12.Swift JSON 和 PList
解析PList
PList文件的Root节点只能是Array或者Dictionary类型。IOS对PList的解析是十分简洁、方便的。由于Root节点只能是Array或者Dictionary类型,所以可以直接用NSArray或者NSDictionary的构造方法就能完成解析。
在NSArray的扩展构造方法中能找到一个便利构造方法
public convenience init?(contentsOfURL url: NSURL)
在NSDictionary的扩展构造方法中能找到一个便利构造方法
public convenience init?(contentsOfURL url: NSURL)
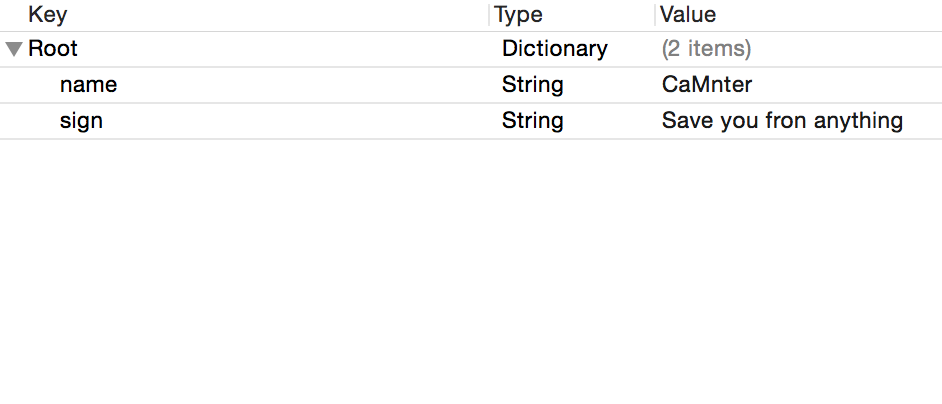
待解析的dictPList.plist
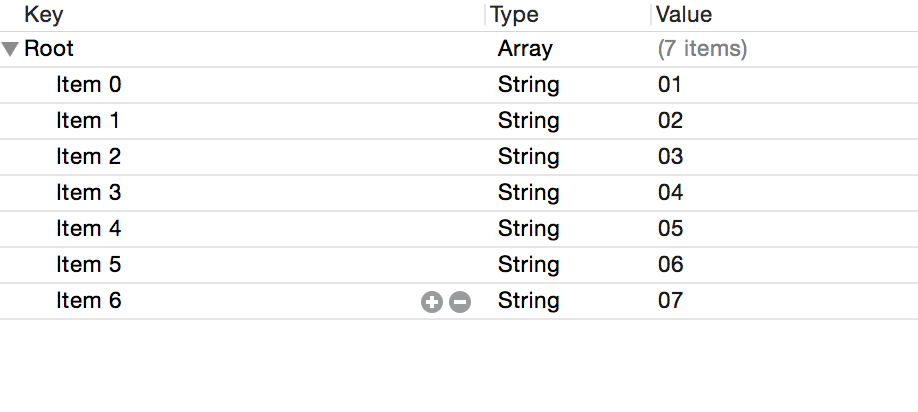
待解析的arrayPList.plist
ViewController.swift
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
// 解析Root为Array的PList
let arrayPList:NSArray = NSArray(contentsOfURL: NSURL(fileURLWithPath: NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("arrayPList", ofType: "plist")!))!
// 解析Root为Dictionary的PList
let dictPList:NSDictionary = NSDictionary(contentsOfURL: NSURL(fileURLWithPath: NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("dictPList", ofType: "plist")!))!
NSLog("\(arrayPList)")
NSLog("\(dictPList)")
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
}
如果要生成PList文件的话,同样的办法,将NSArray或者NSDictionary传入NSData的构造方法中,最后调用NSData的writeToFile(path: String, atomically useAuxiliaryFile: Bool) -> Bool。
NSJSONSerialization
IOS提供的NSJSONSerialization,可用于将普通数据转换为JSON格式的NSData、解析JSON文件。当数据通过NSJSONSerialization转换为JSON格式的NSData时,NSData又自带了writeToFile(path: String, atomically useAuxiliaryFile: Bool) -> Bool将自身保存为文件;解析JSON的话,需要NSJSONSerialization的JSONObjectWithData(data: NSData, options opt: NSJSONReadingOptions) throws -> AnyObject方法,将.json文件转换为AnyObject类型,再通过AnyObject的objectForKey(aKey: AnyObject) -> AnyObject?去获取其中的内容。
解析JSON
NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data: NSData, options opt: NSJSONReadingOptions) throws -> AnyObject
生成JSON格式的NSData
NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data: NSData, options opt: NSJSONReadingOptions) throws -> AnyObject
mjson.json
{"name":"CaMnter","sign":"Save you from anything"}ViewController.swift
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
self.parseJSON()
self.exportJSON()
}
// 解析JSON文件,生成JSONObject
func parseJSON(){
do {
// JSONObjectWithData解析JSON文件
let json:AnyObject? = try NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(NSData(contentsOfURL: NSURL(fileURLWithPath: NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("mjson", ofType: "json")!))!, options: NSJSONReadingOptions.AllowFragments)
if let name: AnyObject = json?.objectForKey("name"){
NSLog("\(name)")
}
if let sign: AnyObject = json?.objectForKey("sign"){
NSLog("\(sign)")
}
}catch let error as NSError {
NSLog("\(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
// NSData生成JSONObject
func exportJSON(){
let dict = ["name":"CaMnter","sign":"Save you from anything"]
do{
// dataWithJSONObject生成JSON格式的NSData
let jsonData:NSData! = try NSJSONSerialization.dataWithJSONObject(dict, options: NSJSONWritingOptions.PrettyPrinted)
let jsonString:NSString = NSString(data: jsonData, encoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding)!
NSLog("\(jsonString)")
}catch let error as NSError {
NSLog("\(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
}























 3301
3301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








