对于Hash,我们是怎样来处理冲突的。现在就来介绍一些经典的Hash冲突处理的方法。主要包括
(1)开放地址法
(2)拉链法
(3)再哈希法
(4)建立公共溢出区
(1)开放地址法
基本思想:当发生地址冲突时,按照某种方法继续探测Hash表中其它存储单元,直到找到空位置为止。描述如下
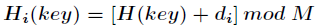
其中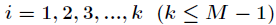 ,
,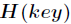 为关键字
为关键字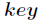 的直接Hash地址,
的直接Hash地址,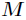 为Hash表的长度,
为Hash表的长度,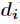 为
为
每次再探测时的地址增量。根据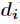 的不同取法,有不同的称呼。
的不同取法,有不同的称呼。
线性探测再散列 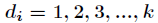
二次探测再散列 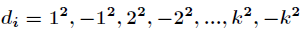
伪随机再散列 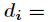 伪随机数
伪随机数
(2)拉链法
拉链法又叫链地址法,适合处理冲突比较严重的情况。基本思想是把所有关键字为同义词的记录存储在同一个
线性链表中。
代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
-
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 35;
-
- struct node
- {
- int key;
- int len;
- bool flag;
- node *next;
- };
-
- node list[N];
-
- void Init(node list[])
- {
- for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
- {
- list[i].len = 0;
- list[i].flag = 0;
- list[i].next = NULL;
- }
- }
-
- void Insert(node list[], int val, int m)
- {
- int id = val % m;
- if(!list[id].flag)
- {
- list[id].key = val;
- list[id].flag = 1;
- }
- else
- {
- node *p = new node();
- p->key = val;
- p->next = list[id].next;
- list[id].next = p;
- }
- }
-
-
- void Print(node list[], int m)
- {
- for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
- {
- node *p = list[i].next;
- if(!list[i].flag)
- printf("The %dth record is NULL!\n", i);
- else
- {
- printf("The %dth record is %d", i, list[i].key);
- list[i].len++;
- while(p)
- {
- printf("->%d", p->key);
- p = p->next;
- list[i].len++;
- }
- puts("");
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- double ASL(node list[], int m)
- {
- double ans = 0;
- for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
- ans += (list[i].len + 1) * list[i].len / 2.0;
- return ans / m;
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- int n, m;
- Init(list);
- scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
- for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
- {
- int val;
- scanf("%d", &val);
- Insert(list, val, m);
- }
- Print(list, m);
- printf("The Average Search Length is %.5lf\n", ASL(list, m));
- return 0;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
关于拉链法还可以参考:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=1191
(3)再哈希法
再哈希法又叫双哈希法,有多个不同的Hash函数,当发生冲突时,使用第二个,第三个,....,等哈希函数
计算地址,直到无冲突。虽然不易发生聚集,但是增加了计算时间。
(4)建立公共溢出区
建立公共溢出区的基本思想是:假设哈希函数的值域是[1,m-1],则设向量HashTable[0...m-1]为基本
表,每个分量存放一个记录,另外设向量OverTable[0...v]为溢出表,所有关键字和基本表中关键字为同义
词的记录,不管它们由哈希函数得到的哈希地址是什么,一旦发生冲突,都填入溢出表。
来源:http://blog.csdn.net/ACdreamers/article/details/38980951
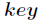
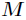
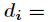










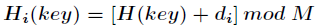
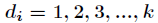
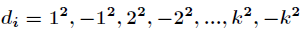
















 362
362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








