转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/stormhan/p/5467187.html
由于刚刚开始学习Cuda,还没有整理出一个完整的Cuda类,只是在Nvidia提供的kenerl架构上做修改。
但用于初体验GPU给我们带来的好处也绰绰有余了。
直接贴代码:
/*
矩阵乘法,CPU版本和GPU版本的对比
*/
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <malloc.h>
//用于指示不同的GPU 优化版本
enum Type
{
Mode1 = 1, //Mode 1 :将每一个C[i][j]都分别分配一个线程
Mode2 = 2 //Mode 2 :不让一个线程完整计算一个C[i][j],通过C(i,j) = sum { A(i,k)*B(k,j) }发现,我们还可以再细度划分:
// sub(i,j) = sum{A(i,ksub+offsetA)*B(ksub+offsetB,j)} 0<=ksub < blockSize
// C(i, j) = sum{ Csub(i, j) }
// 就是把矩阵分成n*n个大的子块,然后每一个block负责计算子块i 和 子块j的子乘积,计算完毕后加起来则可。这里主要使用了共享显存作优化。
};
cudaError_t addWithCuda(float *c, const float *a, const float *b, unsigned int WA, unsigned int HA, unsigned int WB, unsigned int HB, Type mode);
__global__ void MatrixMulGPU_1(float *c, const float *a, const float *b, unsigned int WA, unsigned int WB)
{
float sum = 0;
//找出该线程所在的行和列
int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
//线程Thread(row, col)负责计算C(row, col)
for (int i = 0; i < WB; ++i)
{
sum += a[row * WA + i] * b[i * WB + col];
}
c[row * WB + col] = sum;
}
template<int BLOCK_SIZE> __global__ void MatrixMulGPU_2(float *c, const float *a, const float *b, unsigned int WA, unsigned int WB)
{
// Block index
int bx = blockIdx.x;
int by = blockIdx.y;
// Thread index
int tx = threadIdx.x;
int ty = threadIdx.y;
// Index of the first sub-matrix of A processed by the block
int aBegin = WA * BLOCK_SIZE * by;
// Index of the last sub-matrix of A processed by the block
int aEnd = aBegin + WA - 1;
// Step size used to iterate through the sub-matrices of A
int aStep = BLOCK_SIZE;
// Index of the first sub-matrix of B processed by the block
int bBegin = BLOCK_SIZE * bx;
// Step size used to iterate through the sub-matrices of B
int bStep = BLOCK_SIZE * WB;
// Csub is used to store the element of the block sub-matrix
// that is computed by the thread
float Csub = 0;
// Loop over all the sub-matrices of A and B
// required to compute the block sub-matrix
for (int i = aBegin, j = bBegin;
i <= aEnd;
i += aStep, j += bStep)
{
// Declaration of the shared memory array As used to
// store the sub-matrix of A
__shared__ float As[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
// Declaration of the shared memory array Bs used to
// store the sub-matrix of B
__shared__ float Bs[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
// Load the matrices from device memory
// to shared memory; each thread loads
// one element of each matrix
As[ty][tx] = a[i + WA * ty + tx];
Bs[ty][tx] = b[j + WB * ty + tx];
// Synchronize to make sure the matrices are loaded
__syncthreads();
// Multiply the two matrices together;
// each thread computes one element
// of the block sub-matrix
#pragma unroll
for (int k = 0; k < BLOCK_SIZE; ++k)
{
Csub += As[ty][k] * Bs[k][tx];
}
// Synchronize to make sure that the preceding
// computation is done before loading two new
// sub-matrices of A and B in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
// Write the block sub-matrix to device memory;
// each thread writes one element
int k = WB * BLOCK_SIZE * by + BLOCK_SIZE * bx;
c[k + WB * ty + tx] = Csub;
}
//GPU version
void MatrixMulCPU(float *_C, const float* _A, const float* _B, int WA, int HA, int WB, int HB)
{
if (WA != HB)
{
printf("the matrix A and B cannot be multipled!");
exit(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < HA; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < WB; ++j)
{
for (int k = 0; k < WA; ++k)
{
_C[i * WA + j] += _A[i * WA + k] * _B[k * WB + j];
}
}
}
}
//给初始的矩阵一个随机值
void randomInit(float* _data, int _size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
_data[i] = rand() / (float)RAND_MAX * 100;
}
}
//print the matrix
void printMatrix(float* m_Matrix, int W, int H)
{
for (int i = 0; i < W * H; ++i)
{
printf("%2.1f ", m_Matrix[i]);
