sc < 0) {
//sc<0表示已经有线程在进行扩容工作
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
//条件1:检查是对容量n的扩容,保证sizeCtl与n是一块修改好的
//条件2与条件3:应该是进行sc的最小值或最大值判断。
//条件4与条件5: 确保tranfer()中的nextTable相关初始化逻辑已走完。
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
//有新线程参与扩容则sizeCtl加1
transfer(tab, nt);
}
//没有线程在进行扩容,将sizeCtl的值改为(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
rs即resizeStamp(n),与RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT配合可以求出新的sizeCtl的值,分情况如下:
- sc >= 0
表示没有线程在扩容,使用CAS将sizeCtl的值改为(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)。 - sc < 0
已经有线程在扩容,将sizeCtl+1并调用transfer()让当前线程参与扩容。
这两个值算完就是sizeCtl。高15位是指定容量标记,低16位表示有m+1个线程在并行扩容。
3.2 tryPresize()
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
// 计算新容量,为2的n次方
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1);
int sc;
// 下面和addCount类似
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table; int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
}
}
else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break;
else if (tab == table) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt;
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
}
}
}
3.3transfer()
transfer是真正进行扩容的方法。
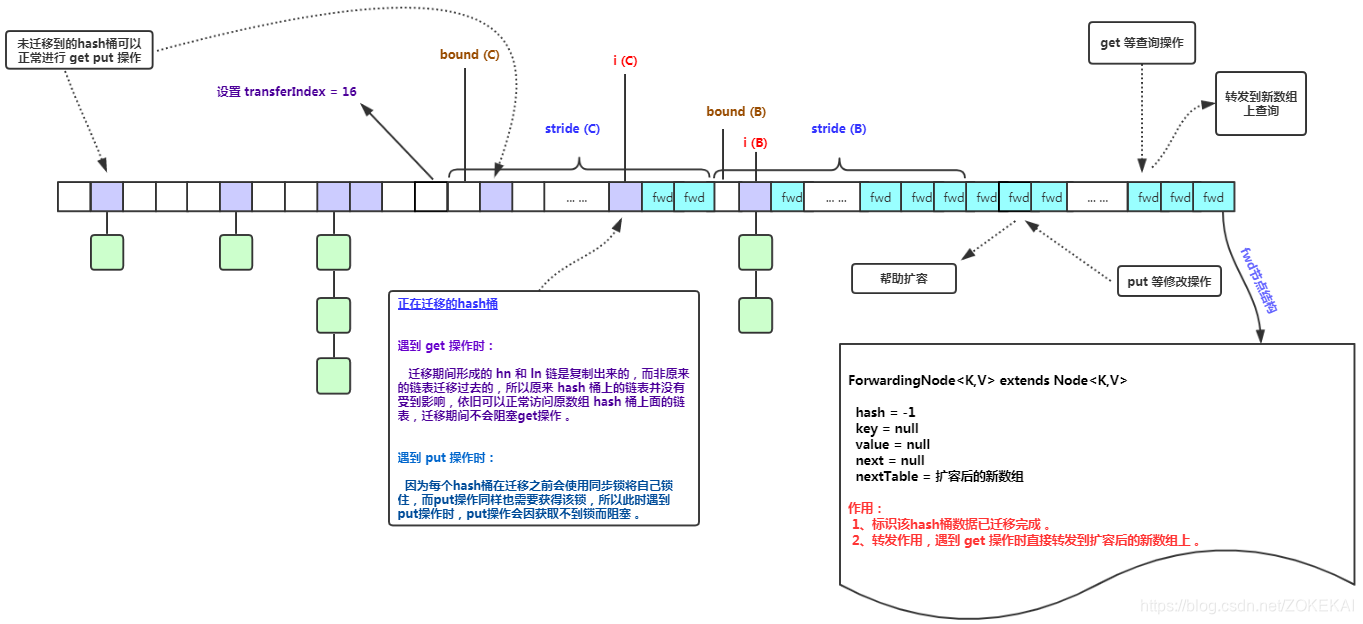
迁移过程图例:
单线程:

多线程:

