今天看了鸿神他的博文之后有点感触,对就像他们所说事件分发这东西不是一二句话就能解释明白的,真正要了解他们的内部机制怎样运行还是需要去研究源码,因为那里基本可以找到答案
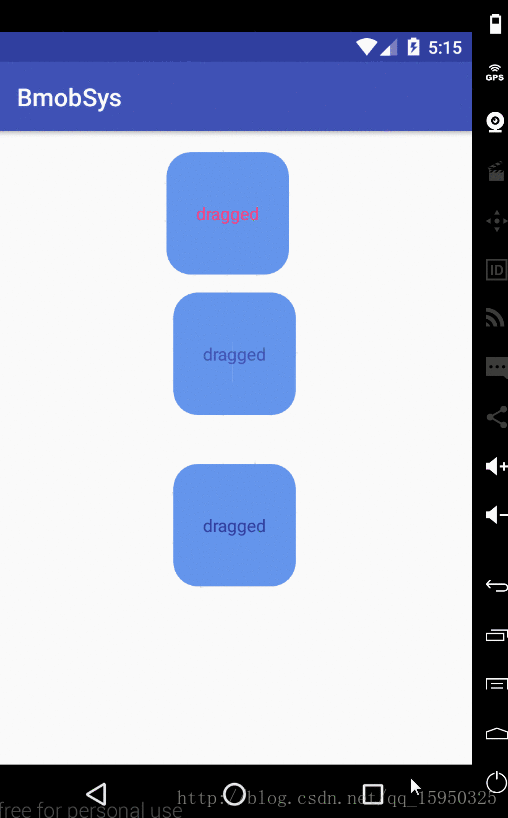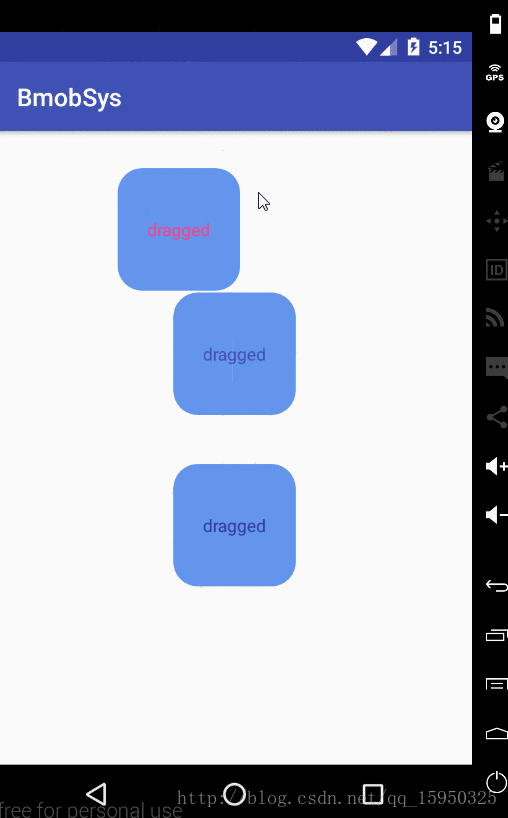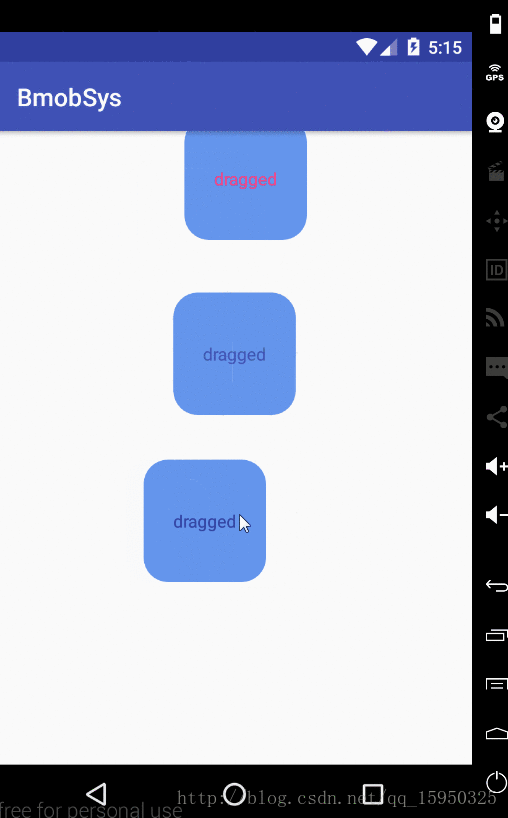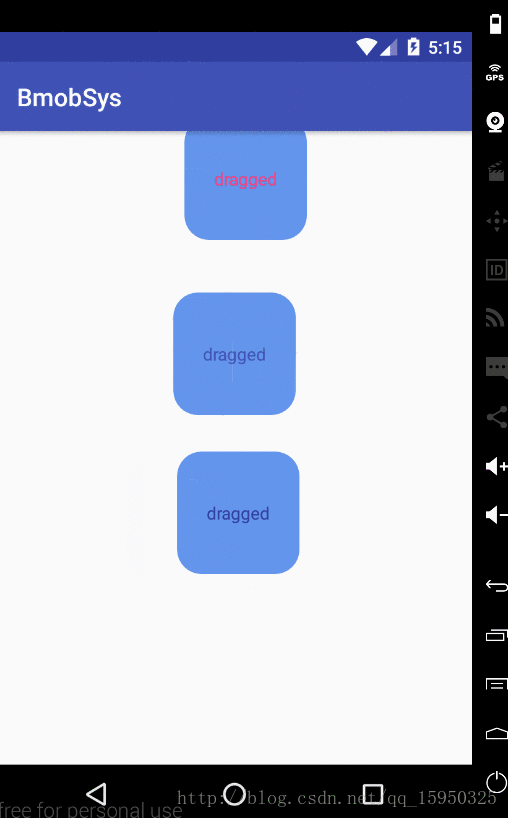
首先看下效果
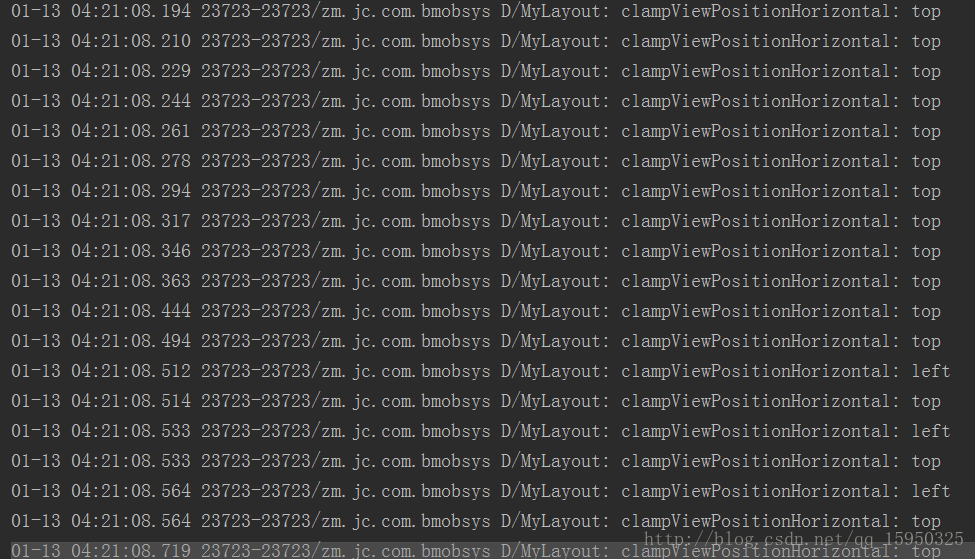
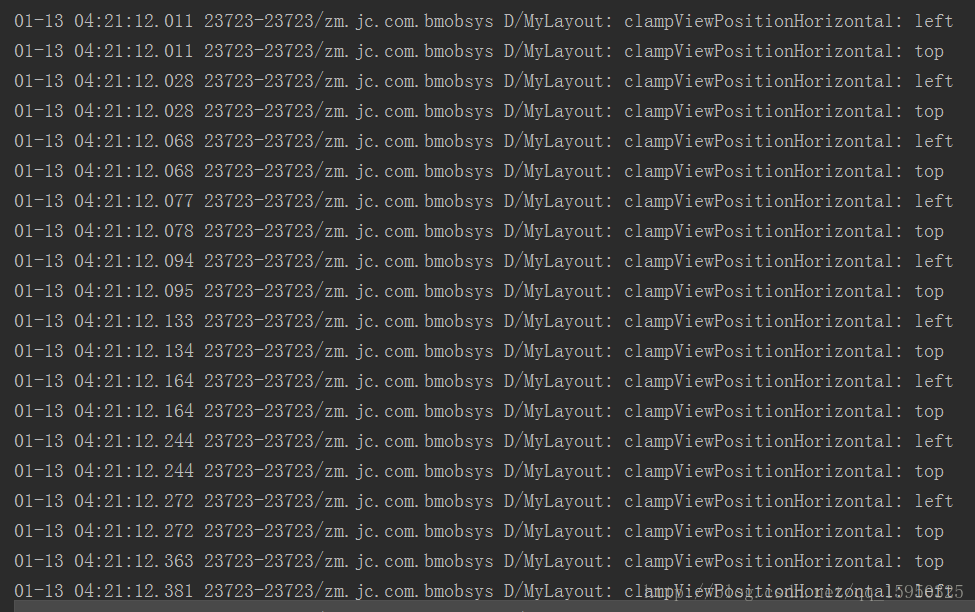
然后看下log日志根据你的拖拽看他是向上还是向左移动
这个方法比较重要
创建实例需要3个参数,第一个就是当前的ViewGroup,第二个sensitivity,主要用于设置touchSlop:
源码可以看到
public static ViewDragHelper create(ViewGroup forParent, float sensitivity, Callback cb) {
final ViewDragHelper helper = create(forParent, cb);
helper.mTouchSlop = (int) (helper.mTouchSlop * (1 / sensitivity));
return helper;
}再看下面ViewDragHelper创建时会调用create方法,然后获取一个实例那么允许VDH使用不同的内部兼容性实现不同的平台
/**
* Apps should use ViewDragHelper.create() to get a new instance.
