这两个函数原型如下:
__CRT_INLINE time_t __cdecl mktime(struct tm *_Tm);
__CRT_INLINE double __cdecl difftime(time_t _Time1,time_t _Time2);
mktime函数
mktime函数会把参数把 timeptr 所指向的结构转换为自 1970 年 1 月 1 日以来持续时间的秒数,如果发生错误时则返回-1。
参数结构体原型如下:
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* 秒,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_min; /* 分,范围从 0 到 59 */
int tm_hour; /* 小时,范围从 0 到 23 */
int tm_mday; /* 一月中的第几天,范围从 1 到 31 */
int tm_mon; /* 月份,范围从 0 到 11 */
int tm_year; /* 自 1900 起的年数 */
int tm_wday; /* 一周中的第几天,范围从 0 到 6 */
int tm_yday; /* 一年中的第几天,范围从 0 到 365 */
int tm_isdst; /* 夏令时 */
};
下面直接通过一段代码来演示。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int ret,time_cnt;
struct tm info;
info.tm_year = 2022 - 1900;
info.tm_mon = 1 - 1;
info.tm_mday = 25;
info.tm_hour = 11;
info.tm_min = 28;
info.tm_sec = 50;
info.tm_isdst = -1;
ret = mktime(&info);
time_cnt = time(NULL);
if( ret == -1 ) {
printf("Error: unable to make time using mktime\n");
} else {
printf("%d %d",ret,time_cnt);
}
return 0;
}
首先定义时间结构体,然后给结构体中的变量赋值,将当前时间值赋给变量,然后在通过time函数获取当前时间的秒数,最后将mktime函数转换后的秒数和time函数返回的秒数打印出来。
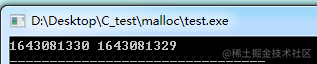
通过结果可以看到两个函数的秒数相差1,这是由于程序在编译执行的时候延时了一秒,说明mktime函数转换后的秒数和time函数返回的秒数是一样的。
difftime函数
difftime函数有两个时间参数,这个函数的主要作用返回这两个时间就参数的差,也就是这两个时间值相差的秒数。
一般可以通过这个函数来计算某段代码运行的时间。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
time_t start_t, end_t;
double diff_t;
printf("程序启动...\n");
time(&start_t);
sleep(2);
printf("运行结束!\n");
time(&end_t);
diff_t = difftime(end_t, start_t);
printf("\n开始时间: %d 结束时间: %d 代码运行时间: %fs\n", start_t,end_t,diff_t);
return 0;
}
定义两个变量来记录程序运行前的时间值和程序运行后的时间值,然后通过延时函数来模拟程序的运行过程,最后通过difftime函数来计算函数运行的时长。

通过打印的结果可看出,延时函数的执行时间为2s,程序中的延时也是2s,说明函数计算的结果是正确的。在这里要注意一点difftime函数的返回值是double类型的数据。








 本文详细介绍了C语言中用于时间处理的两个关键函数:mktime和difftime。mktime函数将结构体tm转换为自1970年以来的秒数,而difftime函数则计算两个时间点之间的差值(以秒为单位)。通过示例代码展示了如何使用这两个函数,以及它们在实际应用中的效果。文章还提供了计算代码运行时间的示例,验证了difftime函数的准确性。
本文详细介绍了C语言中用于时间处理的两个关键函数:mktime和difftime。mktime函数将结构体tm转换为自1970年以来的秒数,而difftime函数则计算两个时间点之间的差值(以秒为单位)。通过示例代码展示了如何使用这两个函数,以及它们在实际应用中的效果。文章还提供了计算代码运行时间的示例,验证了difftime函数的准确性。
















 1601
1601

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