源码:
// tab是旧table,nextTab是新table
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
//stride表示每个线程处理桶的最小数目。
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];//table两倍扩容
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;//扩容总进度,>=transferIndex的桶都已分配出去。
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
// ForwardingNode的作用:新建一个占位对象,该占位对象的 hash 值为 -1 该占位对象存在时表示集合正在扩容状态,key、value、next 属性均为 null ,nextTable 属性指向扩容后的数组
//该占位对象主要有两个用途:
// 1、占位作用,用于标识数组该位置的桶已经迁移完毕,处于扩容中的状态。
// 2、作为一个转发的作用,扩容期间如果遇到查询操作,遇到转发节点,会把该查询操作转发到新的数组上去,不会阻塞查询操作
boolean advance = true;
//advance用于控制是否继续处理下一个桶,为 true 则表示已经处理完当前桶,可以继续迁移下一个桶的数据
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
//finish表示何时扩容结束
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
//这个循环用于处理一个 stride 长度的任务,i 后面会被赋值为该 stride 内最大的下标,而 bound 后面会被赋值为该 stride 内最小的下标
//通过循环不断减小 i 的值,从右往左依次迁移桶上面的数据,直到 i 小于 bound 时结束该次长度为 stride 的迁移任务
//结束这次的任务后会通过外层 addCount、helpTransfer、tryPresize 方法的 while 循环达到继续领取其他任务的效果
//简而言之,循环会寻找下一个需要处理的节点
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
//transferIndex <= 0 说明数组的hash桶已被线程分配完毕,没有了待分配的hash桶,将 i 设置为 -1 ,后面的代码根据这个数值退出当前线的扩容操作
i = -1;
advance = false;//false表示没处理完当前桶
}
//只有首次进入for循环才会进入这个判断里面去,设置 bound 和 i 的值,也就是领取到的迁移任务的数组区间
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
//确定当前线程每次分配的待迁移桶的范围为[bound, nextIndex)
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
// i<0表示当前线程的任务已经做完,后两个判断是边界检查
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
//扩容结束后做后续工作,将 nextTable 设置为 null,表示扩容已结束,将 table 指向新数组,sizeCtl 设置为扩容阈值
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
//每当一条线程扩容结束就会更新一次 sizeCtl 的值,进行减 1 操作
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
//如果下面为false,说明该线程不是扩容大军里面的最后一条线程,直接return
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
//如果为true,修改标志位,并且重新检查有没有遗漏的
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
//重新检查一遍
//正常情况下,tab应该全都是ForwardingNode
//如果出现问题,多个线程同时申请到了一个transfer,此时当前线程领取的任务作废
//重新检查时候要处理作废而没被迁移的桶
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
//桶为null,直接放一个ForwardingNode
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
//数组上遇到hash值为MOVED,也就是 -1 的位置,说明该位置已经被其他线程迁移过了,
//将 advance 设置为 true ,以便继续往下一个桶检查并进行迁移操作
advance = true; // already processed
else {
//数据迁移
synchronized (f) {
//桶内元素迁移加锁
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
//fh >= 0说明是链表
int runBit = fh & n;//n是2的幂次,所以runBit只能为1或者0
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;//lastRun指向最后一个相邻runBit不同的节点
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
//遍历整条链表,找出 lastRun 节点
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
//头插,以lastRun分界拆成hn和ln
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
//四个参数分别是hash值,key,value,next节点,所以是头插法
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
//ln 链设置到新数组下标为 i 的位置上
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
//hn 链设置到新数组下标为 i + n(n为原数组长度) 的位置上
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
//在原table中设置ForwardingNode节点以提示该桶扩容完成。
advance = true;
//advance 设置为 true 表示当前 hash 桶已处理完,可以继续处理下一个 hash 桶
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
//红黑树处理与链表类似
//同样也是使用高位和低位两条链表进行迁移
//在迁移过程中,判断是否需要转换成红黑树
//1、如果符合条件则直接将 TreeNode 链表转为红黑树,再设置到新数组中去
//2、如果不符合条件则将 TreeNode 转换为普通的 Node 节点,再将该普通链表设置到新数组中去
......
}
}
}
}
}
}
扩容过程中的链表复制过程:

为什么要分成高低位链表:
ConcurrentHashMap的hash算法决定了扩容后的节点只有两个去处,i或者 i+n。
3.4. helpTransfer()
添加删除节点时,如果table[i]在扩容,就会调用helpTransfer()。
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
//调用transfer
transfer(tab, nextTab);
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
4、get()方法
get方法可以保证取出的值一定是最新的,但是get并没有加锁,因为Node是volatile的。
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)//在扩容迁移过程中,eh<0,调用find查询
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
get图解:
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/tp7309/article/details/76532366
https://blog.csdn.net/ZOKEKAI/article/details/90051567
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI0MzI1Mjg5Nw==&mid=2247483756&idx=1&sn=356b23cb9649579a0e4853010b6fb23e
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016124883





















 672
672











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