if (i % W == 0 && i != 0) printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
bool CheckAnswer(const float* _C, const float* _D, unsigned int size)
{
bool isRight = true;
for (int i = 0; i < size && isRight == true; ++i)
{
if (_C[i] != _D[i])
isRight = false;
}
return isRight;
}
int main()
{
const int width_A = 1024;
const int height_A = 1024;
const int width_B = 1024;
const int height_B = 1024;
float *B = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * height_B * width_B);
float *A = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * height_A * width_A);
float *C = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
float *D = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
float *E = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
memset(A, 0.0, sizeof(float) * height_A * width_A);
memset(B, 0.0, sizeof(float) * height_B * width_B);
memset(C, 0.0, sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
memset(D, 0.0, sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
memset(E, 0.0, sizeof(float) * height_A * width_B);
//产生随机数生成器
srand((unsigned)time(0));
randomInit(B, height_B * width_B);
randomInit(A, height_A * width_A);
//printMatrix(B, width_B, height_B);
//printMatrix(A, width_A, height_A);
//CPU 计算
unsigned int tick1 = GetTickCount();
MatrixMulCPU(C, A, B, width_A, height_A, width_B, height_B);
printf("CPU use time : %dms\n", GetTickCount() - tick1);
//GPU
Type m_Mode = Mode1;
unsigned int tick2 = GetTickCount();
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(D, A, B, width_A, height_A, width_B, height_B, m_Mode);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess)
{
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!\n");
return 1;
}
printf("GPU mode1 use time : %dms\n", GetTickCount() - tick2);
m_Mode = Mode2;
unsigned int tick3 = GetTickCount();
cudaStatus = addWithCuda(E, A, B, width_A, height_A, width_B, height_B, m_Mode);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess)
{
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!\n");
return 1;
}
printf("GPU mode2 use time : %dms\n", GetTickCount() - tick3);
//检查GPU, CPU 计算的结果是否相同
if (!CheckAnswer(C, D, height_A * width_B) && !CheckAnswer(C, E, height_A * width_B))
printf("The answer is wrong!");
else printf("The answer is right!");
// cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess)
{
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(float *c, const float *a, const float *b, unsigned int WA, unsigned int HA, unsigned int WB, unsigned int HB, Type mode)
{
float *dev_a = 0;
float *dev_b = 0;
float *dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, HA * WB * sizeof(float));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, HA * WA * sizeof(float));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, HB * WB * sizeof(float));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, HA * WA * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, HB * WB * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
//为每一个C[i][j]设置一个线程进行计算
int block_size = 16;
dim3 Threads(block_size, block_size);
dim3 Blocks(WB / block_size, HA / block_size);
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
if (mode == Mode1)
{
MatrixMulGPU_1 << <Blocks, Threads >>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b, WA, WB);
}
if (mode == Mode2)
{
MatrixMulGPU_2<16> << <Blocks, Threads >> >(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b, WA, WB);
}
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
}
// cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, HA * WB * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
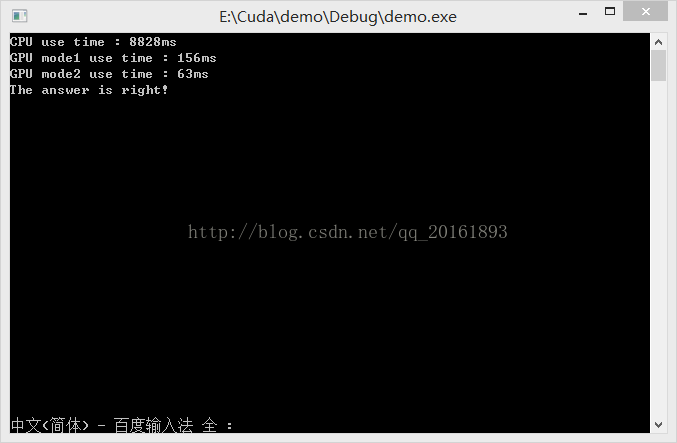
}代码中,使用了CPU的计算和两种GPU的运算,最终的运行结果如下:
可以明显的看出,GPU的运行速度比CPU快很多,并且将任务越细分,运行的速度也更快。
后续我还想通过更多的方式(比如texture binding)来继续进行优化。






















 1288
1288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








