假设给定图中有N个顶点,那个最小生成树有N-1条边,算法的主要步骤
- 按每条边权重的大小从小到大对所有边进行排序。
- 选择权重最小的边。 检查它和当前的生成树是否构成环? 如果没有构成环,则包括此边。 否则,丢弃它。
- 重复步骤#2,直到生成树中有
(N-1)条边。
我们可以通过并查集来检查是不是有环。
举个例子,如下图
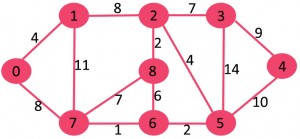
这个图中,我们有9个点和14条边,那么最小生成树有8条边。首先将所有边按照权重排序
After sorting:
Weight Src Dest
1 7 6
2 8 2
2 6 5
4 0 1
4 2 5
6 8 6
7 2 3
7 7 8
8 0 7
8 1 2
9 3 4
10 5 4
11 1 7
14 3 5

所以我们可以取出权重最小的边,也就是7->6。我们发现没有构成环,所以继续取出剩余边中权重最小的边,也就是8->2。
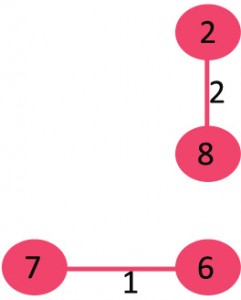
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出6->5
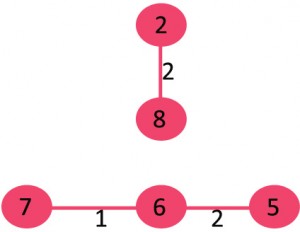
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出0->1
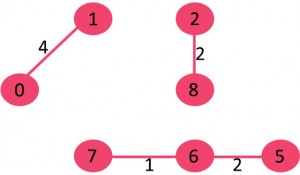
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出2->5
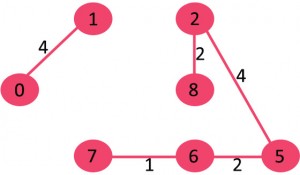
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出8->6,我们发现会构成环,所有我们将8->6丢弃。接着考虑2->3
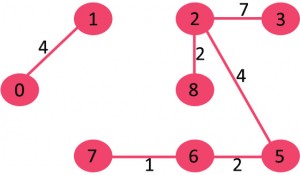
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出7->8,我们发现会构成环,所有我们将7->8丢弃。接着考虑0->7
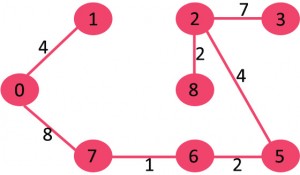
我们发现没有构成环,接着取出1->2,我们发现会构成环,所有我们将1->2丢弃。接着考虑3->4
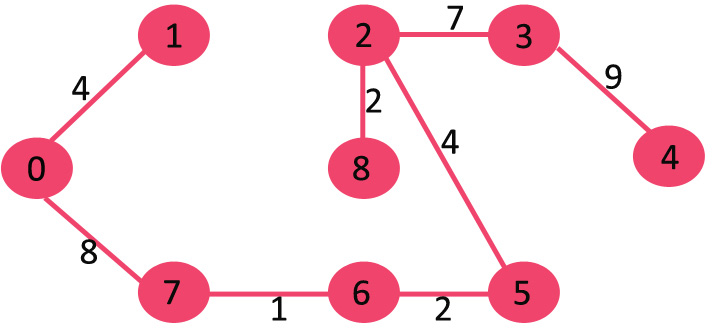
我们发现此时已经有N-1条边了,算法在此处停止。
最后代码如下
#Class to represent a graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices #No. of vertices
self.graph = [] # default dictionary to store graph
self.parent = list(range(self.V))
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v, w):
self.graph.append([u, v, w])
# A utility function to find set of an element i
# (uses path compression technique)
def find(self, i):
if self.parent[i] != i:
self.parent[i] = self.find(self.parent[i])
return self.parent[i]
# The main function to construct MST using Kruskal's algorithm
def KruskalMST(self):
result = [] #This will store the resultant MST
i = 0 # An index variable, used for sorted edges
e = 0 # An index variable, used for result[]
# Step 1: Sort all the edges in non-decreasing
# order of their weight. If we are not allowed to change the
# given graph, we can create a copy of graph
self.graph = sorted(self.graph, key=lambda item: item[2])
# Number of edges to be taken is equal to V-1
while e < self.V -1 :
# Step 2: Pick the smallest edge and increment
# the index for next iteration
u, v, w = self.graph[i]
i = i + 1
x, y = self.find(u), self.find(v)
# If including this edge does't cause cycle,
# include it in result and increment the index
# of result for next edge
if x != y:
e = e + 1
result.append([u, v, w])
self.parent[x] = y
# Else discard the edge
# print the contents of result[] to display the built MST
print("Following are the edges in the constructed MST")
for u, v, weight in result:
print("%d -- %d == %d" % (u, v, weight))
# Driver code
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1, 10)
g.addEdge(0, 2, 6)
g.addEdge(0, 3, 5)
g.addEdge(1, 3, 15)
g.addEdge(2, 3, 4)
g.KruskalMST()
reference:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/kruskals-minimum-spanning-tree-algorithm-greedy-algo-2/
如有问题,希望大家指出!!!






















 1331
1331

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