* This will allow VDH to use internal compatibility implementations for different
* platform versions.
*
* @param context Context to initialize config-dependent params from
* @param forParent Parent view to monitor
*/
private ViewDragHelper(Context context, ViewGroup forParent, Callback cb) {
if (forParent == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parent view may not be null");
}
if (cb == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Callback may not be null");
}
mParentView = forParent;
mCallback = cb;
final ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(context);
final float density = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
mEdgeSize = (int) (EDGE_SIZE * density + 0.5f);
mTouchSlop = vc.getScaledTouchSlop();
mMaxVelocity = vc.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
mMinVelocity = vc.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity();
mScroller = ScrollerCompat.create(context, sInterpolator);
}
然后介绍一下ViewDragHelper
**
* ViewDragHelper is a utility class for writing custom ViewGroups. It offers a number
* of useful operations and state tracking for allowing a user to drag and reposition
* views within their parent ViewGroup.
*/
ViewDragHelper是一个用于编写自定义ViewGroups的实用程序类。它提供了一个数字
*用于允许用户拖动和重新定位的有用操作和状态跟踪
*在其父ViewGroup中的视图这下集合上面的效果图相信大家应该不陌生了!
public static final int EDGE_LEFT = 1 << 0;
表明左边缘应受影响。
public static final int EDGE_RIGHT = 1 << 1;
表明右边缘应受影响。
public static final int EDGE_TOP = 1 << 2;
表明顶部边缘应受影响。
public static final int EDGE_BOTTOM = 1 << 3;
表明 底部边缘受影响
public static final int EDGE_ALL = EDGE_LEFT | EDGE_TOP | EDGE_RIGHT | EDGE_BOTTOM;
这个表示上下左右边缘都会受影响
**
* Edge flag indicating that the left edge should be affected.
*/
/**
* Edge flag indicating that the right edge should be affected.
*/
/**
* Edge flag indicating that the top edge should be affected.
*/
public static final int EDGE_TOP = 1 << 2;
/**
* Edge flag indicating that the bottom edge should be affected.
*/
public static final int EDGE_BOTTOM = 1 << 3;
/**
* Edge flag set indicating all edges should be affected.
*/
public static final int EDGE_ALL = EDGE_LEFT | EDGE_TOP | EDGE_RIGHT | EDGE_BOTTOM;下面再看下CallBack
/**
* A Callback is used as a communication channel with the ViewDragHelper back to the
* parent view using it. <code>on*</code>methods are invoked on siginficant events and several
* accessor methods are expected to provide the ViewDragHelper with more information
* about the state of the parent view upon request. The callback also makes decisions
* governing the range and draggability of child views.
*/
public abstract static class Callback {
/**
* Called when the drag state changes. See the <code>STATE_*</code> constants
* for more information.
*
* @param state The new drag state
*
* @see #STATE_IDLE
* @see #STATE_DRAGGING
* @see #STATE_SETTLING
*/回调用作具有ViewDragHelper的通信通道,父视图使用它的方法在siginficant事件和几个方法上被调访问器方法应该为ViewDragHelper提供更多信息关于请求时父视图的状态。回调等
释放
/**
* 释放的时候自动自动弹回
* @param releasedChild
* @param xvel
* @param yvel
*/
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
if(releasedChild==mAutoBackView)
{
mDragger.settleCapturedViewAt(mAutoBackOriginPosition.x,mAutoBackOriginPosition.y);
}
//边界检测
mDragger.setEdgeTrackingEnabled(ViewDragHelper.EDGE_LEFT);
}禁止拖拽
onLayout之后保存了最开启的位置信息,最主要还是重写Callback中的onViewReleased,我们在onViewReleased中判断如果是mAutoBackView则调用settleCapturedViewAt回到初始的位置。大家可以看到紧随其后的代码是invalidate();方法因为其内部使用的是mScroller.startScroll,所以别忘了需要invalidate()以及结合computeScroll方法一起。
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
//mEdgeTrackerView禁止直接移动
return child == mDragView || child == mEdgeTrackerView;
}效果如下
最后上全部代码
package zm.jc.com.bmobsys.dialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v4.widget.ViewDragHelper;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* Created by John on 2017/1/13.
*/
public class MyLayout extends LinearLayout {
private ViewDragHelper mDragger;//v4包
private static final String TAG = "MyLayout";
public MyLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mDragger= ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f, new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return true;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
// final int leftBound=getPaddingLeft();
// final int rightBound=getWidth()- mDragger.getWidth() - leftBound;
// final int newLeft=Math.min(Math.max(left.leftBound),rightBound);
Log.d(TAG, "clampViewPositionHorizontal: left ");
return left;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
Log.d(TAG, "clampViewPositionHorizontal: top ");
return top;
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
return mDragger.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mDragger.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
}






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








