1.一个简单的例子
function Shape(){
}
function Circle(radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
Shape.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate');
}
Circle.prototype.draw = function(){
console.log("draw");
}
const s = new Shape();
const c = new Circle(1);
 实现继承后:
实现继承后:
function Shape(){
}
function Circle(radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
Shape.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate');
}
// 下面这句实现了继承
Circle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Circle.prototype.draw = function(){
console.log("draw");
}
const s = new Shape();
const c = new Circle(1);
 有一点需要说明:
有一点需要说明:

2.继承给构造函数带来的问题
我们不使用继承时,一个对象的原型中有这样一个属性:constructor,它指向这个对象的构造函数。
例如:
 从技术上来讲,我们不仅可以使用
从技术上来讲,我们不仅可以使用new Circle()来创建对象,还可以使用new Circle.prototype.constructor()来创建对象。
但当我们使用了继承:Circle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
情况会发生改变:
 这样的结果就是,我们无法动态使用构造函数创建对象了。
这样的结果就是,我们无法动态使用构造函数创建对象了。
因此,作为最佳实践,当我们重设了原型对象后,也应该同时重设构造器属性。
// 下面这句实现了继承
Circle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Circle.prototype.constructor = Circle;

3.属性继承
function Shape(color){
this.color = color;
}
function Circle(radius,color){
Shape.call(this,color);//调用Shape的call方法,把this映射到新建的circle对象上
this.radius = radius;
}
Shape.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate');
}
// 下面这句实现了继承
Circle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Circle.prototype.constructor = Circle;
Circle.prototype.draw = function(){
console.log("draw");
}
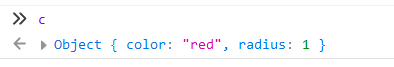
const s = new Shape();
const c = new Circle(1,'red');
4.封装继承的方法
创建一个类,让它继承自Shape类,完整的设置继承链的做法是这样的:
function Square(size){
this.size = size;
}
Square.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Square.prototype.constructor = Square;
但这样的代码难以复用,特别是在有多级继承的情况下,会变得复杂、混乱。
因此,我们来重构这个代码,把它变为一个可以复用的函数。
function extend(Child,Parent){
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
}
5.方法重写
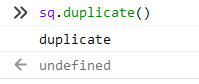
Shape.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate');
}
extend(Circle,Shape);
//Override
Circle.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate circle!');
}
**注意:**重写一定要在继承之后。
Javascript中原型继承的特性:当我们访问对象的成员时,javascript编译器会沿着继承路径向上寻找,并执行它遇到的第一个实现.
如何在子类重写了父类方法之后继续调用父类的方法?
// 调用父类的duplicate方法
// 方法一
Shape.prototype.duplicate();
// 方法二
Shape.prototype.duplicate.call(this);
6.多态
function extend(Child,Parent){
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
}
function Shape(color){
this.color = color;
}
function Circle(radius,color){
Shape.call(this,color);//调用Shape的call方法,把this映射到新建的circle对象上
this.radius = radius;
}
function Square(){
}
Shape.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate');
}
extend(Circle,Shape);
extend(Square,Shape);
//Override
Circle.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate circle!');
}
Square.prototype.duplicate = function(){
console.log('duplicate square!');
}
const shapes = [
new Circle(),
new Square()
];
for(let shape of shapes){
shape.duplicate();
}

7.组合Mixins
const canEat = {
eat : function(){
this.hunger--;
console.log('eating');
}
};
const canWalk = {
walk : function(){
console.log('walking');
}
}
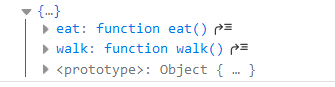
const person = Object.assign({}, canEat, canWalk) // 拷贝canEat和canWalk的所有成员到空对象
console.log(person);
 改进:
改进:
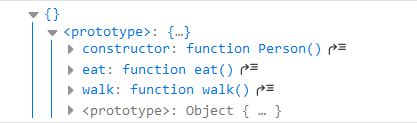
function Person(){
}
Object.assign(Person.prototype, canEat, canWalk) // 拷贝canEat和canWalk的所有成员到空对象
const person = new Person();
console.log(person);
 再举一个例子:
再举一个例子:
const canSwim = {
swim : function(){
console.log('swimming');
}
}
function GoldFish(){
}
Object.assign(GoldFish.prototype, canEat, canSwim);
const goldFish = new GoldFish();
console.log(goldFish);
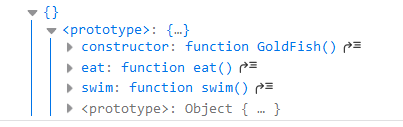 将Object.assgin()封装为mixin函数:
将Object.assgin()封装为mixin函数:
function mixin(target,...sources){
Object.assign(target,...sources);
};
const canEat = {
eat : function(){
this.hunger--;
console.log('eating');
}
};
const canWalk = {
walk : function(){
console.log('walking');
}
}
const canSwim = {
swim : function(){
console.log('swimming');
}
}
function Person(){
}
function GoldFish(){
}
mixin(Person.prototype, canEat, canWalk); // 拷贝canEat和canWalk的所有成员到空对象
const person = new Person();
console.log(person);
mixin(GoldFish.prototype, canEat, canSwim);
const goldFish = new GoldFish();
console.log(goldFish);























 2431
2431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








